java--线程池
线程池
概念:
线程池,其实就是一个容纳多个线程的容器,其中的线程可以反复使用,省去了频繁创建线程对象的操作,无需反复创建线程而消耗过多资源。
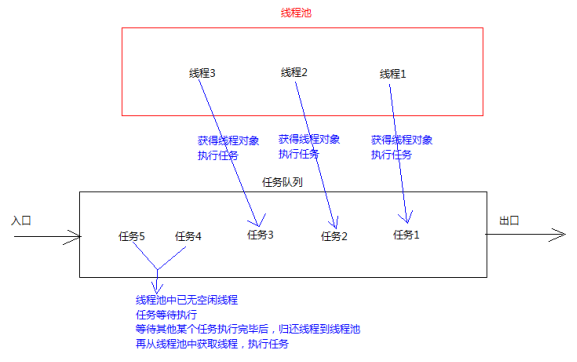
使用线程池方式--Runnable接口
通常,线程池都是通过线程池工厂创建,再调用线程池中的方法获取线程,再通过线程去执行任务方法。
步骤:
1、Executors:线程池创建工厂类
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads):返回线程池对象
2、ExecutorService:线程池类
Future<?> submit(Runnable task):获取线程池中的某一个线程对象,并执行
3、Future接口:用来记录线程任务执行完毕后产生的结果。线程池创建与使用
使用线程池中线程对象的步骤:
①创建线程池对象
②创建Runnable接口子类对象
③提交Runnable接口子类对象
④关闭线程池
演示:
public class demo1 implements Runnable{
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
System.out.println("run....."+i);
}
}
}
public class xianchengchi {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取线程池对象(从线程池工厂获得)
ExecutorService es=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//创建Runnable接口子类对象(创建任务对象)
demo1 run=new demo1();
//提交Runnable接口子类对象(线程池选一条线程执行你提交过来的任务)
es.submit(run);
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
System.out.println("main....."+i);
}
//关闭线程池
es.shutdown();
}
}
使用线程池方式-Callable接口
Callable接口:
与Runnable接口功能相似,用来指定线程的任务。其中的call()方法,用来返回线程任务执行完毕后的结果,call方法可抛出异常。
步骤:
1、ExecutorService:线程池类
2、<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task):获取线程池中的某一个线程对象,并执行线程中的call()方法
3、Future接口:用来记录线程任务执行完毕后产生的结果。线程池创建与使用
使用线程池中线程对象的步骤:
①创建线程池对象
②创建Callable接口子类对象
③提交Callable接口子类对象
④关闭线程池
//Callable泛型就是你call()的返回值类型
public class MyCallable implements Callable<String>{
public String call(){
return "这是Call方法";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//获取线程池
ExecutorService es=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//创建Callable子类
MyCallable mc=new MyCallable();
//提交callable子类
Future<String> f=es.submit(mc);
String str=f.get();//获取Future对象的内容用get()
System.out.println(str);
es.shutdown();
}
练习:
1、异步计算0—100和&0—200的和
public class jisuan implements Callable<Integer>{
private Integer a;
jisuan(Integer a){
this.a=a;
}
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<=a;i++){
sum+=i;
}
return sum;
}
}
//异步计算0——100和&0-200的和
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//获取线程池
ExecutorService es=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//创建Callable子类
jisuan js=new jisuan(100);
jisuan js2=new jisuan(200);
//提交callable子类
Future<Integer> f=es.submit(js);
Future<Integer> f2=es.submit(js2);
//从Future中获取返回值
System.out.println(f.get());
System.out.println(f2.get());
//关闭线程池
es.shutdown();
}
2、返回两个数相加的结果
public class qiuhe implements Callable<Integer>{
private int a;
private int b;
public qiuhe(int a, int b) {
super();
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int sum=0;
sum=a+b;
return sum;
}
}
public class demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService es=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
qiuhe qh1=new qiuhe(100,50);
qiuhe qh2=new qiuhe(200,50);
Future<Integer> f1=es.submit(qh1);
Future<Integer> f2=es.submit(qh2);
System.out.println(f1.get());
System.out.println(f2.get());
es.shutdown();
}
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号