Python:Python基础(一)
-
基本数据类型补充
set
set集合,是一个无序且不重复的元素集合
1、创建set
①s = set( )
②s = { }
注:出现{}并不是指字典创建,字典里面是键值对,而set里面是无序且不重复的元素
2、转换
只要是可迭代的对象都可以转换
#列表转换成set集合 li = [11,22,33,44] s = set(li) print(s) #打印结果:{33, 11, 44, 22} #set集合转换成元祖 tu = tuple(s) print(tu) #打印结果:(33, 11, 44, 22)
3、set提供的方法
添加一个元素:add()
se = {11,22,33,}
se.add(44)
print(se)
#打印结果:{33, 11, 44, 22}
更新:update()
注:只能添加可迭代的类型
A = {44,55}
B = {22,33,44,55,66}
A.update(B)
print(A)
#打印结果:{33, 66, 22, 55, 44}
A = {44,55}
A.update([4,5])
print(A)
#打印结果:{5, 44, 4, 55}
A = {44,55}
A.update(4,5)
print(A)
#报错
移除元素(获取任意一个元素并删除):pop()
B = {22,33,44,55,66}
ret = B.pop()
print(B)
print(ret)
#打印结果:
{66, 44, 22, 55}
33
清除内容:clear()
se = {11,22,33,}
se.clear()
print(se)
#打印结果:set()
并集:union()
A = {44,55}
B = {22,33,44,55,66}
ret = A.union(B)
print(ret)
#打印结果:{33, 66, 22, 55, 44}
A中存在,B中不存在:difference()
A = {11,22,33}
B = {22,55}
r1 = A.difference(B)
print(r1)
#打印结果:{33, 11}
#B中存在,A中不存在
A = {11,22,33}
B = {22,55}
r2 = B.difference(A)
print(r2)
#打印结果:{55}
找A中存在B中不存在的元素(从当前集合中删除和B中相同的元素),并更新:difference_update()
A = {11,22,33}
B = {22,55}
A.difference_update(B)
print(A)
#打印结果:{33, 11}
交集:intersection()
A = {11,22,33}
B = {22,55}
ret = A.intersection(B)
print(ret)
#打印结果:{22}
取交集并更新到A中:intersection_uptate()
A = {11,22,33}
B = {22,55}
A.intersection_update(B)
print(A)
#打印结果:{22}
对称交集(两个集合中不同的元素):symmetric_difference()
A = {44,55}
B = {22,33,44,55,66}
ret = A.symmetric_difference(B)
print(ret)
#打印结果:{33, 66, 22}
A = {44,55}
B = {22,33,44,55,66}
ret = B.symmetric_difference(A)
print(ret)
#打印结果:{33, 66, 22}
对称交集(两个集合中不同的元素),并更新集合:symmetric_difference_update()
A = {44,55}
B = {22,33,44,55,66}
# ret = A.symmetric_difference(B)
A.symmetric_difference_update(B)
print(A)
#打印结果:{33, 66, 22}
移除指定元素,不存在不报错:discard()
注:remove,不存在要报错
A = {11,22,33}
A.discard(11)
print(A)
#打印结果:{33, 22}
是否有交集。如果没有交集,返回True,有交集返回False:isdisjoint()
A = {11,22,33}
B = {22,55}
ret = A.isdisjoint(B)
print(ret)
#打印结果:False
A = {11,22,33}
B = {44,55}
ret = A.isdisjoint(B)
print(ret)
#打印结果:True
是否是子序列:issubset()
#A是B的子序列,返回True,A不是B的子序列,返回False
A = {11,22,33}
B = {11,22}
ret = A.issubset(B)
print(ret)
#打印结果:False
A = {22,33}
B = {11,22,33}
ret = A.issubset(B)
print(ret)
#打印结果:True
是否是父序列:issuperset()
#A是B的父序列,返回True,A不是B的父序列,返回False
A = {11,22,33,44,55}
B = {22,33}
ret = A.issuperset(B)
print(ret)
#打印结果:True
A = {44,55}
B = {22,33,44,55,66}
ret = A.issuperset(B)
print(ret)
#打印结果:False
练习:寻找差异
new_dict,old_dict,字典中的key相同的
new_dict[key]值 --> old_dict[key]的值
old中存在,new不存在,old中删除
new_dict.keys存在,在old中添加
1 old_dict = { 2 "k1": 11, 3 "k2": 22, 4 "k3": 100, 5 } 6 new_dict = { 7 "k1": 33, 8 "k4": 22, 9 "k7": 100, 10 } 11 #将字典转换成set集合并获得key 12 old_keys = set(old_dict.keys()) 13 new_keys = set(new_dict.keys()) 14 #找到相同的key 15 update_key = old_keys.intersection(new_keys) 16 #把new字典中的值替换到old里面 17 for i in update_key: 18 old_dict[i] = new_dict[i] 19 #print(old_dict) 20 #找出old中存在new中不存在的key 21 del_keys = old_keys.difference(new_keys) 22 #删除old中有的,new中没有的 23 for i in del_keys: 24 del old_dict[i] 25 #找出new中有的,old中没有的 26 add_keys = new_keys.difference(old_keys) 27 #把new中有的old中没有的添加到old中 28 for i in add_keys: 29 old_dict[i] = new_dict[i] 30 print(old_dict) #打印结果:{'k4': 22, 'k7': 100, 'k1': 33}
-
三元运算
三元运算(三目运算),是对简单的条件语句的缩写。
#书写格式: result = 值1 if 条件 else 值2 #如果条件成立,那将值1赋值给result变量,否则,将值2赋值给result变量
示例:
name = "alex" if 1 == 1 else "eric" print(name) #打印结果:alex name = "alex" if 1 == 0 else "eric" print(name) #打印结果:eric
-
深浅拷贝
一、数字(int)和字符串(str)
对于数字和字符串,深拷贝、浅拷贝和赋值都一样,因为永远指向同一个内存地址。
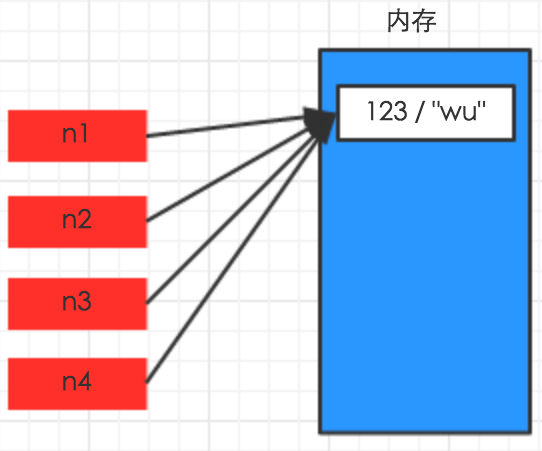
二、其他(列表、元祖、字典)
对于列表、字典、元组来说,进行深拷贝、浅拷贝和赋值时,内存地址的变化有所不同。
1、赋值
赋值,只是创建一个变量,该变量指向原来内存地址
示例:
n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]}
n2 = n1
print(id(n1))
print(id(n2))
#打印结果:3032705905992
#打印结果:3032705905992
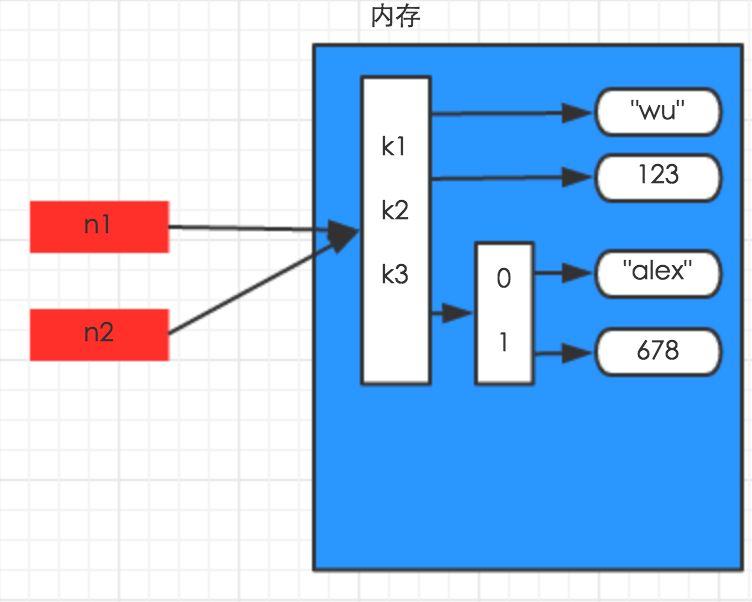
2、浅拷贝
浅拷贝,只拷贝最外层
import copy n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]} n2 = copy.copy(n1) print(id(n1)) print(id(n2)) #打印结果:2207499007304 #打印结果:2207499453000
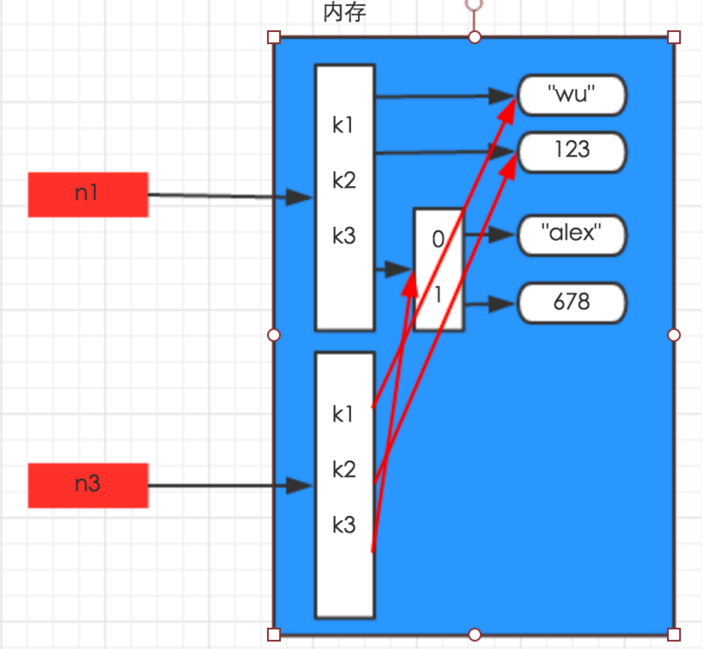
3、深拷贝
深拷贝,除了最内层,其他层都拷贝。
import copy n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]} n2 = copy.deepcopy(n1) print(id(n1)) print(id(n2)) #打印结果:2292897068360 #打印结果:2292901306184
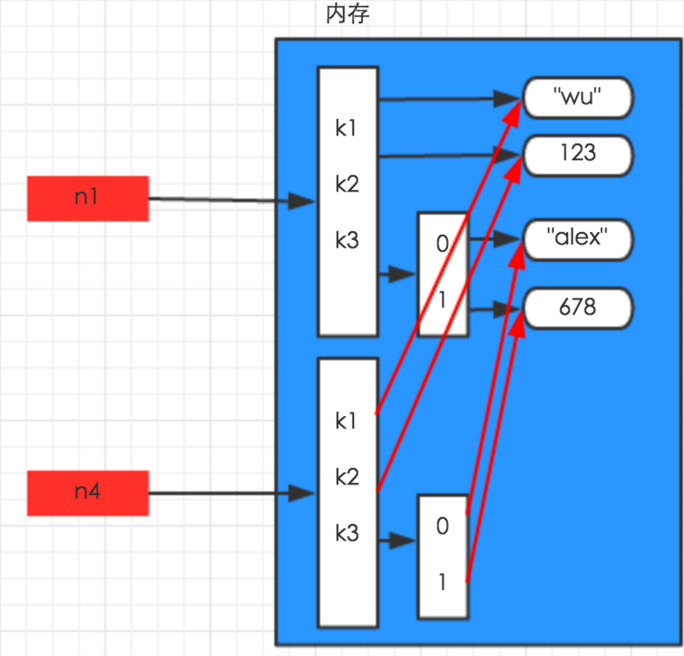
-
函数
创建函数
- 1.函数的关键字:def
- 2.函数名:函数的名称,用于日后根据函数名调用函数
- 3.()
- 4.:
- 5.函数体:函数中进行一系列的逻辑运算
- 6.返回值:当函数执行结束后,可以给调用者返回数据
a.return xxx
注:没有return:默认返回 None
b.一旦遇到return,函数内部return以下代码不再执行
- 7.参数:为函数体提供数据
def 函数名(参数): ... 函数体 ... 返回值
返回值
def 发送短信(): 发送短信的代码... if 发送成功: return True else: return False #如果短信发送成功,打印结果:True #如果短信发送失败,打印结果:False
参数
形式参数:定义函数是()里面的参数
实际参数:调用函数时()里面的参数
普通参数:数量要一致,并且要一一对应
指定参数:执行函数时,指定的形式参数
默认参数:定义函数时,给参数设定一个默认值。注:默认值放在参数尾部
动态参数:*args(*:列表、元祖、字符串)
**kwargs(**:字典)
局部变量和全局变量
全局变量
命名规则:大写
全局变量能被局部变量读取,不能修改。如果要修改要加一个:global
局部变量
命名规则:小写
仅仅在代码块中使用
练习题:
1、写函数,计算传入字符串中【数字】、【字母】、【空格] 以及 【其他】的个数
是否是数字:.isdigit()
是否是字母:.isalpha()
是否是空格:.isspace()
是否是字母和数字:.isalnum()

1 def fumc1(s): 2 al_num = 0 3 space_num = 0 4 digit_num = 0 5 others_num = 0 6 for i in s: 7 if i.isdigit(): 8 digit_num += 1 9 elif i.isspace(): 10 space_num += 1 11 elif i.isalpha(): 12 al_num += 1 13 else: 14 others_num += 1 15 16 return(al_num,space_num,digit_num,others_num) 17 18 19 r = fumc1("Hello *Hello1Hello2Hello") 20 print(r) 21 #打印结果:(20, 1, 2, 1)
2、写函数,判断用户传入的对象(字符串、列表、元组)长度是否大于5。
判断对象是否属于该类:.isinstance(arg,str)
判断对象是否属于该类:.isinstance(arg,list)
判断对象是否属于该类:.isinstance(arg,tuple)

def obj_len(arg): if isinstance(arg,str) or isinstance(arg,list) or isinstance(arg,tuple): if len(arg) > 5: return True else: return False #return None temp = "123" ret = obj_len(temp) print(ret) #打印结果:False
3、写函数,检查用户传入的对象(字符串、列表、元组)的每一个元素是否含有空内容。

def has_space(args): ret = True for c in args: if c.isspace(): ret = False break return ret result = has_space("213123 _)( afd") print(result) #打印结果:False
4、写函数,检查传入列表的长度,如果大于2,那么仅保留前两个长度的内容,并将新内容返回给调用者。

def f(arg): if len(arg) > 2: return arg[0:2] #return arg a = [1,2,3,4,5] r = f(a) print(r) #打印结果:[1, 2]
5、写函数,检查获取传入列表或元组对象的所有奇数位索引对应的元素,并将其作为新列表返回给调用者。

def f(arg): ret = [] for i in range(len(arg)): if i %2 == 1: ret.append(arg[i]) else: pass return ret li = [11,22,33,44,55] r = f(li) print(r) #打印结果:[22, 44]
6、写函数,检查传入字典的每一个value的长度,如果大于2,那么仅保留前两个长度的内容,并将新内容返回给调用者。

def f5(arg): ret = {} #循环所有的键值 for key,value in arg.items(): #当值的长度大于2 if len(value) > 2: ret[key] = value[0:2] else: ret[key] = value return ret dic = {"k1":"v1v1","k2":[11,22,33,44],"k3":"12"} r = f5(dic) print(r) #打印结果:{'k1': 'v1', 'k3': '12', 'k2': [11, 22]}




