Reachability from the Capital (bfs好题)
Reachability from the Capital
There are nn cities and mm roads in Berland. Each road connects a pair of cities. The roads in Berland are one-way.
What is the minimum number of new roads that need to be built to make all the cities reachable from the capital?
New roads will also be one-way.
Input
The first line of input consists of three integers n, mand s (1≤n≤5000,0≤m≤5000,1≤s≤n) — the number of cities, the number of roads and the index of the capital. Cities are indexed from 1 to n.
The following mm lines contain roads: road ii is given as a pair of cities uiui, vivi (1≤ui,vi≤n ui≠vi). For each pair of cities (u,v), there can be at most one road from u to v. Roads in opposite directions between a pair of cities are allowed (i.e. from u to v and from v to u).
Output
Print one integer — the minimum number of extra roads needed to make all the cities reachable from city s. If all the cities are already reachable from s, print 0.
Examples
9 9 1
1 2
1 3
2 3
1 5
5 6
6 1
1 8
9 8
7 1
3
5 4 5
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 1
1
Note
The first example is illustrated by the following:
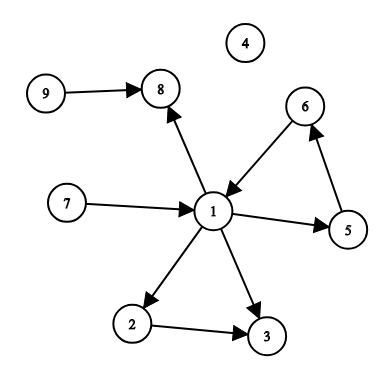
For example, you can add roads (6,4), (7,9), (1,7) to make all the cities reachable from s=1.
The second example is illustrated by the following:
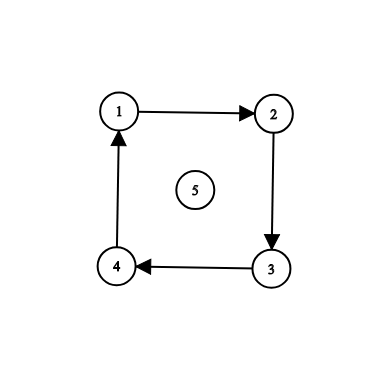
In this example, you can add any one of the roads (5,1), (5,2), (5,3), (5,4) to make all the cities reachable from s=5.
题意:n个城市,m条路,s为起点,单行路。 问至少加几条路可以使得从起点出发到达任何一个城市。
思路:%大佬%大佬 大佬tql
第一次bfs找到与起点连接的所有城市,并且把和起点不连接的城市全用book数组标记。第二次bfs找一找那些和起点不连接的城市和哪些同样不和起点连接的城市连接。按个数的多少排序。
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<cstdio>
3 #include<cstring>
4 #include<vector>
5 #include<queue>
6 #include<algorithm>
7 using namespace std;
8 const int maxn=1e4+10;
9 vector<int>v[maxn];
10 struct node{
11 int id;
12 int num;
13 }e[maxn];
14 int vis3[maxn];
15 int vis1[maxn];
16 int book[maxn];
17 int len=0;
18 int m,n,s;
19 int sum;
20 int vis[maxn];
21 int cmp(node a,node b)
22 {
23 return a.num>b.num;
24 }
25 int bfs(int x)
26 {
27 memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
28 queue<int>q;
29 q.push(x);
30 vis[x]=1;
31 int ans=0;
32 while(!q.empty())
33 {
34 int head=q.front();
35 q.pop();
36 for(int i=0;i<v[head].size();i++)
37 {
38 int to=v[head][i];
39 if(!vis[to])
40 {
41 vis[to]=1;
42 ans++;
43 q.push(to);
44 }
45
46 }
47 }
48 return ans;
49 }
50 int bfs1(int x)
51 {
52 memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
53 queue<int>q;
54 q.push(x);
55 vis[x]=1;
56 book[x]=0;
57 int ans=0;
58 while(!q.empty())
59 {
60 int head=q.front();
61 q.pop();
62 for(int i=0;i<v[head].size();i++)
63 {
64 int to=v[head][i];
65 if(!vis[to])//格外注意这块的书写
66 {
67 if(book[to])
68 {
69 book[to]=0;
70 ans++;
71 }
72
73 vis[to]=1;
74
75 q.push(to);
76 }
77
78 }
79 }
80 return ans;
81 }
82 int bfs2(int x)
83 {
84 memset(vis3,0,sizeof(vis3));
85 queue<int>q;
86 q.push(x);
87 vis3[x]=1;
88 int ans=0;
89 while(!q.empty())
90 {
91 int head=q.front();
92 q.pop();
93 for(int i=0;i<v[head].size();i++)
94 {
95 int to=v[head][i];
96 if(!vis3[to])
97 {
98 vis3[to]=1;
99 if(book[to])
100 ans++;
101 q.push(to);
102 }
103
104 }
105 }
106 return ans;
107 }
108 int main()
109 {
110 int x,y;
111 cin>>n>>m>>s;
112 while(m--)
113 {
114 scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
115 v[x].push_back(y);
116 }
117 sum=bfs(s);
118 if(sum==n-1)
119 puts("0");
120 else
121 {
122 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
123 {
124 if(vis[i])
125 continue;
126 book[i]=1;//将不与原点相连的点标记为1
127
128 }
129 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
130 {
131 if(book[i]==0)//因为没写这个if卡了我一晚上5个小时,不过大佬没用一分钟就帮我找到了错%%%%%%
132 continue;
133 e[len].id=i;
134 e[len++].num=bfs2(i);
135 }
136 sort(e,e+len,cmp);
137 int res=n-1-sum;
138 int tmp=0;
139 for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
140 {
141 if(book[e[i].id]==0)
142 continue;
143 tmp++;
144 int t=bfs1(e[i].id);
145 if(t!=0)
146 {
147 res-=(t+1);
148
149 }
150 else
151 {
152 res--;
153 }
154 if(res==0)
155 break;
156 }
157 printf("%d\n",tmp);
158 }
159 }




