【codeforces 870F】Paths
Description
You are given a positive integer n. Let's build a graph on vertices 1, 2, ..., n in such a way that there is an edge between vertices u and v if and only if gcd(u,v)≠1. Let d(u, v) be the shortest distance between u and v, or 0 if there is no path between them. Compute the sum of values d(u, v) over all 1 ≤ u < v ≤ n.The gcd (greatest common divisor) of two positive integers is the maximum positive integer that divides both of the integers.
Input
Single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 107).Output
Print the sum of d(u, v) over all 1 ≤ u < v ≤ n.Examples
input
6
output
8
input
10
output
44
Note
All shortest paths in the first example: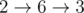


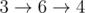


题意:
给定数字n,建立一个无向图。对于所有1~n之间的数字,当数字gcd(u,v)≠1时将u、v连一条边,边权为1。d(u, v)表示u到v的最短路,求所有d(u, v)的和,其中1 ≤ u < v ≤ n。
分析:
对于1以及所有大于n/2的的质数,与其他数字均不联通,直接剔除。
对于剩下的数字:
1.当gcd(u,v)≠1时,d(u, v)==1。即对于数字u,小于u且d(u, v)==1的数字个数为x - 1 - φ(x)。
2.令p[u]表示数字u的最小质因子,则当p[u]·p[v] ≤ n时,d(u, v)==2。维护数组num、sum,num[i]代表最小质因子为i的数字个数,sum数组为num数组的前缀和。统计Σnum[i]·sum[n/i]可以覆盖所有p[u]·p[v] ≤ n的情况,其中减去自身与自身被统计的情况,剩下的所有数对都被统计了两次,其中包含gcd(u,v)≠1的情况,需进行相应处理,详见代码。
3.剩下的数对最短路一定为3,因为 u→2·p[u]→2·p[v]→v这条路一定存在。可通过数对总数减去d(u, v)==1与d(u, v)==2的情况得到。


1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #define LL long long 5 using namespace std; 6 const int N=1e7+5; 7 int n,m,tot,now,pri[N],p[N],phi[N],num[N],sum[N]; 8 LL one,two,three; 9 int main() 10 { 11 scanf("%d",&n); 12 phi[1]=1; 13 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) 14 { 15 if(!p[i]){p[i]=pri[++tot]=i;phi[i]=i-1;} 16 for(int j=1;j<=tot;j++) 17 { 18 if(i*pri[j]>n)break; 19 p[i*pri[j]]=pri[j]; 20 if(i%pri[j]==0){phi[i*pri[j]]=phi[i]*pri[j];break;} 21 else phi[i*pri[j]]=phi[i]*(pri[j]-1); 22 } 23 } 24 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)one+=i-1-phi[i]; 25 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)num[p[i]]++; 26 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)sum[i]=sum[i-1]+num[i]; 27 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)two+=1ll*num[i]*sum[n/i]; 28 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)if(1ll*p[i]*p[i]<=n)two--; 29 two=two/2-one;m=n-1; 30 for(int i=tot;i>=1;i--) 31 if(pri[i]*2>n)m--; 32 else break; 33 three=1ll*m*(m-1)/2-one-two; 34 printf("%I64d\n",one+two*2+three*3); 35 return 0; 36 }


