树大作业
大作业--------树
1.树的存储结构说明
typedef int TreeData;
//树节点类型
typedef struct _treenode
{
TreeData data; //数据域
struct _treenode *child; //指向首孩子的指针
struct _treenode *brother; //指向右兄弟的指针
}TreeNode;
//树类型
typedef struct _tree
{
int len; //树节点的个数(不算头节点)
TreeNode *head; //指向头节点的指针
}Tree;
struct PATH //找路径
{
int pos;
int count;
//int time;
} ;
2.树的函数说明
2.1.1函数名
Tree *CreateTree ();
2.1.2代码
Tree *CreateTree ()
{
//创建一棵树
Tree *tree = (Tree*)malloc(sizeof(Tree)/sizeof(char));
//创建头节点
tree->head = (TreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode)/sizeof(char));
tree->head->child = NULL; //此时树为空
tree->head->brother = NULL;
tree->len = 0; //树节点个数为0
return tree;
}
2.1.3功能及思路
- 功能:建树
- 思路:建一个空树
2.2.1函数名
int InsertTree(Tree *tree, TreeData data, int pos, int count, int flag)
2.2.2代码
int InsertTree(Tree *tree, TreeData data, int pos, int count, int flag)
{
//创建树节点
TreeNode *node =(TreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode)/sizeof(char));
//初始化树节点
node->data = data;
node->child = NULL;
node->brother = NULL;
if (count == 0)//如果步数为0,则是插入的根节点
{
tree->head->child = node;
cout<<node->data;
tree->len++; //树节点+1
return 1;
}
else
{
//指针指向头节点,开始找节点位置
TreeNode *tmp = tree->head;
int way;
int num=0;
while(pos>0)//进行取反
{
num=pos%2+num*2;
pos=pos/2;
}
pos=num;
cout<<endl;
cout<<"path:";//输出路径
while (count > 0 && tmp != NULL)
{
//取每个二进位的值,判断往哪个方向走
way = pos & 1;
pos = pos >> 1;
if (way == CHILD)
{
tmp = tmp->child;
cout<<"1";
}
else
{
tmp = tmp->brother;
cout<<"0";
}
count--;
}
if (flag == CHILD)//根据flag判断要插入的是前一个节点的孩子还是右兄弟
{
tmp->child = node;
cout<<"child:"<<tmp->child->data;
}
else
{
tmp->brother = node;
cout<<"brother:"<<tmp->brother->data;
}
tree->len++; //插入成功,树节点+1
}
return 1;
}
2.2.3功能及思路
- 功能:插入
- 思路:首孩子为1,兄弟为0
用count是要走步数,从头节点开始走。
用flag表示是作为前一个节点是首孩子还是兄弟
2.3.1函数名
void Display(TreeNode *Tnode,int gap,char node[][20])
2.3.2代码
void Display(TreeNode *Tnode,int gap,char node[][20])
{
if (Tnode == NULL)
return;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < gap;i++)
printf ("-");
cout<<Tnode->data<<":";
for(int j=0;node[Tnode->data][j];j++)
printf ("%c",node[Tnode->data][j]);
printf("\n");
TreeNode * child = Tnode->child;
Display (child,gap+1,node);//一步一杠
TreeNode * brother = Tnode->brother;
Display (brother,gap,node);
}
2.3.3功能及思路
- 功能:输出
- 思路:根据二维数组,按相应顺序输出字符串并输出相应格式
2.4.1函数名
void Save(TreeNode *Tnode,int gap,char node[][20])
2.4.2代码
void Save(TreeNode *Tnode,int gap,char node[][20])
{
if (Tnode == NULL)
return;
ofstream writeFile;
writeFile.open("tree.txt",ios::out|ios::app);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < gap;i++)
printf ("-");
for(int j=0;node[Tnode->data][j];j++)
printf ("%c",node[Tnode->data][j]);
printf("\n");
for (i = 0; i < gap;i++)
writeFile<<"-";
for(int j=0;node[Tnode->data][j];j++)
writeFile<<node[Tnode->data][j];
writeFile<<endl;
TreeNode * child = Tnode->child;
Save (child,gap+1,node);//一步一杠
TreeNode * brother = Tnode->brother;
Save(brother,gap,node);
}
2.4.3功能及思路
- 功能:写入文件
- 思路:与输出相似,并将其写入文件里面
2.5.1函数名
TreeNode *FindNode(TreeNode *&T,int x)
2.5.2代码
TreeNode *FindNode(TreeNode *&T,int x)//找到所需删除的结点的位置 ,并删除
{
TreeNode *p;//再建一个指针,进行递归遍历,直到找到所要删除的结点
if(T==NULL)
return NULL;
else if(T->data==x)
{
if(T!=NULL)
{
if(T->child)
destroy(T->child);
free(T);
T = T->brother;
}
return T;
}
else
{
p=FindNode(T->child,x);
if(p!=NULL)
return p;
else
return FindNode(T->brother,x);
}
}
2.5.3功能及思路
- 功能:删除
- 思路:进行递归遍历
找到所需删除的结点的位置
进行删除
2.6.1函数名
void destroy(TreeNode *&T)
2.6.2代码
void destroy(TreeNode *&T)//用递归删掉结点
{
if(T!=NULL)
{
if(T->child)
destroy(T->child);
if(T->brother)
destroy(T->brother);
free(T);
T = NULL;
}
}
2.6.3功能及思路
- 功能:销毁函数
- 思路:挨个删除孩子和兄弟,直到为空
2.7.1函数名
void Find(TreeNode* T,string str,int ch[],char node[][20])
2.7.2代码
void Find(TreeNode* T,string str,int ch[],char node[][20])
{
TreeNode* p;
if(T&&Flag==0)
{
if(T->child==NULL)
{
if(node[T->data]==str)
{
Flag=1;
}
}
else
{
Find(T->brother,str,ch,node);
Find(T->child,str,ch,node);
if(Flag==1&&(T->brother==NULL||T->child->data==ch[i-1]))
{
ch[i]=T->data;
i++;
}
}
}
return;
}
2.7.3功能及思路
- 功能:输入标签元素,查找该元素的路径
- 思路:元素都放在叶子节点里,先找叶子节点
判断叶子节点里的元素是否与标签元素相同
不同继续遍历查找
2.8.1函数名
void Printf(TreeNode *Tnode,int ch[],char node[][20],string str)
2.8.2代码
void Printf(TreeNode *Tnode,int ch[],char node[][20],string str)
{
if (Tnode == NULL)
return;
int i=0,j,k;
while(ch[i])
{
i++;
}
for(j=i;j>=0;j--)
{
k=0;
while(node[ch[j]][k])
{
cout<<node[ch[j]][k];
k++;
}
}
cout<<str;
for(j=0;j<=i;j++)
{
k=0;
while(node[ch[j]][k])
{
cout<<node[ch[j]][k];
if(k==0)
{
cout<<'/';
}
k++;
}
}
return;
}
2.8.3功能及思路
- 功能:输出
- 思路:遍历输出,并注意“/”的格式问题
2.9.1函数名
2.9.2代码
int main()
{
int i=0,k=0,len=0,j=0;
static char node[50][20];
char str[1000];
string STR;
int data,ch[100];
ifstream readoutFile;
readoutFile.open("html.txt",ios::in);
while(!readoutFile.eof())
{
readoutFile >>str[i++];//从文档中取出
}
readoutFile.close();
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
cout<<str[j];
cout<<endl<<endl;
while(j<i)//存进二维数组
{
if(str[j]=='<')
{
node[k][len++]=str[j++];
while(str[j-1]!='>')
node[k][len++]=str[j++];
k++;
len=0;
}
if(str[j-1]=='>'&&str[j]!='<')
{
node[k][len++]=str[j++];
while(str[j]!='<')
node[k][len++]=str[j++];
k++;
len=0;
}
}
//输出展示
for(int j=0;j<k-2;j++){
cout<<j;
for(int q=0;node[j][q]!='\0';q++)
cout<<node[j][q];
cout<<endl;}
Tree* tree=CreateTree ();//建树 ,只有根节点的那种
j=0;
struct PATH path[100];
int flag1=0;
int pos=0,flag=1,count=0;
for(int i=0;i<k-1;i++)//根据判断开始插入结点
{
if(node[i][0]=='<'&&node[i][1]=='/')
{
if(flag==0)
pos=path[j-1].pos;//成为兄弟
count=path[j-1].count;
flag=0;
flag1=1;
}
else if(node[i][0]=='<'&&node[i][1]!='/')
{
data=i;
InsertTree(tree,data,pos,count,flag);
if(flag==1)
pos=pos*2+1;//孩子 1
if(flag==0)
pos=pos*2;//兄弟 0
count++;
path[j].pos=pos;
path[j].count=count;
j++;
flag=1;
flag1=0;
}
else
{
data=i;
InsertTree(tree,data,pos,count,flag);
j--;
}
}
cout<<endl;
Save(tree->head->child,0,node);
Display(tree->head->child,0,node);
cout<<"输入你要查找的标签";
cin>>STR;
Find(tree->head->child,STR,ch,node);
if(Flag==0)
{
cout<<"找不到该标签!";
}
else
{
cout<<"查找路径为:";
Printf(tree->head->child,ch,node,STR);
cout<<endl;
}
system("pause");
int x;
char item='\0';
while(item!='1')
{
cout<<"请输入要删除的结点:";
cin>>x;
FindNode(tree->head->child,x);
Save(tree->head->child,0,node);
Display(tree->head->child,0,node);
cout<<endl<<"删除成功!结束删除输入1,继续则随意输入"<<endl;
cin>>item;
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
2.9.3功能及思路
- 功能:串联所有函数
- 思路:读取文件内容
存进二维数组
进行相关函数的运用
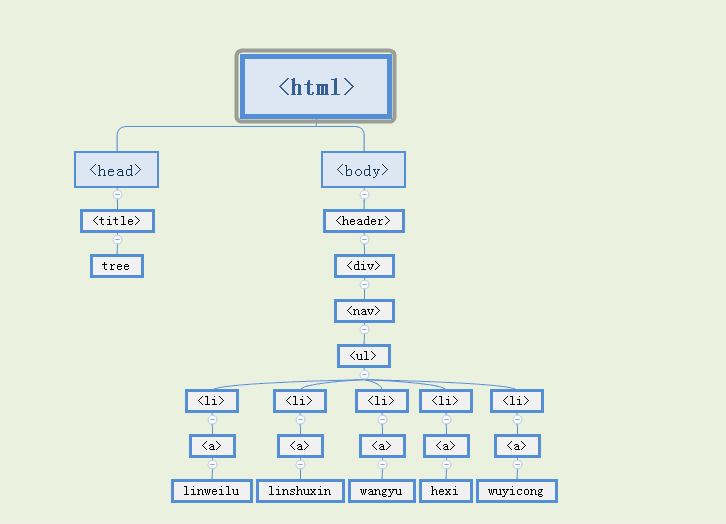
3.树结果演示

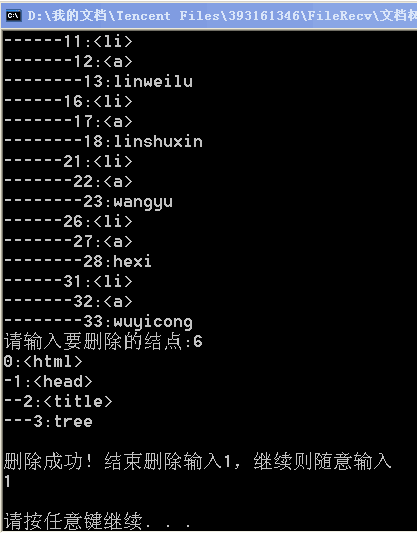


4.碰到问题
建树
- 建树所保存的元素是字符串,可能会有重复的字符串,在删除的时候很难办,后来采用先把元素放在二维数组里面,进行编号,再保存到树里。
- 在判断关系时,通过<和<\来判断二者之间是孩子关系还是兄弟关系。
- 在走路线方面,采用10进制转2进制后进行与运算的移位运算。如果是1,走父子路线,如果是0,走兄弟路线。但与运算从后面开始与的,所以只能将10进制转2进制倒过来运算,判断路径。
- 孩子标1,兄弟标0,将每一个路径输出判断插进去的位置是否正确。
- 在整个程序结束的时候,return 0会报错,最后采用改变结构体,程序就不存在这个问题。
保存
路径
- 定义静态变量时,整个代码会奔溃,最后采用定义全局变量。
删除

博客园
- 组员拍照不积极,带人物的不让上传。
5.小结
- 比较特别的地方:建树函数中,将十进制转二进制再进行与运算,再倒置这个方法,个人觉得好厉害,具写这段代码的成员所说,在思考这个方法中,花了特别多的时间
- 需要改进的地方:路径存储结构在代码中运用特别少,在考虑修改这部分代码
删除函数中,如果输入错误信息,程序会崩溃
6.小组成员分配说明
- 组长:林舒馨:建树,插入
- 组员:何汐:保存,ppt
- 组员:汪雨:路径
- 组员:吴沂聪:删除
- 组员:林玮璐:博客园
7.小组讨论照片