Spring MVC源码分析(三):SpringMVC的HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter的体系结构设计与实现
概述
在我的上一篇文章:Spring源码分析(三):DispatcherServlet的设计与实现中提到,DispatcherServlet在接收到客户端请求时,会遍历DispatcherServlet自身维护的一个HandlerMapping集合,来查找该请求对应的请求处理器,然后由该请求处理器来执行请求处理。
HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter并不是跟名字所描述的这样,即每个HandlerMapping定义一个请求和请求处理器的映射对,这两个接口不是从请求处理方法的角度来定义的,而是从请求处理器的实现类型的角度来定义的。HandlerMapping包含Url和HandlerMethod两种实现,HandlerAdapter包含HttpMethod,Servlet,Controller,HttpRequestHandler四种实现。
主要在抽象类AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中定义,具体实现子类包含BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping和SimpleUrlHandlerMapping。其中BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping的映射map的key为请求URI,value是beanName,即处理匹配这个uri的请求的bean,在spring容器中的beanName,通常是以“/”开头,如beanName为“/foo”的bean处理URI为“/foo”的请求,同时可以指定beanName的别名alias,这样这些别名也作为匹配的请求URI。获取映射关系的源码如下:
public class BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping extends AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping { /** * Checks name and aliases of the given bean for URLs, starting with "/". */ @Override protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) { List<String> urls = new ArrayList<>(); // urls为以这个beanName为value的多个key,即map的key和value // beanName以“/”开头 if (beanName.startsWith("/")) { urls.add(beanName); } // 别名也作为value String[] aliases = obtainApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName); for (String alias : aliases) { if (alias.startsWith("/")) { urls.add(alias); } } return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls); } }
2. 基于HandlerMethod
/** * Encapsulates information about a handler method consisting of a * {@linkplain #getMethod() method} and a {@linkplain #getBean() bean}. * Provides convenient access to method parameters, the method return value, * method annotations, etc. * * <p>The class may be created with a bean instance or with a bean name * (e.g. lazy-init bean, prototype bean). Use {@link #createWithResolvedBean()} * to obtain a {@code HandlerMethod} instance with a bean instance resolved * through the associated {@link BeanFactory}. * @since 3.1 */ public class HandlerMethod { private final Object bean; @Nullable private final BeanFactory beanFactory; private final Class<?> beanType; private final Method method; private final Method bridgedMethod; private final MethodParameter[] parameters; @Nullable private HttpStatus responseStatus; @Nullable private String responseStatusReason; @Nullable private HandlerMethod resolvedFromHandlerMethod; @Nullable private volatile List<Annotation[][]> interfaceParameterAnnotations; ... }
value为匹配的路径;params是匹配的请求参数值;method为处理的http请求方法,consumers为请求的mediaType,produces为响应的mediaType。value,params,consumes,produces都可以设置多个,如下为一个用例:
@RestController @RequestMapping("/home") public class IndexController { @RequestMapping(value = { "/head", "/index" }, method = RequestMethod.GET, headers = { "content-type=text/plain", "content-type=text/html" }, consumers = { "application/JSON", "application/XML" }, produces = { "application/JSON" }) String post() { return "Mapping applied along with headers"; } }
RequestMappingInfo的类设计如下
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> { @Nullable private final String name; private final PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition; private final RequestMethodsRequestCondition methodsCondition; private final ParamsRequestCondition paramsCondition; private final HeadersRequestCondition headersCondition; private final ConsumesRequestCondition consumesCondition; private final ProducesRequestCondition producesCondition; private final RequestConditionHolder customConditionHolder; ... /** * Checks if all conditions in this request mapping info match the provided request and returns * a potentially new request mapping info with conditions tailored to the current request. * <p>For example the returned instance may contain the subset of URL patterns that match to * the current request, sorted with best matching patterns on top. * @return a new instance in case all conditions match; or {@code null} otherwise */ @Override @Nullable public RequestMappingInfo getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) { RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); if (methods == null || params == null || headers == null || consumes == null || produces == null) { return null; } PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); if (patterns == null) { return null; } RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.getMatchingCondition(request); if (custom == null) { return null; } return new RequestMappingInfo(this.name, patterns, methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom.getCondition()); } ... }
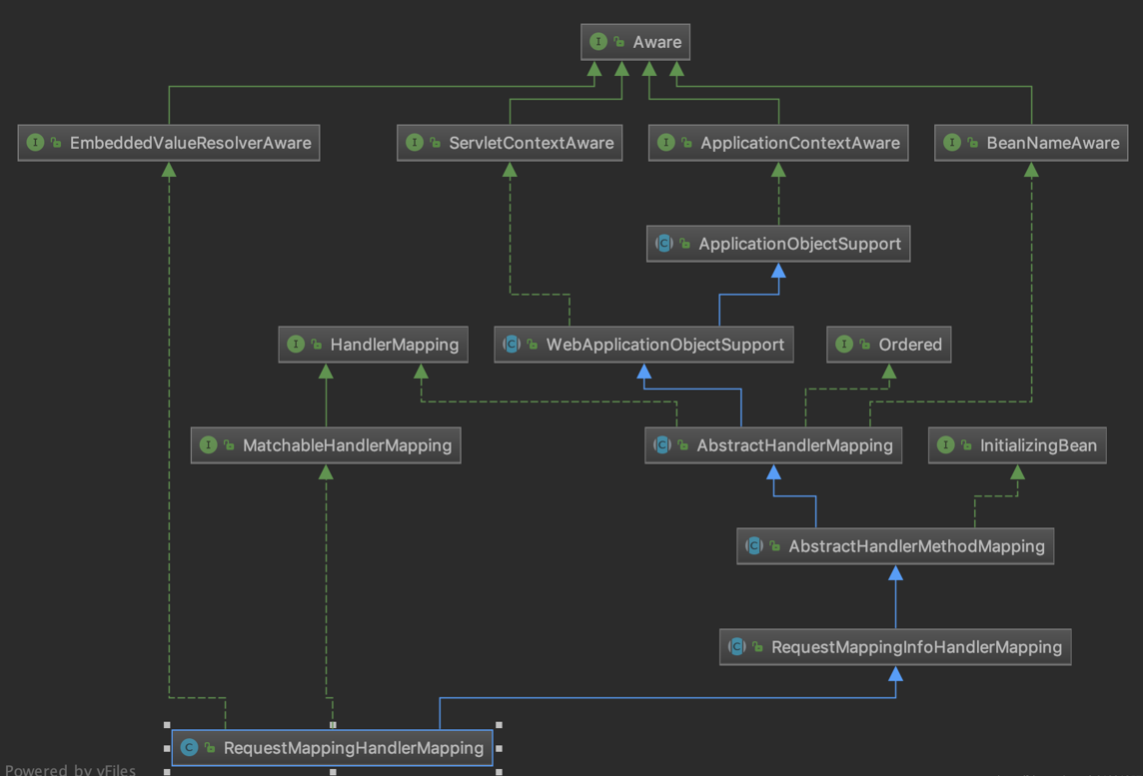
map的创建和初始化
由类的继承体系可知,实现了InitializingBean接口,故spring容器在创建这个bean时,填充好所有属性之后,会调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法,以下为从RequestMappingHandlerMapping -> RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping的afterPropertiesSet实现:
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的afterPropertiesSet方法定义:
@Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration(); this.config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper()); this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher()); this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(this.useSuffixPatternMatch); this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(this.useTrailingSlashMatch); this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch); this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager()); // 调用RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping的afterPropertiesSet方法 super.afterPropertiesSet(); }
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping的afterPropertiesSet方法:定义initHandlerMethods完成请求和请求处理器映射map的初始化,故map的初始化是定义在RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping中的,其整体实现源码如下:
// Handler method detection /** * Detects handler methods at initialization. * @see #initHandlerMethods */ @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { initHandlerMethods(); } /** * Scan beans in the ApplicationContext, detect and register handler methods. * @see #getCandidateBeanNames() * @see #processCandidateBean * @see #handlerMethodsInitialized */ protected void initHandlerMethods() { // 遍历所有bean for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) { if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) { // 查找是handler的bean processCandidateBean(beanName); } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); }
获取所有Object类型的bean:getCandidateBeanNames
// 获取所有Object类型的bean /** * Determine the names of candidate beans in the application context. * @since 5.1 * @see #setDetectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts * @see BeanFactoryUtils#beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors */ protected String[] getCandidateBeanNames() { return (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), Object.class) : obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); }
processCandidateBean:通过isHandler方法,判断某个bean是否是handler,如果是则通过detectHandlerMethods方法,获取该handler的所有方法,然后保存注册到请求和请求处理器映射map。
/** * Determine the type of the specified candidate bean and call * {@link #detectHandlerMethods} if identified as a handler type. * <p>This implementation avoids bean creation through checking * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory#getType} * and calling {@link #detectHandlerMethods} with the bean name. * @param beanName the name of the candidate bean * @since 5.1 * @see #isHandler * @see #detectHandlerMethods */ protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) { Class<?> beanType = null; try { beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { // An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it. if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex); } } // 使用isHandler方法,判断bean是否是 // 请求执行器handler // 这个是一个重要方法,在RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping中实现 if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } /** * Look for handler methods in the specified handler bean. * @param handler either a bean name or an actual handler instance * @see #getMappingForMethod */ protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) { Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ? obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); if (handlerType != null) { Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType, (MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> { try { return getMappingForMethod(method, userType); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" + userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex); } }); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods)); } methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> { Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType); registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping); }); } }
isHandler方法:判断bean是否是handler,这个是在主类RequestMappingHandlerMapping中定义的:判断bean是否使用@Controller或者@RequestMapping注解
/** * {@inheritDoc} * <p>Expects a handler to have either a type-level @{@link Controller} * annotation or a type-level @{@link RequestMapping} annotation. */ @Override protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) { return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) || AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class)); }
从请求和请求处理器映射map查找请求处理器:主要是在DispatcherServlet中调用,对应RequestMappingHandlerMapping的底层实现如下:主要是在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的getHandlerInternal方法定义,AbstractHandlerMethodMapping直接继承于AbstractHandlerMapping。getHandlerInternal的源码实现逻辑如下:
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean { /** * Look up a handler method for the given request. */ @Override protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock(); try { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null); } finally { this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock(); } } /** * Look up the best-matching handler method for the current request. * If multiple matches are found, the best match is selected. * @param lookupPath mapping lookup path within the current servlet mapping * @param request the current request * @return the best-matching handler method, or {@code null} if no match * @see #handleMatch(Object, String, HttpServletRequest) * @see #handleNoMatch(Set, String, HttpServletRequest) */ @Nullable protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>(); List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath); if (directPathMatches != null) { addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request); } if (matches.isEmpty()) { // No choice but to go through all mappings... addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request); } if (!matches.isEmpty()) { Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request)); matches.sort(comparator); Match bestMatch = matches.get(0); if (matches.size() > 1) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches); } if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) { return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH; } Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1); if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) { Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); String uri = request.getRequestURI(); throw new IllegalStateException( "Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}"); } } request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod); handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request); return bestMatch.handlerMethod; } else { return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request); } }
1. 初始化
DispatcherServlet可以包含多个HandlerMapping接口的实现类对象,其中RequestMappingHandlerMapping就是其中一个,用于获取使用@Controller和@RequestMapping注解的类和方法,RequestMappingHandlerMapping获取这些Controller类和其方法,从而生成请求和请求处理器映射map,供DispatcherServlet在接收到请求时查找并调用。
handlerMappings集合中的HandlerMapping对象的创建和初始化时机是在创建DispatcherServlet自身的bean容器WebApplicationContext的时候,具体为在解析WebApplicationContext的配置xml文件,如WEB-INF/myDispatcherServlet-servlet.xml时,通过spring-webmvc子项目的META-INF/spring.handlers获取命名空间处理器MvcNamespaceHandler,MvcNamespaceHandler注册并使用AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser来处理xml文件的annotation-driven标签:
/** * {@link NamespaceHandler} for Spring MVC configuration namespace. * * @author Keith Donald * @author Jeremy Grelle * @author Sebastien Deleuze * @since 3.0 */ public class MvcNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport { @Override public void init() { registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven", new AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser()); ... } }
RequestMappingHandlerMapping类型的HandlerMapping的创建:AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser在解析annotation-driven标签时,调用parse方法:此时创建RequestMappingHandlerMapping类型的bean:
@Override @Nullable public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext context) { ... // 创建RequestMappingHandlerMapping的BeanDefinition, // 之后创建bean实例 RootBeanDefinition handlerMappingDef = new RootBeanDefinition(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class); handlerMappingDef.setSource(source); handlerMappingDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE); handlerMappingDef.getPropertyValues().add("order", 0); handlerMappingDef.getPropertyValues().add("contentNegotiationManager", contentNegotiationManager); if (element.hasAttribute("enable-matrix-variables")) { Boolean enableMatrixVariables = Boolean.valueOf(element.getAttribute("enable-matrix-variables")); handlerMappingDef.getPropertyValues().add("removeSemicolonContent", !enableMatrixVariables); } configurePathMatchingProperties(handlerMappingDef, element, context); readerContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME , handlerMappingDef); RuntimeBeanReference corsRef = MvcNamespaceUtils.registerCorsConfigurations(null, context, source); handlerMappingDef.getPropertyValues().add("corsConfigurations", corsRef); ... }
/** * Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request. * <p>Tries all handler mappings in order. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found */ @Nullable protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this.handlerMappings != null) { for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) { // 找到一个则返回 HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } } return null; }
/** * Handler execution chain, consisting of handler object and any handler interceptors. * Returned by HandlerMapping's {@link HandlerMapping#getHandler} method. */ public class HandlerExecutionChain { private final Object handler; @Nullable private HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors; @Nullable private List<HandlerInterceptor> interceptorList; private int interceptorIndex = -1; ... }
完整请求处理过程
- DispatcherServlet中使用doDispatch方法完成整个请求处理,核心处理逻辑如下
/** * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order. * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters * to find the first that supports the handler class. * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure */ protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; ... // multipart请求加工 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // 查找请求处理器handler // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // 获取请求执行器的执行适配器 // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } // 拦截器链前置处理applyPreHandle if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // 通过请求执行器适配器来调用请求执行器(如handlerMethod)处理请求 // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } // 拦截器链后置处理applyPostHandle applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); ... // 响应客户端 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); }
所以与上面这些请求执行器配套的HandlerAdapter分别为:SimpleServletHandlerAdapter,SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,HttpRequestHandlerAdapter和RequestMappingHandlerAdapter。
如下为SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter的源码:其他类似
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc; /** * Adapter to use the plain {@link Controller} workflow interface with * the generic {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet}. * Supports handlers that implement the {@link LastModified} interface. * * <p>This is an SPI class, not used directly by application code. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet * @see Controller * @see LastModified * @see HttpRequestHandlerAdapter */ public class SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter { @Override public boolean supports(Object handler) { return (handler instanceof Controller); } @Override @Nullable public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response); } @Override public long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler) { if (handler instanceof LastModified) { return ((LastModified) handler).getLastModified(request); } return -1L; } }
获取更多学习资料,可以加群:473984645或扫描下方二维码



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号