1021 Deepest Root (25 分)(经典搜索)
1021 Deepest Root (25 分)
A graph which is connected and acyclic can be considered a tree. The height of the tree depends on the selected root. Now you are supposed to find the root that results in a highest tree. Such a root is called the deepest root.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤104) which is the number of nodes, and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N. Then N−1 lines follow, each describes an edge by given the two adjacent nodes' numbers.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print each of the deepest roots in a line. If such a root is not unique, print them in increasing order of their numbers. In case that the given graph is not a tree, print Error: K components where K is the number of connected components in the graph.
Sample Input 1:
5
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 5
Sample Output 1:
3
4
5
Sample Input 2:
5
1 3
1 4
2 5
3 4
Sample Output 2:
Error: 2 components
题意:首先判断是否为一棵树,如果不是树,输出有几个连通块,是树,按从小到大的顺序输出哪些节点作为根节点可以使整棵树的高度最大。
题解:判断连通块用并查集或者dfs都可以,这个题数据水了,按理说暴搜会T,但是这个题不会,所以一遍for循环每一个节点跑一遍树的高度也可以过。
正解是先随意选择一个点作为根节点,跑一遍搜索,找到最深处的节点并记录,然后从最深处的节点中选一个再跑一遍搜索,再找到最深处的节点,即为
所求根节点。但是,有一个坑:第一次找到的和第二次找到的要去重,例如:
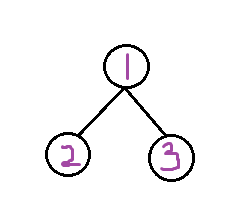
第一遍以1为根节点,得到最深层的节点为1、3,第二次以2或3再搜索,得到1、3或者1、2,即会和第一次搜索的重复。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e4+10;
vector<int>v[maxn];
vector<int>g[maxn];
set<int>s;
set<int>::iterator it;
int f[maxn];
int n,x,y;
int book[maxn];
int vis[maxn],ans[maxn];
void init()
{
for(int i=1;i<maxn;i++)
f[i]=i;
}
int getf(int x)
{
return f[x]==x?x:f[x]=getf(f[x]);
}
void merge(int x,int y)
{
int tx=getf(x);
int ty=getf(y);
if(tx!=ty)
f[tx]=ty;
}
int bfs(int x)
{
int high=1;
queue<int>q;
g[high].push_back(x);
q.push(x);
vis[x]=1;
while(!q.empty())
{
int sum=q.size();
high++;
for(int i=0;i<sum;i++)
{
int head=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int j=0;j<v[head].size();j++)
{
if(vis[v[head][j]])
continue;
vis[v[head][j]]=1;
g[high].push_back(v[head][j]);
q.push(v[head][j]);
}
}
}
return high-1;
}
void dfs(int x)
{
book[x]=1;
for(int i=0;i<v[x].size();i++)
{
if(!book[v[x][i]])
{
book[v[x][i]]=1;
dfs(v[x][i]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
//init();
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
// merge(x,y);
v[x].push_back(y);
v[y].push_back(x);
}
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!book[i])
{
dfs(i);
cnt++;
}
}
/* for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(f[i]==i)
cnt++;
}*/
if(cnt!=1)
{
printf("Error: %d components\n",cnt);
return 0;
}
int high=bfs(1);
cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<g[high].size();i++)
{
s.insert(g[high][i]);
ans[cnt++]=g[high][i];
}
for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++)
g[i].clear();
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
high=bfs(ans[0]);
for(int i=0;i<g[high].size();i++)
s.insert(g[high][i]);
for(it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++)
cout<<(*it)<<endl;
return 0;
}




