JDBC学习总结 -- JDBC 快速入门 教程
先感谢前人的劳动成果,
本教程中含有多处指路,请注意筛选.
详细请阅读官方文档:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/jdbc/basics/index.html (不建议直接上手)
https://www.journaldev.com/2681/jdbc-tutorial
前置知识:基本SQL 语句,JAVA SE基础

JDBC 目录:
1.JDBC概念
2.JDBC处理SQL语句的过程(建表,查表)
- 建立与数据库的连接
- 创建 statement
- 执行 Query
- 处理 结果集(ResultSets)
3.专题介绍
- ResultSet 与 Statement 中的 Prestatement,CallableStatement 详细介绍
- 批处理的使用 + 删除表格
- DataSource 与连接池,事务 (DBCP,简易连接池)
4.结尾
- ORM
- DAO封装自己的JDBC
1. JDBC的概念
JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity)

是一种数据库连接技术,
能实现Java程序对各种数据库的访问。由一组使用Java语言编写的类和接口(JDBC API)
组成,他们位于java.sql以及javax.sql中。
推荐解释指路 中的 (二.JDBC是什么)
作用:
1. 与数据库建立联系.
2. 将编写好的SQL语句发送至数据库执行
3. 对数据库返回的结果进行操作
JDBC API
- java.sql.*
-
javax.sql.*
连接数据库相关的:
DriverManager:
用URL连接数据库,
在4.0版本之前要进行加载. 即用映射加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
相对于DriverManager类,DataSource更适合用于获取操作数据的Connection对象,
它相对灵活,并且支持 JNDI ,可以为servlet容器提供连接池
(可以去找DBCP的资料,这里涉及到了 The Java EE Tutorial.)
连接池解释推荐指路,后续会解释DataSource的使用.
Connection接口:
负责连接数据库并担任传送数据的任务。
数据库SQL相关的:
Statement接口:
负责执行SQL语句。
- PreparedStatement: 预编译,可以让SQL拥有参数,防止SQL注入
- CallableStatement: 可以Statement基础上执行存储过程
ResultSet接口:
负责保存Statement执行后所产生的查询结果。
RowSet接口:
RowSet 比 ResultSet 功能更多,更易使用,所有的RowSet对象都继承于 ResultSet.
2.JDBC处理SQL语句的过程(建表,查表)
使用JDBC 的步骤
- 建立 与数据库的连接 (其中包括用
- 创建 statement
- 执行 Query
- 处理 结果集(ResultSets)
- 关闭 连接
这里,我们使用MySQL 进行演示,
如果你使用是JAVA DB,他自带了JDBC
首先去MySQL官方下载 MYSQL 和 Connector/J.
(以下内容请根据自己环境进行配置)(官方教程使用的是 Apache ANT)
我们要使用 Connector/J
这里我们使用Eclipse - 在项目窗口右击Properties
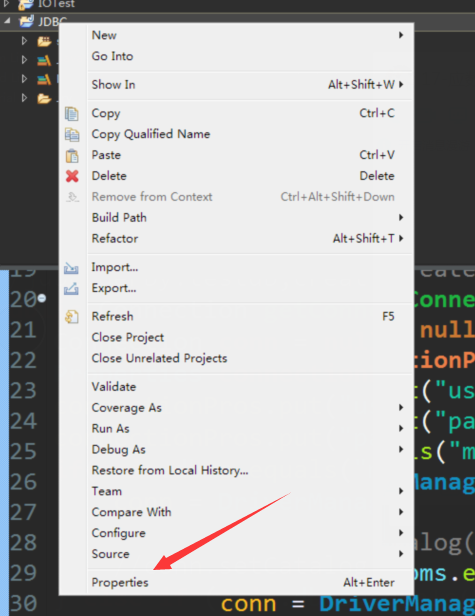
之后选择 JAVA Build Path->中的Libraries ,然后点击右边的 Add External JARS 将Connector/J 中的JAR文件导入

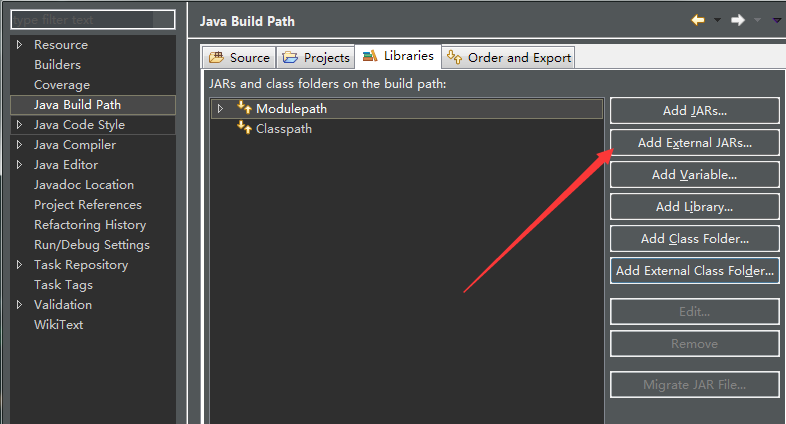
这样就可以开始编写了我们的JDBC了.

1. 建立与数据库的连接,这里使用DriverManager
我们需要用到DBMS的 URL 进行连接
- 一般mysql的URL : jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/
- JDBC URL: jdbc:derby:testdb;create=true

在用正确的用户密码,服务器等等参数连接数据库URL后,
DriverManager 会返回一个Connection,
我们编写一个方法来获取相关的Connection
//根据自己的数据库进行修改
public class JDBCTutorials {
String userName = "root"; //用户名
String password = "password";//用户密码
String dbms = "mysql";//数据库管理系统名称
String serverName = "localhost";//服务器名称
String portNumber = "3306";//服务器接口
String Atribute = "serverTimezone=UTC"
+ "&characterEncoding=utf-8"
+ "&useSSL=false";//时区与SLL连接方式禁用
String dbName = "crashcourse";//需要访问的数据库名称,可以为空,但是得自己用USE语句
//jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/
//jdbc:derby:testdb;create=true
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException{
Connection conn = null;
Properties connectionPros = new Properties();//新建一个Propeties容器
connectionPros.put("user", userName);
connectionPros.put("password", password);
if(this.dbms.equals("mysql")) {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:" + this.dbms + "://" + this.serverName +
":" + this.portNumber + "/" + this.dbName + "?" + this.Atribute,connectionPros);//获取连接
//conn.setCatalog(this.dbName);
} else if (this.dbms.equals("derby")) {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:" + this.dbms + ":"+ this.dbName + ":"
+ ";create=true",connectionPros);
}
System.out.println("Connection DBMS Successfully");
return conn;
}
}
更改相关的参数后,如果出现
"Connection DBMS Successfully"
就说明连接数据库管理系统成功了.返回的Connection就要用到了,
接下来我们需要将SQL语句运用起来.
2. 创建Statement , 和执行Query, ResultSet使用(建表 查表)
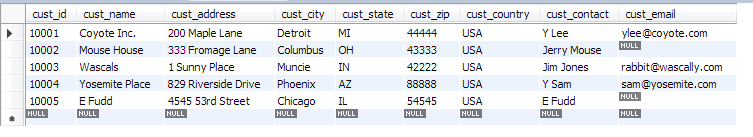
接下来我们需要使用的表格如下:
建立这个表格的SQL语句:
//---------------------------------------建立表格-----------------------------------------
CREATE TABLE customers
(
cust_id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
cust_name char(50) NOT NULL ,
cust_address char(50) NULL ,
cust_city char(50) NULL ,
cust_state char(5) NULL ,
cust_zip char(10) NULL ,
cust_country char(50) NULL ,
cust_contact char(50) NULL ,
cust_email char(255) NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY (cust_id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
//---------------------------------------填充数据-----------------------------------------
INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)
VALUES(10001, 'Coyote Inc.', '200 Maple Lane', 'Detroit', 'MI', '44444', 'USA', 'Y Lee', 'ylee@coyote.com');
INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact)
VALUES(10002, 'Mouse House', '333 Fromage Lane', 'Columbus', 'OH', '43333', 'USA', 'Jerry Mouse');
INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)
VALUES(10003, 'Wascals', '1 Sunny Place', 'Muncie', 'IN', '42222', 'USA', 'Jim Jones', 'rabbit@wascally.com');
INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)
VALUES(10004, 'Yosemite Place', '829 Riverside Drive', 'Phoenix', 'AZ', '88888', 'USA', 'Y Sam', 'sam@yosemite.com');
INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact)
VALUES(10005, 'E Fudd', '4545 53rd Street', 'Chicago', 'IL', '54545', 'USA', 'E Fudd');
那么我们怎么使用上面的SQL语句?

首先,我们要知道之前编写的 getConnection 方法返回了一个connetion
我们现在要再执行SQL语句的方法中使用它, SQL语句也需要先储存到一个String中
public void createTable(Connection con) throws SQLException{
String createSQL = "CREATE TABLE customers\r\n" + //存储SQL语句
"(\r\n" +
" cust_id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,\r\n" +
" cust_name char(50) NOT NULL ,\r\n" +
" cust_address char(50) NULL ,\r\n" +
" cust_city char(50) NULL ,\r\n" +
" cust_state char(5) NULL ,\r\n" +
" cust_zip char(10) NULL ,\r\n" +
" cust_country char(50) NULL ,\r\n" +
" cust_contact char(50) NULL ,\r\n" +
" cust_email char(255) NULL ,\r\n" +
" PRIMARY KEY (cust_id)\r\n" +
") ENGINE=InnoDB;";
try(Statement statement = con.createStatement()){//用connection 创建一个statement
statement.executeUpdate(createSQL);//编译SQL语句
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
这样,建表的SQL语句就完成了.
为什么要把statement的建立写到try中?
因为JAVA7 提供了自动关闭资源的机制
executeUpdate是什么?
与之对于的是execute,executeQuery
- executeQuery 只执行查 (select语句)
- executeUpdate 执行 增删改 (insert或者update/delete(DML)语句,或者 什么也不返回的DDL语句)
- execute 执行 增删改查
我们建立了表,但是表是空的,我们应该怎么样使用SQL的插入语句?
原理类似
public void populateTable(Connection con) throws SQLException{
try(Statement statement = con.createStatement()){
statement.executeUpdate("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" +
"VALUES(10001, 'Coyote Inc.', '200 Maple Lane', 'Detroit', 'MI', '44444', 'USA', 'Y Lee', 'ylee@coyote.com');");
statement.executeUpdate("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact)\r\n" +
"VALUES(10002, 'Mouse House', '333 Fromage Lane', 'Columbus', 'OH', '43333', 'USA', 'Jerry Mouse');");
statement.executeUpdate("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" +
"VALUES(10003, 'Wascals', '1 Sunny Place', 'Muncie', 'IN', '42222', 'USA', 'Jim Jones', 'rabbit@wascally.com');");
statement.executeUpdate("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" +
"VALUES(10004, 'Yosemite Place', '829 Riverside Drive', 'Phoenix', 'AZ', '88888', 'USA', 'Y Sam', 'sam@yosemite.com');");
statement.execute("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact)\r\n" +
"VALUES(10005, 'E Fudd', '4545 53rd Street', 'Chicago', 'IL', '54545', 'USA', 'E Fudd');");//这里需要使用excute,因为返回多个ResultSet
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
接着,写一个查询表的方法
public void viewTable(Connection con,String dbName) throws SQLException{//查询表的功能 String query = "SELECT * FROM customers;";//SQL语句 try(Statement statement = con.createStatement()){//创建Statement ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);//编译SQL语句,用ResultSet存储查询结果 while(resultSet.next()) {//换一行 String custID = resultSet.getString("cust_id");//获取该行列为"cust_id"的的数据 String custName = resultSet.getString("cust_name"); String custAddress = resultSet.getString("cust_address"); System.out.println(custID + ", " + custName + ", " + custAddress); } }catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println(e); } }
注意:
executeQuery 是只能执行一条SQL 语句的,要执行多条需要用到批处理
3.使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
JDBCTutorials jdbcTutorials = new JDBCTutorials();
try (Connection connection = jdbcTutorials.getConnection()){
jdbcTutorials.createTable(connection);
jdbcTutorials.populateTable(connection);
jdbcTutorials.viewTable(connection,"crashcourse");
}catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
执行结果:
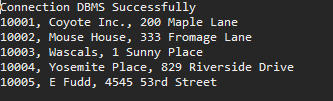
4.关闭步骤
一般步骤是:
} finally {
if (stmt != null) { stmt.close(); }
}
不过后来JAVA 7出那个新特性,可以用try来自动关闭了
try (Statement stmt = con.createStatement()) {
// ...
}

============SQL 语句的处理 以及 连接数据库 的入门结束============
3.专题讲解
1.ResultSet 讲解 推荐阅读:
http://www.iteye.com/topic/560109
https://www.cnblogs.com/zxg-6/p/5598329.html
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/jdbc/jdbc-result-sets.htm (英文)
JAVADOC : https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/sql/ResultSet.html
ResultSet 有不同功能和特性,
1.1 三个特性
- 类型
- 并发性
- 光标保持性
光标是什么?
光标就是指向行的标记,告诉他指向了哪里.
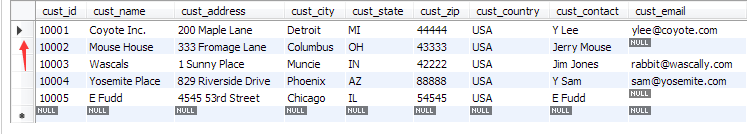
如图,左边的红箭头指向的,这个就是个光标,他指着第一行 (cust_id = 10001 .....)
(1) ResultSet 有三个不同的类型,
默认类型:TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY.
TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY:
光标只能向前滚动, (只能使用 next() )
效率:高
TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE:
前后鼓动的方法 next(),previous() ,回到首尾的方法 first(),last() , 到达指定位置的方法 absolute(int n ) // n代表行数,下标从1开始
光标可以向前向后滚动,对数据库的更改不敏感,
效率:中等
TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE:
光标可以前后移动,对数据库的更改敏感
只对UPDATE操作有效,对INSERT,DELETE无效
(敏感的意思就是你数据库更改后,ResultSet的数据也会更改,比如数据库中第一行第一列的
"苹果"变为"李子",ResultSet也会跟着变化)
效率:低
(2) 并发性
默认类型:CONCUR_READ_ONLY.
CONCUR_READ_ONLY:
只读,在ResultSet中的数据无法更改
CONCUR_UPDATABLE:
在ResultSet中的数据可以更改
注意:有些JDBC drivers 和 数据 不支持并发.
(3)光标保持性
默认类型取决你的DBMS
HOLD_CURSORS_OVER_COMMIT:
在事务commit 或rollback 后,ResultSet 仍然可用 (推荐在大部分ResultSet 都是 CONCUR_READ_ONLY 的情况下使用)
CLOSE_CURSORS_AT_COMMIT:
在事务commit 或rollback 后,ResultSet 不可用
注意:不是所有 数据库支持
(4)检测当前数据库时候支持某种特性
boolean supportsResultSetType(int resultSetType); //类型
boolean supportsResultSetConcurrency(int type, int concurrency);//并发性
boolean supportsResultSetHoldability(int holdability);//保持性
public static void cursorHoldabilitySupport(Connection conn)
throws SQLException {
DatabaseMetaData dbMetaData = conn.getMetaData();
System.out.println("Default cursor holdability: " +
dbMetaData.getResultSetHoldability());//检测是否支持并发性
System.out.println("Supports HOLD_CURSORS_OVER_COMMIT? " +
dbMetaData.supportsResultSetHoldability(
ResultSet.HOLD_CURSORS_OVER_COMMIT));//检测时候支持并发性的某一种
System.out.println("Supports CLOSE_CURSORS_AT_COMMIT? " +
dbMetaData.supportsResultSetHoldability(
ResultSet.CLOSE_CURSORS_AT_COMMIT));
}
1.2 功能
1.2.1 控制光标的函数介绍:
前后滚动的方法 next(),previous()
回到首尾的方法 first(),last()
到达指定位置的方法 absolute(int n) // n代表行数,下标从1开始
relative(int n) 移动到相对于当前位置
移动到最后一行后面,此时没有指向任意行 afterLast()
移动到第一行前面,此时没有指向任意行 beforeFirst()
1.2.2 ResultSet支持用下标进行查询,查询更高效
从左到右,下标从1开始,(即1 代表cust_id 列)
如: int custID = resultSet.getInt(1); // 获取该行第一列的整数
示范代码:
public void viewTable(Connection con,String dbName) throws SQLException{
String query =
"SELECT * FROM customers;";//查询 SQL语句
try(Statement statement = con.createStatement()){//创建Statement
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);//编译SQL语句
while(resultSet.next()) {
int custID = resultSet.getInt(1); // 获取该行第一列的整数,即cust_id的信息
String custName = resultSet.getString(2);
String custAddress = resultSet.getString(3);
System.out.println(custID + ", " + custName + ", " +
custAddress);
}
}catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}

1.2.3 用ResultSet 更新行
用ResultSet.updateFloat(int columnInex , Array x) 去更新行,让行进行改变,
只有在执行Result.updateRow() 之后,改变才会生效.
public void changeTable(Connection con,String dbName) throws SQLException{
String query =
"SELECT * FROM customers;";//SQL语句
try(Statement statement = con.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE)){//创建Statement
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);//编译SQL语句
resultSet.afterLast();//从前往后更新ID,因为他是 PRIMARY KEY不能重复
while(resultSet.previous()) {
int custID = resultSet.getInt(1);
resultSet.updateInt(1, custID+1);//客服ID + 1
resultSet.updateRow();//更改生效
}
}catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}

1.2.4 用ResultSet 插入行
注意:有些JDBC driver不支持 这个功能,如果不支持,会抛出一个 SQLFeatureNotSupportedException 异常
先用 ResultSet.moveToInsertRow(); 将光标移动到要插入的地方
之后用 ResultSet.update() 修改要插入的数据
最后用 ResultSet.insertRow(); 完成插入
public void insertTableReSet(Connection con) throws SQLException{
String query =
"SELECT * FROM customers;";//SQL语句
try (Statement statement = con.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE)){
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);
resultSet.moveToInsertRow();
resultSet.updateInt(1, 10006);
resultSet.updateString(2, "New Man");
resultSet.updateString(3, "3123 street");
resultSet.insertRow();
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}

2.Statement
2.1 Statement 方法
Statement和ResultSet是怎么工作的?
查询到的的数据先存到数据库的缓冲中,ResultSet就是对缓冲数据的应用.
setFetchsize 设置每次获取的数据数(rs.next),当数据数量多,处理时间长,就需要用到
setMaxRows 限制返回的数据集数量,类似SQL 中的LIMIT
getGeneratedKeys() 获取自动生成的主键值.
executeQuery 只执行查 (select语句)
executeUpdate 执行 增删改 (insert或者update/delete(DML)语句,或者 什么也不返回的DDL语句)
execute 执行 增删改查
2.2 PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement 是一个预编译SQL语句,可以用setter传入参数
也就是可以用有参数的SQL语句了,参数代替用 ? 从左往右排序, 下标为1开始.
动态参数化用来查询的 演示代码:
public void viewTablePreparedStatement(Connection con,String dbName) throws SQLException{
String query =
"SELECT * FROM customers WHERE cust_id = ?;";// ? 可以用一个参数代替
try(PreparedStatement statement = con.prepareStatement(query)){//创建Statement
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);//编译SQL语句
int i = 0;
while(resultSet.next()) {
statement.setInt(1, 10001 + i++);//用 10001 + i 替代 第一个 ?
int custID = resultSet.getInt(1);
String custName = resultSet.getString(2);
String custAddress = resultSet.getString(3);
System.out.println(custID + ", " + custName + ", " +
custAddress);
}
}catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
可以用一个循环去设置参数
for(Map.Entry<Integer, String> e: customerCondition.entrySet()) {
statement.setInt(1, e.getKey());
statement.setString(2, e.getValue());
//写执行语句
}
演示代码:
public void viewTablePreparedStatement(Connection con,String dbName) throws SQLException{
String query =
"SELECT * FROM customers WHERE cust_id = ? AND cust_name = ?;";//? 可以用一个参数代替
HashMap<Integer, String> customerCondition = new HashMap<>();
customerCondition.put(10001, "Coyote Inc.");
customerCondition.put(10002, "Mouse House");
customerCondition.put(10003, "Wascals");
customerCondition.put(10004, "Yosemite Place");
customerCondition.put(10005, "New Man");
try(PreparedStatement statement = con.prepareStatement(query)){//创建Statement
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);//编译SQL语句
int i = 0;
for(Map.Entry<Integer, String> e: customerCondition.entrySet()) {
statement.setInt(1, e.getKey());
statement.setString(2, e.getValue());
resultSet.next();
int custID = resultSet.getInt(1);
String custName = resultSet.getString(2);
String custAddress = resultSet.getString(3);
System.out.println(custID + ", " + custName + ", " +
custAddress);
}
}catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
优点:
性能比Statement 好,
还可以防止臭名昭著的 SQL注入 攻击, 简单原理
应该尽量使用PreparedStatement.
缺点:
无法使用 IN 语句,
解放方案
1.多个单条SQL语句拼成与有 IN 语句一样的查询 -- 效率低
2.使用存储过程, (因为存储过程是数据库专有,
推荐在只使用一种数据库 和 不打算换数据库服务器 的情况下使用)
3.动态生成PreparedStatement查询 (但是无法 使用 PreparedStatement caching)
4.使用NULL在PreparedStatement查询.(推荐)
第四种方法的演示代码:
public void viewTablePreaparedStatementNull(Connection con) { final String QUERY = "SELECT * FROM customers WHERE cust_id IN (?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?);"; final int PARAM_SIZE = 10; int[] ids = {10001,10002,10003,10004,10005}; if(ids.length > PARAM_SIZE) { System.out.println("MAXIMUM INPUT SIZE " + PARAM_SIZE); return; } int i = 1; try(PreparedStatement preparedStatement = con.prepareStatement(QUERY)){ for(; i<= ids.length;i++) {//填充参数 preparedStatement.setInt(i, ids[i-1]); } for(; i<=PARAM_SIZE;i++) {//设置未填充的参数为空 preparedStatement.setNull(i, java.sql.Types.INTEGER); } try(ResultSet re = preparedStatement.executeQuery()){ while(re.next()) { System.out.println(re.getInt(1) + " "+ re.getString(2)); } }catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }

2.3 CallableStatement
调用储存过程
SQL语句
DROP procedure IF exists SHOW_CUSTOMERS; DELIMITER // CREATE PROCEDURE SHOW_CUSTOMERS( IN in_cust_id INT, OUT out_cust_name VARCHAR(40) ) BEGIN SELECT cust_name FROM customers WHERE cust_id = in_cust_id INTO out_cust_name; END// DELIMITER ; CALL SHOW_CUSTOMERS(10006,@custID); SELECT @custID;
演示代码:
创建存储过程
public void createStoredProcedure(Connection con) { String dropProcedure = "DROP procedure IF exists SHOW_CUSTOMERS;"; String createProcedure = "CREATE PROCEDURE SHOW_CUSTOMERS(\r\n" + " IN in_cust_id INT,\r\n" + " OUT out_cust_name VARCHAR(40)\r\n" + ")\r\n" + "BEGIN\r\n" + " SELECT cust_name FROM customers\r\n" + " WHERE cust_id = in_cust_id INTO out_cust_name;\r\n" + "END;"; try(CallableStatement cs = con.prepareCall(createProcedure);PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement(dropProcedure)){ ps.executeUpdate(); cs.executeUpdate(); }catch(SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }
使用存储过程
public void useStoredProcedure(Connection con) { try(CallableStatement cs = con.prepareCall("{CALL SHOW_CUSTOMERS(?,?)}")){ cs.setInt(1, 10005); cs.registerOutParameter(2, Types.CHAR); cs.executeQuery(); System.out.println(cs.getString(2)); }catch(SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
3.批处理 + 删除表格
主要用到statement中
addBatch ,executeBatch ,clearBatch 三个方法.
即添加语句,执行语句,清除含有的语句.
接下来我们需要用 批处理 重新创建 填充表格的方法,
为了容易说明, 我们需要删除掉刚刚的表,然后重新创建,再填充.
删表的原理类似与建表
public void dropTable(Connection con) throws SQLException{
String query = "DROP TABLE customers";
try(Statement statement = con.createStatement()){//创建Statement
statement.executeUpdate(query);//编译SQL语句
}catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
删除表之后,我们重新创建表(原理类似),然后再使用填充方法
用批处理写的填充方法:
public void populateTable(Connection con) throws SQLException{
try(Statement statement = con.createStatement()){
con.setAutoCommit(false);//开启事务
statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" +
"VALUES(10001, 'Coyote Inc.', '200 Maple Lane', 'Detroit', 'MI', '44444', 'USA', 'Y Lee', 'ylee@coyote.com');");
statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact)\r\n" +
"VALUES(10002, 'Mouse House', '333 Fromage Lane', 'Columbus', 'OH', '43333', 'USA', 'Jerry Mouse');");
statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" +
"VALUES(10003, 'Wascals', '1 Sunny Place', 'Muncie', 'IN', '42222', 'USA', 'Jim Jones', 'rabbit@wascally.com');");
statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" +
"VALUES(10004, 'Yosemite Place', '829 Riverside Drive', 'Phoenix', 'AZ', '88888', 'USA', 'Y Sam', 'sam@yosemite.com');");
statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact)\r\n" +
"VALUES(10005, 'E Fudd', '4545 53rd Street', 'Chicago', 'IL', '54545', 'USA', 'E Fudd');");
int[] successNum = statement.executeBatch();//返回成功数,并且执行批语句
System.out.println("成功插入:" + Arrays.toString(successNum));
con.commit();
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}finally{
con.setAutoCommit(true);
}
}
4.DataSource 与连接池,事务
1.1DataSource 与连接池
推荐阅读:https://www.cnblogs.com/kevinf/p/3705148.html
一般开源的数据连接池有两种:C3P0 与 DBCP 区别与介绍
接下来我们要用
javax.sql.DataSource;
中 DataSource 来写一个简易连接池.
首先明确几个概念.
连接池:
连接数据库的操作十分昂贵,
所以我们想到可以把已经建立好的连接先存起来,
这就用到了连接池.
动态代理模式:
使用一个代理类 代理 原有的对象, 在代理类中原有对象的方法调用之前,
都要经过代理类的处理,然后再决定是否回到原有对象.
比如: 我们的Connection中有一个close() 方法,意思就是关闭连接,
那么我们需要修改Connecttion.close()的执行方式,这时候就需要
写一个代理类代理Connection类.
简易连接池的思路:
1.实现DataSource接口,批量创建一定 连接(connection) 并且将其加入 容器 中
2.每次使用getConnection(),都从容器中去除一个 连接(connection),如果容器中没有可用容器,提示"数据库繁忙"
3.每次close的时候,保证用完的 连接(connection) 回到容器中.
简易连接池代码:
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.logging.Logger; import javax.management.RuntimeErrorException; import javax.sql.DataSource; public class JDBCPool implements DataSource{ private static LinkedList<Connection> conPool = new LinkedList<Connection>(); static { //InputStream in = JDBCPool.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties"); //Properties pro = new Properties(); try { //pro.load(in); //String driver = pro.getProperty("driver"); //String url = pro.getProperty("url"); //String username = pro.getProperty("username"); //String password = pro.getProperty("password"); //int jdbcPoolInitSize = Integer.parseInt(pro.getProperty("jdbcPoolInitSize")); String driver = "mysql"; String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/crashcourse?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true"; String username = "root"; String password = "***"; int jdbcPoolInitSize = 10; for(int i=0;i<jdbcPoolInitSize;i++) { Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password); System.out.println("初始化数据库 " + (i+1) + "个连接"); conPool.add(connection); } }catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return false; } @Override public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(conPool.size() > 0) { final Connection conn = conPool.removeFirst(); return (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Connection.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[] {Connection.class}, new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if(!"close".equals(method.getName())) { return method.invoke(conn, args); } else { conPool.add(conn); System.out.println("关闭连接,实际还给了连接池"); System.out.println("池中连接数为 " + conPool.size()); return null; } } }); }else { throw new RuntimeErrorException(null, "数据库繁忙"); } } @Override public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { return null; } @Override public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 0; } }
另一个调用类代码:

import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; import java.sql.Types; import java.util.Properties; import java.sql.CallableStatement; import java.sql.Connection; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Map; import javax.sql.DataSource; public class JDBCTutorials { JDBCPool jdbcPool = new JDBCPool(); String userName = "root"; //用户名 String password = "***";//用户密码 String dbms = "mysql";//数据库管理系统名称 String serverName = "localhost";//服务器名称 String portNumber = "3306";//服务器接口 String Atribute = "serverTimezone=UTC" + "&characterEncoding=utf-8" + "&useSSL=false" + "&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";//时区与SLL连接方式禁用 String dbName = "crashcourse";//数据库名称 //jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ //jdbc:derby:testdb;create=true public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException{ Connection conn = jdbcPool.getConnection(); // Connection conn = null; // Properties connectionPros = new Properties(); // connectionPros.put("user", userName); // connectionPros.put("password", password); // if(this.dbms.equals("mysql")) { // conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:" + this.dbms + "://" + this.serverName + // ":" + this.portNumber + "/" + this.dbName + "?" + this.Atribute,connectionPros); // //conn.setCatalog(this.dbName); // } else if (this.dbms.equals("derby")) { // conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:" + this.dbms + ":"+ this.dbName + ":" // + ";create=true",connectionPros); // } // System.out.println("Connection DBMS Successfully"); return conn; } public void viewTable(Connection con,String dbName) throws SQLException{ String query = "SELECT * FROM customers;";//SQL语句 try(Statement statement = con.createStatement()){//创建Statement ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);//编译SQL语句 while(resultSet.next()) { int custID = resultSet.getInt(1); String custName = resultSet.getString(2); String custAddress = resultSet.getString(3); System.out.println(custID + ", " + custName + ", " + custAddress); } }catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println(e); } } public void viewTablePreparedStatement(Connection con,String dbName) throws SQLException{ String query = "SELECT * FROM customers WHERE cust_id = ? AND cust_name = ?;";//? 可以用一个参数代替 HashMap<Integer, String> customerCondition = new HashMap<>(); customerCondition.put(10001, "Coyote Inc."); customerCondition.put(10002, "Mouse House"); customerCondition.put(10003, "Wascals"); customerCondition.put(10004, "Yosemite Place"); customerCondition.put(10005, "New Man"); try(PreparedStatement statement = con.prepareStatement(query)){//创建Statement ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);//编译SQL语句 int i = 0; for(Map.Entry<Integer, String> e: customerCondition.entrySet()) { statement.setInt(1, e.getKey()); statement.setString(2, e.getValue()); resultSet.next(); int custID = resultSet.getInt(1); String custName = resultSet.getString(2); String custAddress = resultSet.getString(3); System.out.println(custID + ", " + custName + ", " + custAddress); } }catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println(e); } } public void viewTablePreaparedStatementNull(Connection con) { final String QUERY = "SELECT * FROM customers WHERE cust_id IN (?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?);"; final int PARAM_SIZE = 10; int[] ids = {10001,10002,10003,10004,10005}; if(ids.length > PARAM_SIZE) { System.out.println("MAXIMUM INPUT SIZE " + PARAM_SIZE); return; } int i = 1; try(PreparedStatement preparedStatement = con.prepareStatement(QUERY)){ for(; i<= ids.length;i++) { preparedStatement.setInt(i, ids[i-1]); } for(; i<=PARAM_SIZE;i++) { preparedStatement.setNull(i, java.sql.Types.INTEGER); } try(ResultSet re = preparedStatement.executeQuery()){ while(re.next()) { System.out.println(re.getInt(1) + " "+ re.getString(2)); } }catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void changeTable(Connection con,String dbName) throws SQLException{ String query = "SELECT * FROM customers;";//SQL语句 try(Statement statement = con.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE)){//创建Statement ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);//编译SQL语句 resultSet.afterLast();//从前往后更新ID,因为他是 PRIMARY KEY不能重复 while(resultSet.previous()) { int custID = resultSet.getInt(1); resultSet.updateInt(1, custID+1);//客服ID + 1 resultSet.updateRow(); } }catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println(e); } } public void dropTable(Connection con) throws SQLException{ final String QUERY = "DROP TABLE customers"; try(Statement statement = con.createStatement()){//创建Statement statement.executeUpdate(QUERY);//编译SQL语句 }catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println(e); } } public void createTable(Connection con) throws SQLException{ String createSQL = "CREATE TABLE customers\r\n" + "(\r\n" + " cust_id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,\r\n" + " cust_name char(50) NOT NULL ,\r\n" + " cust_address char(50) NULL ,\r\n" + " cust_city char(50) NULL ,\r\n" + " cust_state char(5) NULL ,\r\n" + " cust_zip char(10) NULL ,\r\n" + " cust_country char(50) NULL ,\r\n" + " cust_contact char(50) NULL ,\r\n" + " cust_email char(255) NULL ,\r\n" + " PRIMARY KEY (cust_id)\r\n" + ") ENGINE=InnoDB;"; try(Statement statement = con.createStatement()){ statement.executeUpdate(createSQL); }catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e); } } public void populateTableBatch(Connection con) throws SQLException{ try(Statement statement = con.createStatement()){ con.setAutoCommit(false);//关闭事务自动commit 和 rollback statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" + "VALUES(10001, 'Coyote Inc.', '200 Maple Lane', 'Detroit', 'MI', '44444', 'USA', 'Y Lee', 'ylee@coyote.com');"); statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact)\r\n" + "VALUES(10002, 'Mouse House', '333 Fromage Lane', 'Columbus', 'OH', '43333', 'USA', 'Jerry Mouse');"); statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" + "VALUES(10003, 'Wascals', '1 Sunny Place', 'Muncie', 'IN', '42222', 'USA', 'Jim Jones', 'rabbit@wascally.com');"); statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" + "VALUES(10004, 'Yosemite Place', '829 Riverside Drive', 'Phoenix', 'AZ', '88888', 'USA', 'Y Sam', 'sam@yosemite.com');"); statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact)\r\n" + "VALUES(10005, 'E Fudd', '4545 53rd Street', 'Chicago', 'IL', '54545', 'USA', 'E Fudd');"); int[] successNum = statement.executeBatch();//返回成功数 System.out.println("成功插入:" + Arrays.toString(successNum)); con.commit(); }catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e); }finally{ con.setAutoCommit(true); } } public void insertTableReSet(Connection con) throws SQLException{ String query = "SELECT * FROM customers;";//SQL语句 try (Statement statement = con.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE)){ ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query); resultSet.moveToInsertRow(); resultSet.updateInt(1, 10006); resultSet.updateString(2, "New Man"); resultSet.updateString(3, "3123 street"); resultSet.insertRow(); }catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e); } } public void createStoredProcedure(Connection con) { String dropProcedure = "DROP procedure IF exists SHOW_CUSTOMERS;"; String createProcedure = "CREATE PROCEDURE SHOW_CUSTOMERS(\r\n" + " IN in_cust_id INT,\r\n" + " OUT out_cust_name VARCHAR(40)\r\n" + ")\r\n" + "BEGIN\r\n" + " SELECT cust_name FROM customers\r\n" + " WHERE cust_id = in_cust_id INTO out_cust_name;\r\n" + "END;"; try(CallableStatement cs = con.prepareCall(createProcedure);PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement(dropProcedure)){ ps.executeUpdate(); cs.executeUpdate(); }catch(SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } public void useStoredProcedure(Connection con) { try(CallableStatement cs = con.prepareCall("{CALL SHOW_CUSTOMERS(?,?)}")){ cs.setInt(1, 10005); cs.registerOutParameter(2, Types.CHAR); cs.executeQuery(); System.out.println(cs.getString(2)); }catch(SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { JDBCTutorials jdbcTutorials = new JDBCTutorials(); try (Connection connection = jdbcTutorials.getConnection()){ jdbcTutorials.dropTable(connection); jdbcTutorials.createTable(connection); jdbcTutorials.populateTableBatch(connection); jdbcTutorials.insertTableReSet(connection); jdbcTutorials.viewTablePreaparedStatementNull(connection); jdbcTutorials.changeTable(connection,"crashcourse"); System.out.println(); jdbcTutorials.viewTable(connection,"crashcourse"); System.out.println(); jdbcTutorials.createStoredProcedure(connection); jdbcTutorials.useStoredProcedure(connection); }catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println(e); } } }
DBCP使用(JDNI):
推荐阅读:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunseine/p/5947448.html
去官方下三个包 http://commons.apache.org/proper/
基础的BasicDataSource 就是我们的第三类DataSource(连接池,Connection,事务)
public Connection getConnection() { Connection con = null; BasicDataSource ds = new BasicDataSource(); ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/crashcourse?serverTimezone=GMT&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true"); ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); ds.setUsername("root"); ds.setPassword("***"); ds.setMaxTotal(30); try{ con = ds.getConnection( ); }catch(SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return con; }
我们可以用.properties 来保存BasicDataSource的配置
########DBCP配置文件########## #驱动名 driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #url url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb #用户名 username=sa #密码 password=123456 #初试连接数 initialSize=30 #最大活跃数 maxTotal=30 #最大idle数 maxIdle=10 #最小idle数 minIdle=5 #最长等待时间(毫秒) maxWaitMillis=1000 #程序中的连接不使用后是否被连接池回收(该版本要使用removeAbandonedOnMaintenance和removeAbandonedOnBorrow) #removeAbandoned=true removeAbandonedOnMaintenance=true removeAbandonedOnBorrow=true #连接在所指定的秒数内未使用才会被删除(秒)(为配合测试程序才配置为1秒) removeAbandonedTimeout=1
然后写一个类来用它
public class JDBCPool { private static Properties properties = new Properties(); private static DataSource dataSource; static { try (FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream("config/dbcp.properties")){ dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties); properties.load(is); } catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static Connection getConnection() { Connection connection = null; try { connection = dataSource.getConnection(); }catch(SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return connection; } }
1.2 事务
- 数据库中的一组相关的SQL语句,作为一个执行单元,全部执行成功,或者全部不执行,不能拆分的这种SQL语句组合的执行方式叫做事务
-
转账是一种典型的使用事务的案例
转出账户和转入账户必须同时执行成功才能算作是一次转账,如果一方没有执行成功,那么另一方也要不执行
因为JDBC中commit是默认开启,
要使用事务就得将其关闭,并且事务内的连接(Connection)只有一个
Connection.setAutoCommit(false);
在语句的最后使用 Connection.commit(); 提交
或者在中途使用Connection.rollback();回滚
public void populateTableBatch(Connection con) throws SQLException{ try(Statement statement = con.createStatement()){ con.setAutoCommit(false);//开启事务 statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" + "VALUES(10001, 'Coyote Inc.', '200 Maple Lane', 'Detroit', 'MI', '44444', 'USA', 'Y Lee', 'ylee@coyote.com');"); statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact)\r\n" + "VALUES(10002, 'Mouse House', '333 Fromage Lane', 'Columbus', 'OH', '43333', 'USA', 'Jerry Mouse');"); statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" + "VALUES(10003, 'Wascals', '1 Sunny Place', 'Muncie', 'IN', '42222', 'USA', 'Jim Jones', 'rabbit@wascally.com');"); statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact, cust_email)\r\n" + "VALUES(10004, 'Yosemite Place', '829 Riverside Drive', 'Phoenix', 'AZ', '88888', 'USA', 'Y Sam', 'sam@yosemite.com');"); statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO customers(cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country, cust_contact)\r\n" + "VALUES(10005, 'E Fudd', '4545 53rd Street', 'Chicago', 'IL', '54545', 'USA', 'E Fudd');"); int[] successNum = statement.executeBatch();//返回成功数 System.out.println("成功插入:" + Arrays.toString(successNum)); con.commit(); }catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e); con.rollback(); }finally{ con.setAutoCommit(true); } }
=============== 专题介绍结束 ===============
4.结尾
1. ORM (Object relation mapping) 对象关系映射
ORM 是一种思想,将数据库中的数据变成对象,对象变成数据库中的数据。
因为我们编程语言是面对对象的,一切都是对象,而关系数据库是有数学理论发展起来的,
这两者直接有一定区别,ORM就是为了解决这个问题而存在的。
https://blog.csdn.net/ma15732625261/article/details/74332441
ORM 工具介绍:ADO.NET等
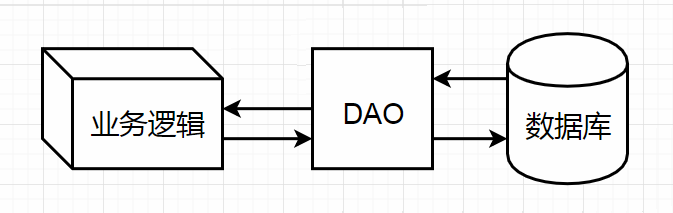
2. DAO 封装自己的JDBC
DAO: DAO 就是一个模型,它将数据库与业务逻辑之间,将访问数据库的代码封装成一个类。(增删改,不包含业务信息)
需要的包:
http://commons.apache.org/proper/
还是用上面的表
写一个Customers 类
public class Customers { int custID; String custName; String custAddress; String custCity; String custState; String custZip; @Override public String toString() { return "Customers [custID=" + custID + ", custName=" + custName + ", custAddress=" + custAddress + ", custCity=" + custCity + ", custState=" + custState + ", custZip=" + custZip + ", custCountry=" + custCountry + ", custContact=" + custContact + ", custEmail=" + custEmail + "]"; } String custCountry; String custContact; String custEmail; public int getCustID() { return custID; } public void setCustID(int custID) { this.custID = custID; } public String getCustName() { return custName; } public void setCustName(String custName) { this.custName = custName; } public String getCustAddress() { return custAddress; } public void setCustAddress(String custAddress) { this.custAddress = custAddress; } public String getCustCity() { return custCity; } public void setCustCity(String custCity) { this.custCity = custCity; } public String getCustState() { return custState; } public void setCustState(String custState) { this.custState = custState; } public String getCustZip() { return custZip; } public void setCustZip(String custZip) { this.custZip = custZip; } public String getCustCountry() { return custCountry; } public void setCustCountry(String custCountry) { this.custCountry = custCountry; } public String getCustContact() { return custContact; } public void setCustContact(String custContact) { this.custContact = custContact; } public String getCustEmail() { return custEmail; } public void setCustEmail(String custEmail) { this.custEmail = custEmail; } }
DAO类:
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils; public class Dao { public void updata(String sql,Object... args) { try(Connection con = JDBCTutorials.getConnection(); PreparedStatement pre = con.prepareStatement(sql)){ for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++) { pre.setObject(i+1, args); } pre.executeUpdate(); }catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") /** * 返回一条查询记录 * @param rs * @return * @throws SQLException */ public <T> T get(Class<T> dataClass,String sql,Object... args){ List<T> list = new LinkedList<>(); list = getForList(dataClass,sql,args); if(list.size() > 0) { return list.get(0); }else { return null; } } /** * 返回多条查询记录 * @param rs * @return * @throws SQLException */ @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public <T> List<T> getForList(Class<T> dataClass,String sql,Object... args){ //1.得到结果集 List<T> list = new LinkedList<T>(); try(Connection con = JDBCTutorials.getConnection(); PreparedStatement pre = con.prepareStatement(sql)){ for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++) { pre.setObject(i+1, args[i]); } try(ResultSet rs = pre.executeQuery()){ //2.处理结果集, 得到Map的List,其中一个Map对象对应着一条记录 //Map 的 Key 是 ReusltSet别名,value为列的值。 List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = handlerResultSetToMap(rs); //3.处理Map 中的List 变为 dataClass 的List //Map的key 为 dataClass的属性名,value 为dataClass的属性值 list = transferMapListToLinkedList(dataClass, mapList); }catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return list; } private <T> List<T> transferMapListToLinkedList(Class<T> dataClass, List<Map<String, Object>> mapList) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException { T entity = null; LinkedList<T> list = new LinkedList<T>(); if(mapList.size()>0) { for(Map<String, Object> mt:mapList) { entity = dataClass.newInstance(); for(Map.Entry<String, Object> m:mt.entrySet()) { String proName = m.getKey(); Object value = m.getValue(); BeanUtils.setProperty(entity, proName, value);//填充entity的属性 } list.add(entity); } } return list; } private List<Map<String, Object>> handlerResultSetToMap(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException { List<Map<String,Object>> mapList = new LinkedList<Map<String,Object>>(); List<String> columnLabel = getColumnLabels(rs); while(rs.next()) { Map<String,Object> mapz = new HashMap<String,Object>(); for(String colName:columnLabel) { Object colObject = rs.getObject(colName); mapz.put(colName, colObject); } mapList.add(mapz); } return mapList; } public List<String> getColumnLabels(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException{ List<String> list = new LinkedList<String>(); ResultSetMetaData resultSetMetaData = rs.getMetaData(); for(int i=0;i<resultSetMetaData.getColumnCount();i++) { list.add(resultSetMetaData.getColumnLabel(i+1)); } return list; } /** * 返回某条记录的字段 * @param sql * @param args * @return */ public <E> E getForValue(String sql,Object... args) { try(Connection con = JDBCTutorials.getConnection(); PreparedStatement pre = con.prepareStatement(sql)){ for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++) { pre.setObject(i+1, args[i]); } try(ResultSet rs = pre.executeQuery()){ if(rs.next()) { return (E)rs.getObject(1); } }catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
DaoTest类
class DaoTest { Dao dao = new Dao(); @Test void testUpdata() { String sql = "SELECT cust_id custID,cust_name custName FROM customers WHERE cust_id = ?;"; Customers customers = dao.get(Customers.class, sql,10003); System.out.println("---"); System.out.println(customers); } @Test void testGet() { String sql = "SELECT cust_id custID,cust_name custName FROM customers WHERE cust_id = ? OR cust_id = ?;"; List<Customers> customers = dao.getForList(Customers.class, sql,10003,10004); for(Customers l:customers) { System.out.println(l); } } @Test void testGetValue() { String sql = "Select MAX(cust_id) FROM customers"; int maxCustID = dao.getForValue(sql); System.out.println(maxCustID); } }
日期:2018-10-18 基础教程写好,后续拓展待补:
2018-10-19 14:20:15 更新拓展.
2018-10-20 21:55:52 第二大部分即将完成,编写连接池概念与原理中
2018-10-22 修正
2018-10-23 13:57:55 完结撒花





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号