020.1.1 collections集合工具类
内容:常见需求以及使用—逆转比较器顺序,最值和同步方法
collections类的方法都是静态方法
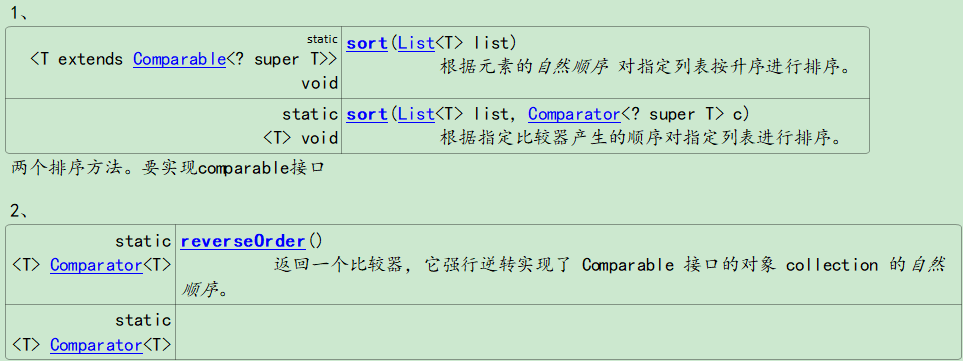
强行逆转比较器的顺序
例子:

//##主函数.java List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("wg"); list.add("wanng"); list.add("qio"); list.add("duai"); System.out.println(list); Collections.sort(list,Collections.reverseOrder(new ComparableByLength())); System.out.println(list); //##ComparableByLength.java public class ComparableByLength implements Comparator { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { String str1 = (String)o1; String str2 = (String)o2; int temp = str1.length() - str2.length(); return temp == 0?str1.compareTo(str2):temp; } }
###############################################
最值和同步方法
泛型使用

public static void main(String[] args) { Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>(); coll.add("ang."); coll.add("wang"); coll.add("xiong"); coll.add("zhong"); String max = getMax(coll); System.out.println(max); } public static<T extends Comparable<? super T>> T getMax(Collection<? extends T> coll){ Iterator<? extends T> it = coll.iterator(); T max = it.next(); while(it.hasNext()){ T temp = it.next(); if(temp.compareTo(max)>0){ max = temp; } } return max; }
迭代器从哪里来,泛型就和谁一样
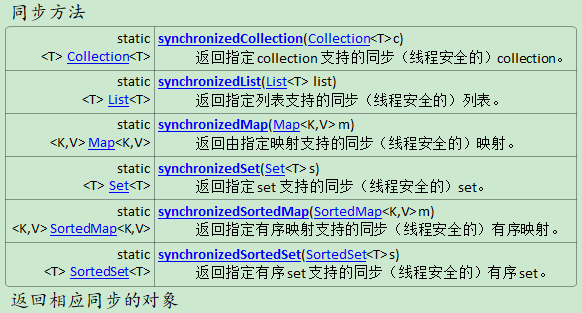
#################example_063Comparable自定义排序

public class Employee implements Comparable<Employee> { private int id; private String name; private int age; public Employee(int id, String name, int age) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public int compareTo(Employee o) { if(id > o.id){ return 1; } else if(id < o.id){ return -1; } return 0; } @Override public String toString() { return "Employee [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }

public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<Employee>(); list.add(new Employee(3, "python", 5)); list.add(new Employee(2, "c", 27)); list.add(new Employee(6, "java", 10)); System.out.println("排序前:"); for(Employee employee: list){ System.out.println(employee); } System.out.println("排序后:"); Collections.sort(list); for(Employee employee:list){ System.out.println(employee); } } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号