数字图像处理之频率域图像增强
、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
图像进行傅立叶运算的物理意义
http://met.fzu.edu.cn/dip/chapter4.html
http://www.360doc.com/content/10/1128/20/2226925_73234298.shtml
http://blog.csdn.net/depraved_survival/article/details/1739743
http://www.360doc.com/content/12/0218/13/8795013_187569365.shtml
、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
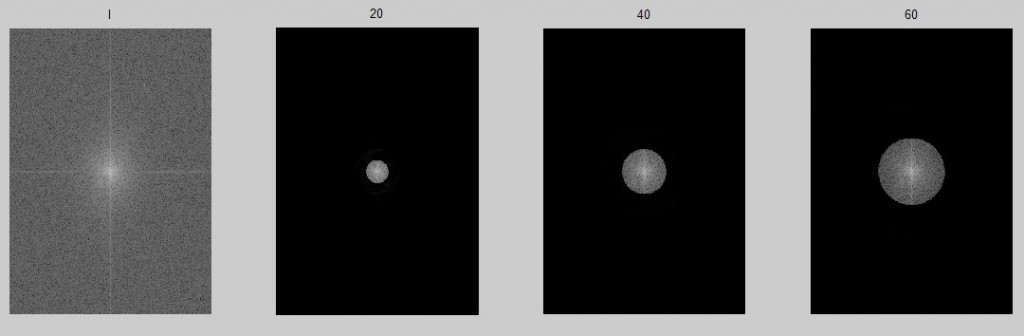
理想低通滤波器,过滤图像中的高频成分即噪声(但是也包含边缘)

、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
高斯低通滤波器
将上面的函数imidealflpf换成imgaussflpf,如下


貌似在抑制噪声的同时,图像的模糊程度更低了,比理想低通滤波器的效果好一点。
、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
高斯高通滤波器

、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
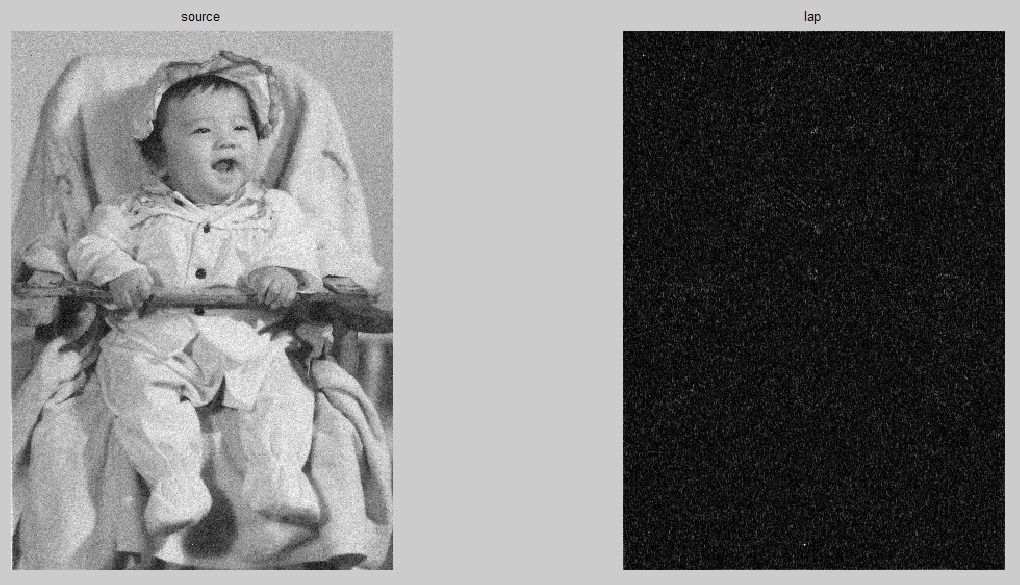
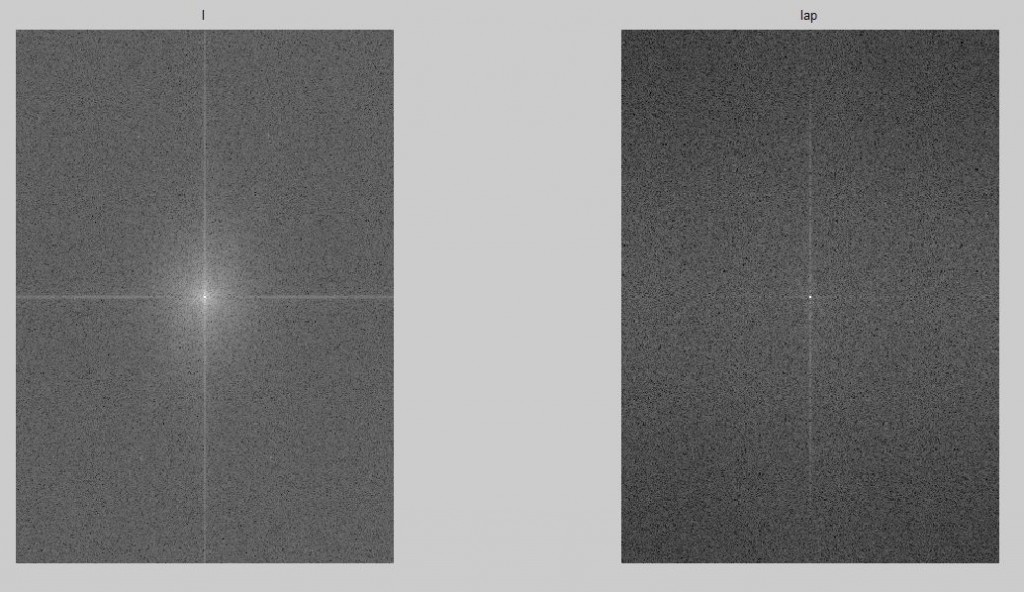
拉普拉斯滤波器
、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
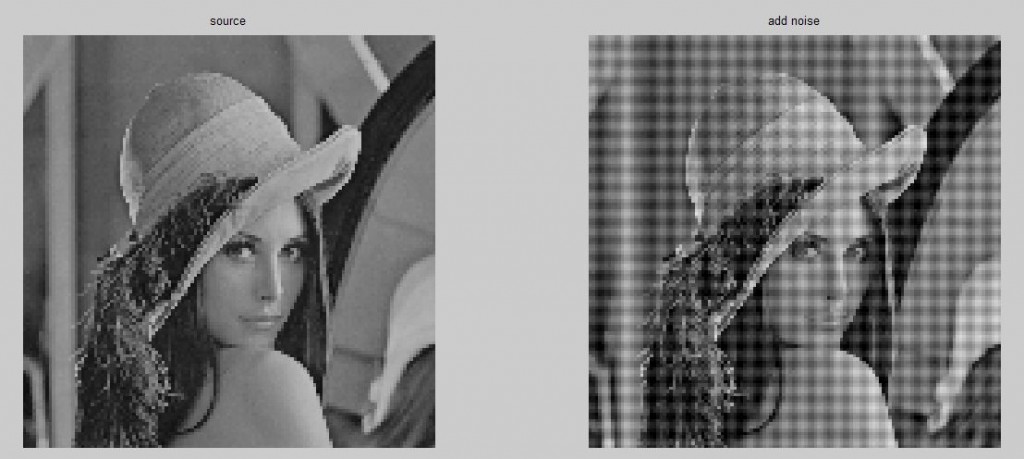
添加周期噪声。使用带阻滤波器消除之p230.

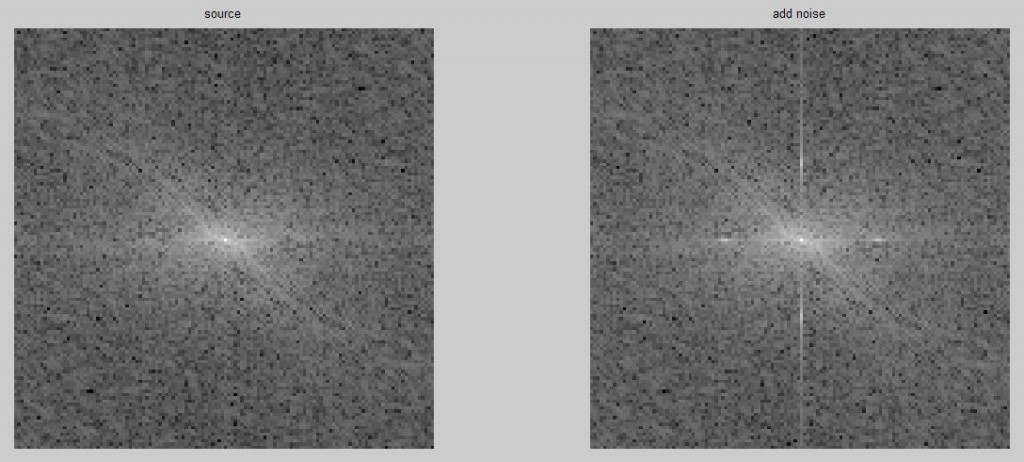
周期性图像的傅立叶频谱中出现了两对相对于坐标轴对称的亮点,它们分别对应于图形图像中水平和竖直方向的正弦噪声。
图像进行傅立叶运算的物理意义
http://met.fzu.edu.cn/dip/chapter4.html
http://www.360doc.com/content/10/1128/20/2226925_73234298.shtml
http://blog.csdn.net/depraved_survival/article/details/1739743
http://www.360doc.com/content/12/0218/13/8795013_187569365.shtml
、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
理想低通滤波器,过滤图像中的高频成分即噪声(但是也包含边缘)
function out = imidealflpf(I, freq)
% imidealflpf函数 构造理想的频域低通滤波器
% I参数 输入的灰度图像
% freq参数 低通滤波器的截止频率
% 返回值:out – 指定的理想低通滤波器
[M,N] = size(I);
out = ones(M,N);
for i=1:M
for j=1:N
if (sqrt(((i-M/2)^2+(j-N/2)^2))>freq)
out(i,j)=0;
end
end
end
function out = imfreqfilt(I, ff)
% imfreqfilt函数 对灰度图像进行频域滤波
% 参数I 输入的空域图像
% 参数ff 应用的与原图像等大的频域滤镜
if (ndims(I)==3) && (size(I,3)==3) % RGB图像
I = rgb2gray(I);
end
if (size(I) ~= size(ff))
msg1 = sprintf('%s: 滤镜与原图像不等大,检查输入', mfilename);
msg2 = sprintf('%s: 滤波操作已经取消', mfilename);
eid = sprintf('Images:%s:ImageSizeNotEqual',mfilename);
error(eid,'%s %s',msg1,msg2);
end
% 快速傅立叶变换
f = fft2(I);
% 移动原点
s = fftshift(f);
% 应用滤镜及反变换
out = s .* ff; %对应元素相乘实现频域滤波
out = ifftshift(out);
out = ifft2(out);
% 求模值
out = abs(out);
% 归一化以便显示
out = out/max(out(:));I=imread('baby_noise.bmp');
figure(1);subplot(1,4,1);imshow(I);title('source');
%求源图像的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(I);%做fft变换
temp=fftshift(temp);%将零点移到中心
temp=log(1+abs(temp));%对幅值做对数变换,以压缩动态范围
figure(2);subplot(1,4,1);imshow(temp,[]);title('I');%temp是double array,是浮点数,需要[].
ff=imidealflpf(I,20);%生成滤镜,频率是20即0-20之间的低频带被保留,大于20的高频带丢失
out=imfreqfilt(I,ff);%应用滤镜,即执行fft
figure(1);subplot(1,4,2);imshow(out);title('ideal lpf ,20');
%求out的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(out);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,4,2);imshow(temp,[]);title('20');
ff=imidealflpf(I,40);
out=imfreqfilt(I,ff);
figure(1);subplot(1,4,3);imshow(out);title('ideal lpf ,40');
%求out的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(out);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,4,3);imshow(temp,[]);title('40');
ff=imidealflpf(I,60);
out=imfreqfilt(I,ff);
figure(1);subplot(1,4,4);imshow(out);title('ideal lpf ,60');
%求out的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(out);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,4,4);imshow(temp,[]);title('60');

、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
高斯低通滤波器
将上面的函数imidealflpf换成imgaussflpf,如下
function out = imgaussflpf(I, sigma)
% imgaussflpf函数 构造频域高斯低通滤波器
% I参数 输入的灰度图像
% sigma参数 高斯函数的Sigma参数
[M,N] = size(I);
out = ones(M,N);
for i=1:M
for j=1:N
out(i,j) = exp(-((i-M/2)^2+(j-N/2)^2)/2/sigma^2);
end
endI=imread('baby_noise.bmp');
figure(1);subplot(1,4,1);imshow(I);title('source');
%求源图像的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(I);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,4,1);imshow(temp,[]);title('I');
ff=imgaussflpf(I,20);%生成滤镜,sigma=20,sigma越大保留的信息越多
out=imfreqfilt(I,ff);%应用滤镜,即执行fft
figure(1);subplot(1,4,2);imshow(out);title('gauss lpf ,20');
%求out的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(out);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,4,2);imshow(temp,[]);title('20');
ff=imgaussflpf(I,40);
out=imfreqfilt(I,ff);
figure(1);subplot(1,4,3);imshow(out);title('gauss lpf ,40');
%求out的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(out);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,4,3);imshow(temp,[]);title('40');
ff=imgaussflpf(I,60);
out=imfreqfilt(I,ff);
figure(1);subplot(1,4,4);imshow(out);title('gauss lpf ,60');
%求out的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(out);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,4,4);imshow(temp,[]);title('60');

貌似在抑制噪声的同时,图像的模糊程度更低了,比理想低通滤波器的效果好一点。
、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
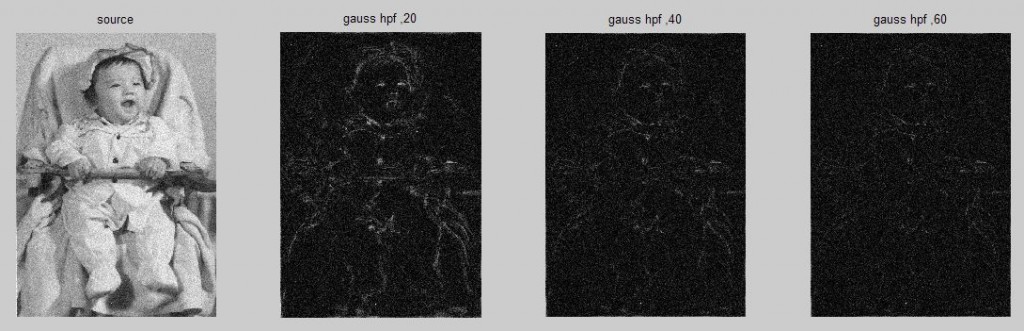
高斯高通滤波器
function out = imgaussfhpf(I, sigma)
% imgaussfhpf函数 构造频域高斯高通滤波器
% I参数 输入的灰度图像
% sigma参数 高斯函数的Sigma参数
[M,N] = size(I);
out = ones(M,N);
for i=1:M
for j=1:N
out(i,j) = 1 - exp(-((i-M/2)^2+(j-N/2)^2)/2/sigma^2);
end
end
I=imread('baby_noise.bmp');
figure(1);subplot(1,4,1);imshow(I);title('source');
%求源图像的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(I);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,4,1);imshow(temp,[]);title('I');
ff=imgaussfhpf(I,20);%生成滤镜,sigma=20,sigma越大,边缘提取越精确
out=imfreqfilt(I,ff);%应用滤镜,即执行fft
figure(1);subplot(1,4,2);imshow(out);title('gauss hpf ,20');
%求out的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(out);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,4,2);imshow(temp,[]);title('20');
ff=imgaussfhpf(I,40);
out=imfreqfilt(I,ff);
figure(1);subplot(1,4,3);imshow(out);title('gauss hpf ,40');
%求out的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(out);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,4,3);imshow(temp,[]);title('40');
ff=imgaussfhpf(I,60);
out=imfreqfilt(I,ff);
figure(1);subplot(1,4,4);imshow(out);title('gauss hpf ,60');
%求out的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(out);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,4,4);imshow(temp,[]);title('60');

、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
拉普拉斯滤波器
function out = imlapf(I)
% imlapff函数 构造频域拉普拉斯滤波器
% I参数 输入的灰度图像
[M,N] = size(I);
out = ones(M,N);
for i=1:M
for j=1:N
out(i,j) = -((i-M/2)^2+(j-N/2)^2);
end
endI=imread('baby_noise.bmp');
figure(1);subplot(1,2,1);imshow(I);title('source');
%求源图像的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(I);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,2,1);imshow(temp,[]);title('I');
ff=imlapf(I);%生成滤镜
out=imfreqfilt(I,ff);%应用滤镜,即执行fft
figure(1);subplot(1,2,2);imshow(out);title('lap');
%求out的fft频谱图
temp=fft2(out);
temp=fftshift(temp);
temp=log(1+abs(temp));
figure(2);subplot(1,2,2);imshow(temp,[]);title('lap');

、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
添加周期噪声。使用带阻滤波器消除之p230.
II=imread('lena.gif');
figure(1);subplot(1,2,1);imshow(II);title('source');
%显视频谱图
ii_f=fft2(II);
ii_f=fftshift(ii_f);
ii_f=abs(ii_f);
ii_f=log(1+ii_f);
figure(2);subplot(1,2,1);imshow(ii_f,[]);title('source');
%加周噪
[M,N]=size(II);
I=double(II);
for i=1:M
for j=1:N
I(i,j)=I(i,j) + 20*sin(20*i) + 20*sin(20*j);
end
end
I=uint8(I);
figure(1);subplot(1,2,2);imshow(I);title('add noise');
%显视频谱图
i_f=fft2(I);
i_f=fftshift(i_f);
i_f=abs(i_f);
i_f=log(1+i_f);
figure(2);subplot(1,2,2);imshow(i_f,[]);title('add noise');

周期性图像的傅立叶频谱中出现了两对相对于坐标轴对称的亮点,它们分别对应于图形图像中水平和竖直方向的正弦噪声。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号