集合类
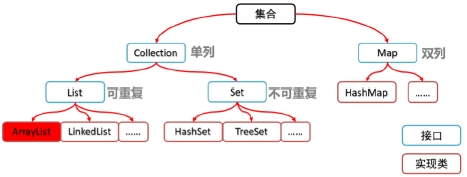
Collection类
-
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> -
常用方法:
public boolean add(E e) : 把给定的对象添加到当前集合中 。 public void clear() :清空集合中所有的元素。 public boolean remove(E e) : 把给定的对象在当前集合中删除。 public boolean contains(E e) : 判断当前集合中是否包含给定的对象。 public boolean isEmpty() : 判断当前集合是否为空。 public int size() : 返回集合中元素的个数。 public Object[] toArray() : 把集合中的元素,存储到数组中。
-
Iterator接口
-
常用方法:
public Iterator iterator() : 获取集合对应的迭代器,用来遍历集合中的元素的。 public E next() :返回迭代的下一个元素。 public boolean hasNext() :如果仍有元素可以迭代,则返回 true
-
如果集合中已经没有元素了,还继续使用迭代器的next方法,将会发生
java.util.NoSuchElementException没有集合元素的错误。
-
List集合接口
-
是一个有序、带索引、可重复的集合
ArrayList集合
-
ArrayList集合底层是一个数组结构,元素增删慢,查找快。
LinkedList集合
-
LinkedList集合是一个双向链表结构,底层是一个链表结构,元素增删快,查询慢。
-
常用方法:
public void addFirst(E e) :将指定元素插入此列表的开头。 public void addLast(E e) :将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾。 public E getFirst() :返回此列表的第一个元素。 public E getLast() :返回此列表的最后一个元素。 public E removeFirst() :移除并返回此列表的第一个元素。 public E removeLast() :移除并返回此列表的最后一个元素。 public E pop() :从此列表所表示的堆栈处弹出一个元素。 public void push(E e) :将元素推入此列表所表示的堆栈。 public boolean isEmpty() :如果列表不包含元素,则返回true。
-
Set集合接口
-
是一个无序、不可重复的集合
HashSet集合
-
保证元素唯一性 的方式依赖于: hashCode 与 equals 方法。
-
给HashSet中存放自定义类型元素时,需要重写对象中的hashCode和equals方法,建立自己的比较方式,才能保证HashSet集合中的对象唯一。
LinkedHashSet集合
-
在HashSet下面有一个子类 java.util.LinkedHashSet ,它是链表和哈希表组合的一个数据存储结构。
-
特点是一个有序的集合。
-
Collections工具类
-
常用方法
public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<T> c, T... elements) :往集合中添加一些元素。 public static void shuffle(List<?> list) 打乱顺序 :打乱集合顺序。 public static <T> void sort(List<T> list) :将集合中元素按照默认规则排序。 public static <T> void sort(List<T> list,Comparator<? super T> ) :将集合中元素按照指定规则排序。
-
Comparator比较器
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<String>() { @Override public int compare(String o1, String o2) { return o2.charAt(0) ‐ o1.charAt(0); } }); //如果要按照升序排序, 则o1 小于o2,返回(负数),相等返回0,01大于02返回(正数) 如果要按照 降序排序 则o1 小于o2,返回(正数),相等返回0,01大于02返回(负数)
Map集合接口
-
常用方法
public V put(K key, V value) : 把指定的键与指定的值添加到Map集合中。 public V remove(Object key) : 把指定的键 所对应的键值对元素 在Map集合中删除,返回被删除元素的值。 public V get(Object key) 根据指定的键,在Map集合中获取对应的值。 boolean containsKey(Object key) 判断集合中是否包含指定的键。 public Set<K> keySet() : 获取Map集合中所有的键,存储到Set集合中。 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() : 获取到Map集合中所有的键值对对象的集合(Set集合)。
-
Map集合遍历方式
-
Map集合不能直接使用迭代器或者foreach进行遍历。但是转成Set之后就可以使用了。
-
方法一:
-
获取集合中的所有键组成集合map.keySet();
-
遍历键集合,通过Key值找到Value值。
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String,String>(); //获取所有的键 获取键集 Set<String> keys = map.keySet(); // 遍历键集 得到 每一个键 for (String key : keys) { //key 就是键 //获取对应值 String value = map.get(key); System.out.println(key+"的CP是:"+value); }
-
-
方法二:
-
Map 中存放的是两种对象,一种称为key(键),一种称为value(值),它们在在 Map 中是一一对应关系,这一对对象又称做 Map 中的一个Entry(项) 。 Entry 将键值对的对应关系封装成了对象。
-
Entry表示了一对键和值,那么也同样提供了获取对应键和对应值得方法。
-
public K getKey() :获取Entry对象中的键。
-
public V getValue() :获取Entry对象中的值。
-
-
在Map集合中也提供了获取所有Entry对象的方法:
-
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() : 获取到Map集合中所有的键值对对象的集合(Set集合)
Set<Entry<String,String>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Entry<String, String> entry : entrySet) { // 解析 String key = entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key+"的CP是:"+value); }
-
-
-
-
HashMap集合
-
HashMap保证成对元素唯一,并且查询速度很快
-
-
LinkedHashMap集合
-
在HashMap的基础上还保证,元素存取有序。
-
JDK 9 新特性
public class HelloJDK9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> str1=Set.of("a","b","c");
//str1.add("c");这里编译的时候不会错,但是执行的时候会报错,因为是不可变的集合
System.out.println(str1);
Map<String,Integer> str2=Map.of("a",1,"b",2);
System.out.println(str2);
List<String> str3=List.of("a","b");
System.out.println(str3);
}
}
-
of()方法只是Map,List,Set这三个接口的静态方法,其父类接口和子类实现并没有这类方法,比如 HashSet,ArrayList等;
-
返回的集合是不可变的;
Debug追踪
-
f5执行下一行代码
-
f6执行下一行代码如果方法里面有嵌套的方法回调到那个嵌套的方法
-
f7从一个方法跳出,到一行代码中
-
f8从一个断点跳到下一个断点
日常练习
红名单校验和短信群发系统
package groupSMS;
import java.util.*;
/*
*
1、以下手机号码段(每隔一个号添加一次)添加到Map集合中,
2、从控制台输入要发送信息的号码,如果发送多个,请用英文“,”号隔开,输入短信内容。
3、编写一个短信发送类,号码发送前,先判断号码是否为空,再判断是否为红名单用户(手机号码在集合中),
如果为红名单,输出红名单数据,并计算红名单校验耗费的时间,如果条件都满足,发送短信,短信发送成功概率为98%,最后展示发送成功的短信号码和内容。
末四位的号码区间在1000-9999
*
* */
public class RedList {
public static ArrayList<String> redList =new ArrayList<>();
public void createRedList(String[] headNum,String[][] middleNum){
if (headNum.length!=middleNum.length){
System.out.println("头号码数组和中间号码数组不匹配,请重新输入");
return;
}else{
for (int i = 0; i < headNum.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < middleNum[i].length; j++) {
for (int k = 1000;k<=9999;k+=2){
redList.add(headNum[i]+middleNum[i][j]+k);
}
}
}
}
}
}
class GroupSMS {
public static ArrayList<String> groupNUM =new ArrayList<>();
public static ArrayList<String> noLegalNum =new ArrayList<>();
public static ArrayList<String> isRedList =new ArrayList<>();
public static ArrayList<String> sendList =new ArrayList<>();
public static ArrayList<String> successList =new ArrayList<>();
public static String TXT;
public static void SendSMS(){
String phoneNum = GroupSMSUtil.getPhoneNum();
GroupSMSUtil.groupNUM(phoneNum);
for (String s : groupNUM) {
boolean legal = GroupSMSUtil.isLegal(s);
if (!legal){
noLegalNum.add(s);
}else {
sendList.add(s);
}
}
System.out.println("红名单检验时长为:"+GroupSMSUtil.timeSUM(groupNUM)+"毫秒");
GroupSMSUtil.getTXT();
for (String s : sendList) {
if (GroupSMSUtil.getRandom()){
successList.add(s);
}
}
System.out.println("=================================");
System.out.println("输入的电话号码:"+groupNUM.toString());
System.out.println("不合法电话号码:"+noLegalNum.toString());
System.out.println("红名单电话号码:"+isRedList.toString());
System.out.println("发送的电话号码:"+sendList.toString());
System.out.println("成功的电话号码:"+successList.toString());
System.out.println(successList.size()!=0?("短信发送成功,发送的内容:"+TXT):("短信发送失败!!"));
System.out.println("=================================");
}
}
class GroupSMSUtil{
//判断电话号码是否合法
public static boolean isLegal(String phoneNum) {
for (int i = 0; i < phoneNum.length(); i++) {
if (phoneNum.charAt(i)<48||phoneNum.charAt(i)>57){
return false;
}
}
return (phoneNum.length() == 11) && (phoneNum.charAt(0) == '1');
}
//判断电话号码是否为红名单
public static boolean isRedList(String phoneNum) {
return RedList.redList.contains(phoneNum);
}
//获取执行时间
public static long getTime(){
return new Date().getTime();
}
//获取成功概率
public static boolean getRandom(){
return (new Random().nextInt(100))<=98;
}
//获取输入的电话字符串
public static String getPhoneNum(){
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
String str;
System.out.println("请输入电话号码,相邻号码用“,”隔开");
while (true){
str=sc.nextLine();
if (str.length()%12==11){
break;
}
System.out.println("请合法性输入");
}
return str;
}
//整理群发电话集合
public static void groupNUM(String str){
String[] split = str.split(",");
for (String s : split) {
GroupSMS.groupNUM.add(s);
}
}
//红名单校验时长
public static long timeSUM(Collection<String> col){
long start = GroupSMSUtil.getTime();
for (String s : col) {
boolean redList = GroupSMSUtil.isRedList(s);
if (redList){
GroupSMS.isRedList.add(s);
GroupSMS.sendList.remove(s);
}
}
long end = GroupSMSUtil.getTime();
return end - start;
}
//获取文本
public static void getTXT(){
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要发送的内容");
String s = sc.nextLine();
GroupSMS.TXT=s;
}
}
package groupSMS;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] headNum = new String[]{"136", "137", "181", "180", "150"};
String[][] middleNum = new String[][]
{{"0371", "0766", "7335", "7362", "6385", "0769", "7494", "3381", "7496", "7370"},
{"3383", "3319", "0088", "8361", "3315", "8168", "8151", "0386"},
{"3788", "3789", "3782", "3787", "0394", "3567", "2234", "0382"},
{"3951", "0169", "3991", "3955", "3928", "3788", "0387", "3997", "3923"},
{"0381", "3719", "0371", "3816", "0389", "3681", "9326", "3837", "3802"}};
RedList redList =new RedList();
redList.createRedList(headNum,middleNum);
GroupSMS.SendSMS();
}
}


