The Shortest Path in Nya Graph (最短路+建图难点)
The Shortest Path in Nya Graph
The Nya graph is an undirected graph with "layers". Each node in the graph belongs to a layer, there are N nodes in total.
You can move from any node in layer x to any node in layer x + 1, with cost C, since the roads are bi-directional, moving from layer x + 1 to layer x is also allowed with the same cost.
Besides, there are M extra edges, each connecting a pair of node u and v, with cost w.
Help us calculate the shortest path from node 1 to node N.
InputThe first line has a number T (T <= 20) , indicating the number of test cases.
For each test case, first line has three numbers N, M (0 <= N, M <= 10 5) and C(1 <= C <= 10 3), which is the number of nodes, the number of extra edges and cost of moving between adjacent layers.
The second line has N numbers l i (1 <= l i <= N), which is the layer of i th node belong to.
Then come N lines each with 3 numbers, u, v (1 <= u, v < =N, u <> v) and w (1 <= w <= 10 4), which means there is an extra edge, connecting a pair of node u and v, with cost w.OutputFor test case X, output "Case #X: " first, then output the minimum cost moving from node 1 to node N.
If there are no solutions, output -1.Sample Input
2 3 3 3 1 3 2 1 2 1 2 3 1 1 3 3 3 3 3 1 3 2 1 2 2 2 3 2 1 3 4
Sample Output
Case #1: 2 Case #2: 3
题意是给 n个点,m个边,C
m条边u,v,w,w是边权
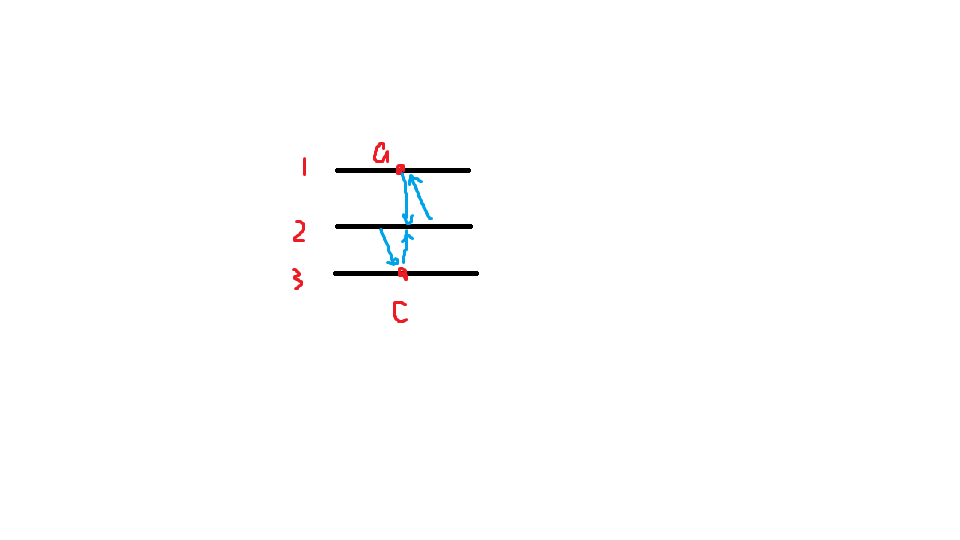
除此之外给你一个个 layer[i],表示点i属于第 layer[i]层!
关于层的性质有两个 【如果相邻两层都存在节点,则x层任意节点可以与x+1层任意节点互通,代价为C】
当然如果有一层为空,则空层是无法与上下层相通的哦!相当于断层!
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<queue> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std; const int maxn=2e5+100; struct node{ int to; int w; int next; }e[maxn*4]; int c[maxn]; int cnt; int vis[maxn],head[maxn],dis[maxn]; void init() { memset(dis,inf,sizeof(dis)); memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); cnt=0; } void add(int x,int y,int c) { e[cnt].to=y; e[cnt].next=head[x]; e[cnt].w=c; head[x]=cnt++; } struct Node{ int pos; int w; Node(){} Node(int pos,int w):pos(pos),w(w){} friend bool operator < (Node a,Node b) { return a.w>b.w; } }; int dijkstra(int st,int ed) { priority_queue<Node>q; q.push(Node(st,0)); dis[st]=0; while(!q.empty()) { Node u=q.top(); q.pop(); if(vis[u.pos]) continue; vis[u.pos]=1; for(int i=head[u.pos];i!=-1;i=e[i].next) { int v=e[i].to; if(!vis[v]&&dis[v]>dis[u.pos]+e[i].w) { dis[v]=dis[u.pos]+e[i].w; q.push(Node(v,dis[v])); } } } if(dis[ed]==inf) return -1; return dis[ed]; } int a,b,cost; int x,y,z; int casen; int n,m; //我们需要假设有2n个点,1-n是题目给出的n个点,n+1-2n是这些点可能所在的层。 int main() { cin>>casen; int ca=1; while(casen--) { init(); scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&cost); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d",&x); c[x]=1; add(i,n+x,0);//这里是点和所在层建立关系 不能建双向边的原因是假设有两个点在同一层 //比如有三个点,点1在第一层,点2也在第一层,虚拟第一层为点4,那么1-4有一条距离为0的点,4-1有一条距离为0的点 //2-4有一条距离为0的点,4-2有一条距离为0的点,那么1-2距离就成为0了,这是不对的。 if(x>1) { add(i,x+n-1,cost); } if(x<n) { add(i,x+n+1,cost); } //这两个if建立单向边的原因是,如果三层,中间一层没有点,建立双向边会导致最上和最下的两层可以相通,而事实上是不通的 //如图 } for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); add(x,y,z); add(y,x,z); } printf("Case #%d: %d\n",ca++,dijkstra(1,n)); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号