spring基础回顾
一、spring项目构建
使用idea创建项目
二、Sping IOC容器
1、简单实例
package entity; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 10:04 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Phone { private String name; private String money; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getMoney() { return money; } public void setMoney(String money) { this.money = money; } public void init(){ System.out.println("初始化"); } public void destory(){ System.out.println("销毁"); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="Phone" class="entity.Phone"> <property name="name" value="IP12"></property> <property name="money" value="6799软妹币"></property> </bean> </beans>
package test; import entity.Phone; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionReader; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 10:08 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // BeanFactory Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("config/spring.xml"); BeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); BeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader((BeanDefinitionRegistry) factory); beanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); Phone phone = (Phone) factory.getBean("Phone"); System.out.println(phone.getName()+"售价为:"+phone.getMoney()); } }
执行:

2、BeanFactory和ApplicationContext
Spring ApplicationContext 容器
Application Context 是 BeanFactory 的子接口,也被称为 Spring 上下文。
Application Context 是 spring 中较高级的容器。和 BeanFactory 类似,它可以加载配置文件中定义的 bean,将所有的 bean 集中在一起,当有请求的时候分配 bean。 另外,它增加了企业所需要的功能,比如,从属性文件中解析文本信息和将事件传递给所指定的监听器。这个容器在 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext interface 接口中定义。
ApplicationContext 包含 BeanFactory 所有的功能,一般情况下,相对于 BeanFactory,ApplicationContext 会更加优秀。当然,BeanFactory 仍可以在轻量级应用中使用,比如移动设备或者基于 applet 的应用程序。
最常被使用的 ApplicationContext 接口实现:
-
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:该容器从 XML 文件中加载已被定义的 bean。在这里,你需要提供给构造器 XML 文件的完整路径。
-
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:该容器从 XML 文件中加载已被定义的 bean。在这里,你不需要提供 XML 文件的完整路径,只需正确配置 CLASSPATH 环境变量即可,因为,容器会从 CLASSPATH 中搜索 bean 配置文件。
- WebXmlApplicationContext:该容器会在一个 web 应用程序的范围内加载在 XML 文件中已被定义的 bean。
// BeanFactory // Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("config/spring.xml"); // BeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); // BeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader((BeanDefinitionRegistry) factory); // beanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); // Phone phone = (Phone) factory.getBean("Phone"); // System.out.println(phone.getName()+"售价为:"+phone.getMoney()); // ApplicationContext ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/spring.xml"); Phone phone = (Phone) applicationContext.getBean("Phone"); System.out.println(phone.getName()+"售价为:"+phone.getMoney());
3、Bean的作用域、生命周期、后置处理器、定义继承。
作用域:
singleton
在spring IoC容器仅存在一个Bean实例,Bean以单例方式存在,默认值-->
prototype 每次从容器中调用Bean时,都返回一个新的实例,即每次调用getBean()时,相当于执行newXxxBean()-->
简单的说:
singleton 只有一个实例,也即是单例模式。
prototype访问一次创建一个实例,相当于new。
应用场合:
需要回收重要资源(数据库连接等)的事宜配置为singleton,如果配置为prototype需要应用确保资源正常回收。
2.有状态的Bean配置成singleton会引发未知问题,可以考虑配置为prototype。
struts2的action交由spring管理的时候,spring默认是singleton的,而struts2的action显然是有状 态的,所以必须显示设置为scope="prototype",prototype为原型模式,每次action请求过来都会创建一个action但是对 那些Dao的实现类推介scope="singleton" ,因为这些类没有状态,用singleton只需维护一个实例,显然性能高一些


生命周期:
Phone类添加init和destory方法
package entity; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 10:04 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Phone { private String name; private String money; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getMoney() { return money; } public void setMoney(String money) { this.money = money; } public void init(){ System.out.println("初始化"); } public void destory(){ System.out.println("销毁"); } }
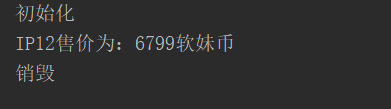
<bean id="Phone" class="entity.Phone" scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"> <property name="name" value="IP12"></property> <property name="money" value="6799软妹币"></property> </bean>
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/spring.xml"); Phone phone = (Phone) applicationContext.getBean("Phone"); System.out.println(phone.getName()+"售价为:"+phone.getMoney()); // 关闭hook执行销毁方法 ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) applicationContext).registerShutdownHook();
执行:
后置处理器:
添加MyPostProcess类
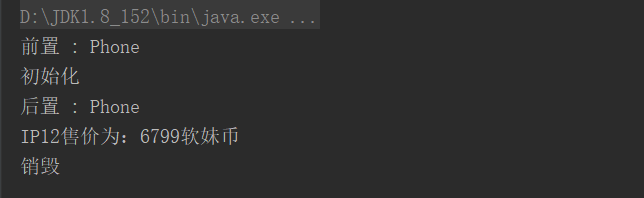
package entity; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 11:17 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class MyPostProcess implements BeanPostProcessor { public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("前置 : " + beanName); return bean; // you can return any other object as well } public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("后置 : " + beanName); return bean; // you can return any other object as well } }
bean添加
<bean class="entity.MyPostProcess"></bean>
执行:
定义继承
添加Phone2。
package entity; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 11:49 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Phone2 { private String name; private String money; private String city; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getMoney() { return money; } public void setMoney(String money) { this.money = money; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } }
bean配置
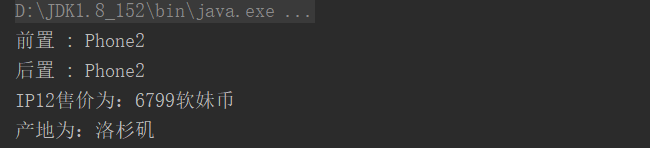
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="Phone" class="entity.Phone" scope="singleton" abstract="true"> <property name="name" value="IP12"></property> <property name="money" value="6799软妹币"></property> </bean> <bean id="Phone2" class="entity.Phone2" parent="Phone"> <property name="city" value="洛杉矶"></property> </bean> <bean class="entity.MyPostProcess"></bean> </beans>
package test; import entity.Phone; import entity.Phone2; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DeprecatedBeanWarner; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionReader; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 10:08 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // BeanFactory // Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("config/spring.xml"); // BeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); // BeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader((BeanDefinitionRegistry) factory); // beanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); // Phone phone = (Phone) factory.getBean("Phone"); // System.out.println(phone.getName()+"售价为:"+phone.getMoney()); // ApplicationContext // Application Context 是 BeanFactory 的子接口,也被称为 Spring 上下文。 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/spring.xml"); Phone2 phone = (Phone2) applicationContext.getBean("Phone2"); System.out.println(phone.getName()+"售价为:"+phone.getMoney()); System.out.println(phone.getCity()+"产地为:"+phone.getCity()); // 关闭hook执行销毁方法 ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) applicationContext).registerShutdownHook(); } }
执行:
三、依赖注入
1、构造函数依赖注入
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 17:06 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text { public void textm(){ System.out.println("Text的方法___________11111111111"); } }
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 16:52 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text1 { public void textm1(){ System.out.println("Text1方法_____________111111"); } public void textm2(){ System.out.println("Text1方法_____________22222222"); } }
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 16:54 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text2 { private Text1 text1; private Text text; public Text2(Text1 text1,Text text){ this.text1 = text1; this.text = text; } public void text2m1(){ text.textm(); text1.textm1(); text1.textm2(); } }
bean配置:
<bean id="Text" class="di.Text"> </bean> <bean id="Text1" class="di.Text1"> </bean> <bean id="Text2" class="di.Text2"> <constructor-arg ref="Text1"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg ref="Text"></constructor-arg> </bean>
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/spring.xml"); Text2 text2 = (Text2) applicationContext.getBean("Text2"); text2.text2m1(); // 关闭hook执行销毁方法 ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) applicationContext).registerShutdownHook();
运行输出:

2、设置函数的依赖注入
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 17:24 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text3 { public void text3m(){ System.out.println("text3方法。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。"); } }
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 17:24 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text4 { public void text4m(){ System.out.println("text4方法。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。"); } }
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 17:24 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text5 { private Text3 text3; private Text4 text4; public void setText3(Text3 text3) { this.text3 = text3; } public void setText4(Text4 text4) { this.text4 = text4; } public void text5m(){ text3.text3m(); text4.text4m(); } }
bean配置:
<bean id="Text3" class="di.Text3"> </bean> <bean id="Text4" class="di.Text4"> </bean> <bean id="Text5" class="di.Text5"> <property name="Text3" ref="Text3"></property> <property name="Text4" ref="Text4"></property> </bean>
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/spring.xml"); Text5 text5 = (Text5) applicationContext.getBean("Text5"); text5.text5m(); // 关闭hook执行销毁方法 ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) applicationContext).registerShutdownHook();
运行结果:

3、注入内部beans
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 17:34 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text6 { public void text6m(){ System.out.println("text6方法。。。。。。。。。。。。"); } }
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 17:34 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text7 { private Text6 text6; public Text6 getText6() { return text6; } public void setText6(Text6 text6) { this.text6 = text6; } public void text7m(){ text6.text6m(); } }
bean配置:
<bean id="Text7" class="di.Text7"> <property name="Text6"> <bean id="Text6" class="di.Text6"></bean> </property> </bean>
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/spring.xml"); Text7 text7 = (Text7) applicationContext.getBean("Text7"); text7.text7m(); // 关闭hook执行销毁方法 ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) applicationContext).registerShutdownHook();
运行结果:

4、集合和值传递
package di; import java.util.List; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/7 17:24 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text4 { private String name4; private List<String> list; public String getName4() { return name4; } public void setName4(String name4) { this.name4 = name4; } public List<String> getList() { return list; } public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } public void text4m(){ System.out.println("text4方法。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。值为:"+name4); System.out.println("text4方法。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。list值为:"+list); } }
<bean id="Text4" class="di.Text4">
<property name="name4" value="Text4name值"></property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>IP4</value>
<value>IP5</value>
<value>IP6</value>
<value>IP7</value>
<value>IP8</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
运行结果:

四、自动装配
1、byName和byType自动装配
byName:根据属性名自动装配。此选项将检查容器并根据名字查找与属性完全一致的bean,并将其与属性自动装配。
byType:如果容器中存在一个与指定属性类型相同的bean,那么将与该属性自动装配;如果存在多个该类型bean,那么抛出异常,并指出不能使用byType方式进行自动装配;如果没有找到相匹配的bean,则什么事都不发生
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/8 9:40 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text8 { public void textm(){ System.out.println("Text8类————————————方法"); } }
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/8 9:41 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text9 { private Text8 text8; public Text8 getText8() { return text8; } public void setText8(Text8 text8) { this.text8 = text8; } public void text9m(){ text8.textm(); } }
beans配置:byName或者byType
<bean id="text8" class="di.Text8" > </bean> <bean id="Text9" class="di.Text9" autowire="byName"> </bean>
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/spring.xml"); Text9 text9 = (Text9) applicationContext.getBean("Text9"); text9.text9m(); // 关闭hook执行销毁方法 ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) applicationContext).registerShutdownHook();
运行结果:

2、构造函数的自动装配constructor
这种模式与 byType 非常相似,但它应用于构造器参数。Spring 容器看作 beans,在 XML 配置文件中 beans 的 autowire 属性设置为 constructor。然后,它尝试把它的构造函数的参数与配置文件中 beans 名称中的一个进行匹配和连线。如果找到匹配项,它会注入这些 bean,否则,它会抛出异常。
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/8 10:32 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text10 { public void textm(){ System.out.println("Text10类______________________________方法"); } }
package di; /** * @Author LLF * @Date Created in 2020/12/8 10:32 * @Description * @Version 1.0 **/ public class Text11 { private Text10 text10; public Text11(Text10 text10){ this.text10 = text10; } public void text11m(){ text10.textm(); } }
beans配置:
<bean id="text10" class="di.Text10"></bean> <bean id="text11" class="di.Text11" autowire="constructor"> </bean>
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/spring.xml"); Text11 text11 = (Text11) applicationContext.getBean("text11"); text11.text11m();
运行结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号