Codeforces 804D Expected diameter of a tree
Pasha is a good student and one of MoJaK's best friends. He always have a problem to think about. Today they had a talk about the following problem.
We have a forest (acyclic undirected graph) with n vertices and m edges. There are q queries we should answer. In each query two vertices v and u are given. Let V be the set of vertices in the connected component of the graph that contains v, and U be the set of vertices in the connected component of the graph that contains u. Let's add an edge between some vertex 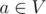 and some vertex in
and some vertex in 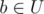 and compute the value d of the resulting component. If the resulting component is a tree, the value d is the diameter of the component, and it is equal to -1 otherwise. What is the expected value of d, if we choose vertices a and b from the sets uniformly at random?
and compute the value d of the resulting component. If the resulting component is a tree, the value d is the diameter of the component, and it is equal to -1 otherwise. What is the expected value of d, if we choose vertices a and b from the sets uniformly at random?
Can you help Pasha to solve this problem?
The diameter of the component is the maximum distance among some pair of vertices in the component. The distance between two vertices is the minimum number of edges on some path between the two vertices.
Note that queries don't add edges to the initial forest.
The first line contains three integers n, m and q(1 ≤ n, m, q ≤ 105) — the number of vertices, the number of edges in the graph and the number of queries.
Each of the next m lines contains two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n), that means there is an edge between vertices ui and vi.
It is guaranteed that the given graph is a forest.
Each of the next q lines contains two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n) — the vertices given in the i-th query.
For each query print the expected value of d as described in the problem statement.
Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6. Let's assume that your answer is a, and the jury's answer is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct, if 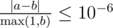 .
.
3 1 2
1 3
3 1
2 3
-1
2.0000000000
5 2 3
2 4
4 3
4 2
4 1
2 5
-1
2.6666666667
2.6666666667
In the first example the vertices 1 and 3 are in the same component, so the answer for the first query is -1. For the second query there are two options to add the edge: one option is to add the edge 1 - 2, the other one is 2 - 3. In both ways the resulting diameter is 2, so the answer is 2.
In the second example the answer for the first query is obviously -1. The answer for the second query is the average of three cases: for added edges 1 - 2 or 1 - 3 the diameter is 3, and for added edge 1 - 4 the diameter is 2. Thus, the answer is 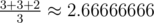 .
.
题意:
给出一个森林,q次询问,每次问把x,y两点所属的树之间任意连接一条边形成新的树的直径的期望,如果x和y在同一棵树中输出-1;
代码:
//这题算出复杂度也就解出来了。先枚举一棵树中的节点然后二分找另一棵树中的节点满足两个节点之间的距离不小于max(树1直径, //树2直径),他们的贡献就是各自在自己树中最远能到达的端点的距离相加再+1,否则贡献就是max(树1直径,树2直径),这样看似是 //q*n*long(n),但是注意到所有的树的大小总和是n所以最坏是sqrt(n)棵树每棵树大小是sqrt(n),所以是q*sqrt(n)*long(n); #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<map> #include<algorithm> #include<vector> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int MAXN=100009; int fa[MAXN],head[MAXN],tot,n,cnt,m,q,d[MAXN],f[MAXN],deep,o,oo,root[MAXN]; int a[MAXN],aa; double size[MAXN]; map<pair<int,int>,double>mp; vector<ll>v[MAXN],vv[MAXN]; struct Edge { int u,v,next; }edge[MAXN*2]; void init() { tot=cnt=0; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); memset(fa,-1,sizeof(fa)); memset(f,0,sizeof(f)); memset(d,-1,sizeof(d)); } void add(int x,int y) { edge[tot].u=x;edge[tot].v=y; edge[tot].next=head[x]; head[x]=tot++; edge[tot].u=y;edge[tot].v=x; edge[tot].next=head[y]; head[y]=tot++; } void dfs1(int x,int father,int p) { v[p].push_back(x); for(int i=head[x];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next){ int y=edge[i].v; if(y==father) continue; fa[y]=p; dfs1(y,x,p); } } void dfs2(int x,int father,int sum,bool w) { if(w!=0) f[x]=max(f[x],sum); if(sum>=deep){ deep=sum; if(w==0) o=x; else if(w==1) oo=x; } for(int i=head[x];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next){ int y=edge[i].v; if(y==father) continue; dfs2(y,x,sum+1,w); } } int main() { //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); init(); scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q); for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); add(x,y); } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(fa[i]!=-1) continue; fa[i]=++cnt; v[cnt].clear();vv[cnt].clear(); dfs1(i,0,cnt); root[cnt]=i; } for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++){ deep=0; dfs2(root[i],0,0,0); deep=0; dfs2(o,0,0,1); d[i]=deep; dfs2(oo,0,0,2); aa=v[i].size(); for(int j=0;j<aa;j++) a[j]=f[v[i][j]]; v[i].clear(); for(int j=0;j<aa;j++) v[i].push_back(a[j]); sort(v[i].begin(),v[i].end()); a[aa]=0; for(int j=aa-1;j>=0;j--) a[j]=a[j+1]+v[i][j]+1; for(int j=0;j<=aa;j++) vv[i].push_back(a[j]); } while(q--){ int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); if(fa[x]==fa[y]) printf("-1\n"); else{ pair<int,int>p1(fa[x],fa[y]); if(mp[p1]>0) printf("%.6f\n",mp[p1]); else{ double ans=0; int xx=fa[x],yy=fa[y]; if(v[xx].size()<=v[yy].size()){ for(int i=0;i<v[xx].size();i++){ ll tmp=lower_bound(v[yy].begin(),v[yy].end(),max(d[xx],d[yy])-v[xx][i]-1)-v[yy].begin(); ans+=(vv[yy][tmp]+v[xx][i]*(v[yy].size()-tmp))+tmp*max(d[xx],d[yy]); } }else{ for(int i=0;i<v[yy].size();i++){ ll tmp=lower_bound(v[xx].begin(),v[xx].end(),max(d[xx],d[yy])-v[yy][i]-1)-v[xx].begin(); ans+=(vv[xx][tmp]+v[yy][i]*(v[xx].size()-tmp))+tmp*max(d[xx],d[yy]); } } double tmp1=v[xx].size(),tmp2=v[yy].size(); ans/=(tmp1*tmp2); printf("%.6f\n",ans); mp[p1]=ans; } } } return 0; }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
· 【杂谈】分布式事务——高大上的无用知识?
2016-11-11 HDU3371 最小生成树