项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 人工智能实战2019 这个作业的要求在哪 作业要求 我在这个课程的目标是 了解人工智能相关知识,提高编程能力 这个作业在哪个具体方面帮助我实现目标 熟悉梯度下降算法 作业正文 (https://www.cnblogs.com/-myq123/p/10593493.html
一 . 代码及结果
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pathlib import Path
x_data_name = "D:/Desktop/TemperatureControlXData.dat"
y_data_name = "D:/Desktop/TemperatureControlYData.dat"
class CData(object):
def __init__(self, loss, w, b, epoch, iteration):
self.loss = loss
self.w = w
self.b = b
self.epoch = epoch
self.iteration = iteration
def ReadData():
Xfile = Path(x_data_name)
Yfile = Path(y_data_name)
if Xfile.exists() & Yfile.exists():
X = np.load(Xfile)
Y = np.load(Yfile)
return X.reshape(1,-1),Y.reshape(1,-1)
else:
return None,None
def ForwardCalculationBatch(W,B,batch_x):
Z = np.dot(W, batch_x) + B
return Z
def BackPropagationBatch(batch_x, batch_y, batch_z):
m = batch_x.shape[1]
dZ = batch_z - batch_y
dB = dZ.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)/m
dW = np.dot(dZ, batch_x.T)/m
return dW, dB
def UpdateWeights(w, b, dW, dB, eta):
w = w - eta*dW
b = b - eta*dB
return w,b
def InitialWeights(num_input, num_output):
W = np.random.normal(size=(num_output, num_input))
B = np.zeros((num_output, 1))
return W,B
def CheckLoss(W, B, X, Y):
m = X.shape[1]
Z = np.dot(W, X) + B
LOSS = (Z - Y)**2
loss = LOSS.sum()/m/2
return loss
def GetBatchSamples(X,Y,batch_size,iteration):
num_feature = X.shape[0]
start = iteration * batch_size
end = start + batch_size
batch_x = X[0:num_feature,start:end].reshape(num_feature,batch_size)
batch_y = Y[0,start:end].reshape(1,batch_size)
return batch_x, batch_y
def GetMinimalLossData(dict_loss):
key = sorted(dict_loss.keys())[0]
w = dict_loss[key].w
b = dict_loss[key].b
return w,b,dict_loss[key]
if __name__ == '__main__':
eta=0.05
max_epoch=100
b_size=[5,10,15]
i=0
while(i<3):
batch_size=b_size[i]
W, B = InitialWeights(1,1)
dict_loss = {}
# read data
X, Y = ReadData()
# count of samples
num_example = X.shape[1]
num_feature = X.shape[0]
max_iteration = (int)(num_example / batch_size)
for epoch in range(max_epoch):
print("epoch=%d" %epoch)
for iteration in range(max_iteration):
batch_x, batch_y = GetBatchSamples(X,Y,batch_size,iteration)
# get z from x,y
batch_z = ForwardCalculationBatch(W, B, batch_x)
# calculate gradient of w and b
dW, dB = BackPropagationBatch(batch_x, batch_y, batch_z)
# update w,b
W, B = UpdateWeights(W, B, dW, dB, eta)
# calculate loss for this batch
loss = CheckLoss(W,B,X,Y)
print(epoch,iteration,loss,W,B)
prev_loss = loss
dict_loss[loss] = CData(loss, W, B, epoch, iteration)
# end for
# end for
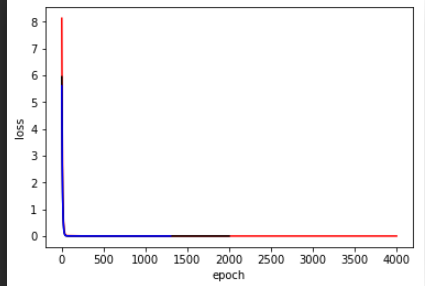
color = ['red','black','blue']
loss = []
for key in dict_loss:
loss.append(key)
plt.plot(loss,color=color[i],label='batchsize='+str(b_size[i]))
i=i+1
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.show()
二 . 附加问题
1.为什么是椭圆而不是圆?如何把这个图变成一个圆?
因为w,b两者的传播速度不一样,所以loss函数投影的xy平面会是椭圆,如果两者一致椭圆就会退化为圆
2.为什么中心是个椭圆区域而不是一个点?
用计算机离散的算极值,只能是小于某个小量,因此取值一定是个区域。


