0302 线程状态、线程安全
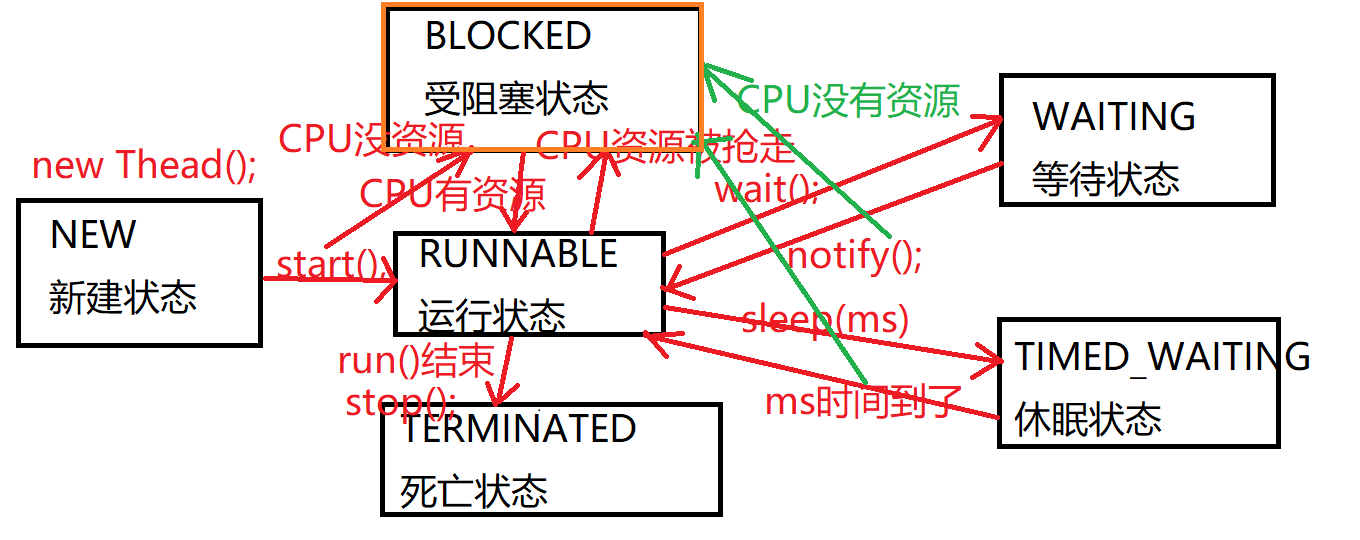
线程状态
1、新建状态
2、受阻塞状态
3、运行状态
4、死亡状态
5、休眠状态
6、等待状态
线程安全
当多条线程共用一份资源的时候就睡产生线程安全,比如电影院我们有100张票,同时有三个渠道去卖这100张票,看一下案例思维图

我们来模拟一下这个场景
首先创建一个线程类 实现Runnable接口,并且重写run方法
public class Ticket implements Runnable{
private int num=100;
//卖票
public void run() {
while(true){
if(num>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖出了第"+num--+"张票");
}
}
}
}
创建一个测试类,创建三条线程去卖票
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建线程任务
Ticket t=new Ticket();
//创建三条线程
Thread t1=new Thread(t);
Thread t2=new Thread(t);
Thread t3=new Thread(t);
//开启线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
根据运行结果会发现,会有第0张和第-1张 还有可能会出现多条线程卖同一张票的情况

这就出现了线程安全问题,解决这个线程安全的方法
1、同步代码块
2、同步方法
3、lock接口
用到的是Synchronized关键字
1、同步代码块格式
synchronized (锁对象) {
可能会产生线程安全问题的代码
}
同步代码块的锁对象可以是任意对象,但要保证该对象是唯一的
代码展示
public class Ticket02 implements Runnable{
private int num=100;
//定义一个锁对象
private Object obj=new Object();
//卖票
public void run() {
while(true){
synchronized (obj) {
if(num>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖出了第"+num--+"张票");
}
}
}
}
}
2、同步方法
格式:
public synchronized void method(){
可能会产生线程安全问题的代码
}
代码展示
public class Ticket03 implements Runnable{
private int num=100;
//卖票
public void run() {
while(true){
sale();
}
}
//同步方法
public synchronized void sale(){
if(num>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖出了第"+num--+"张票");
}
}
}
3、lock接口
在loc接口中有两个方法
(1)lock()获取锁
(2)unlock()释放锁
因为lock是个接口 那我们需要创建他的子类对象ReentrantLock去使用
代码展示
public class Ticket04 implements Runnable{
private int num=100;
//定义锁对象
private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock();
//卖票
public void run() {
while(true){
//获取锁
lock.lock();
if(num>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖出了第"+num--+"张票");
}
//释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
那我们回想一下StringBuffer和StringBuilder这两个类完全相同,唯一的区别是StringBuilder比StringBuffer速度要快,是因为StringBuffer底层方法都用了Synchronized关键字,也就是说StringBuffer类能够保证线程安全,但StringBuilder类是不保证线程安全的,所以StringBuilder类适合在单线程中使用。


