spring容器管理对象的方式
1、spring容器中Bean对象的使用范围控制
a、控制对象创建方式(使用范围),在<bean>元素中使用scope属性控制,scope可以支持singleton或prototype,默认值是singleton
<bean scope= "singleton"> 该组件在spring容器里只有一个bean对象。每次取出的bean都是同一个bean,相当于单例模式
<bean scope = "prototype">该组件每次使用getBean("")都会返回一个新的对象
例如我们自定义了一个ExampleBean类:
public class ExampleBean { public void execute() { System.out.println("调用了execute方法"); } }
在applicationContext.xml中进行配置,默认使用scope="singleton"
<!-- 创建一个ExampleBean对象 --> <bean id ="example" class="com.zlc.test.ExampleBean"></bean>
我们测试一下每次取出的bean是否为同一个bean:
public static void main(String[] args) { String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; //创建容器对象 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); //得到Example对象 ExampleBean e1 = ac.getBean("example",ExampleBean.class); ExampleBean e2 = ac.getBean("example",ExampleBean.class); System.out.println(e1 == e2); }
运行结果:
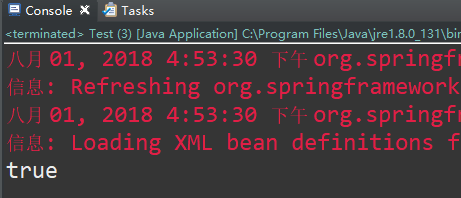
由此可见:每次我们从容器中取出的对象都是同一个对象
接下来我们将scope改成"prototype",例如:
<!-- 创建一个ExampleBean对象 --> <bean id ="example" class="com.zlc.test.ExampleBean" scope="prototype"></bean>
重新运行上面的代码,看看两次取出的对象是否一致,运行结果如下:
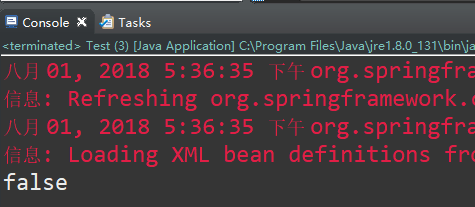
由此可知,当scope设置为"prototype"时,每次从Spring容器中获取该对象时,容器都会返回一个新的对象
2、spring容器中对象(组件)的初始化控制
在某些时候,我们需要在创建完对象后,对其进行一些初始化操作,例如解析某个xml文件,读取某些相关的配置信息等,使用spring容器管理和创建该对象(组件时),我们就可以指定某些初始化控制。
(1)在构造器中进行某些初始化操作,例如:
public class ExampleBean { public ExampleBean() { System.out.println("正在进行初始化操作。。。。"); } public void execute() { System.out.println("调用了execute方法"); } }
public static void main(String[] args) { String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; //创建容器对象 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); //得到Example对象 ExampleBean e1 = ac.getBean("example",ExampleBean.class); ExampleBean e2 = ac.getBean("example",ExampleBean.class); System.out.println(e1 == e2); }
运行代码,我们可以看到在spring使用构造器创建该对象(组件)时,调用了构造器中的初始化方法:
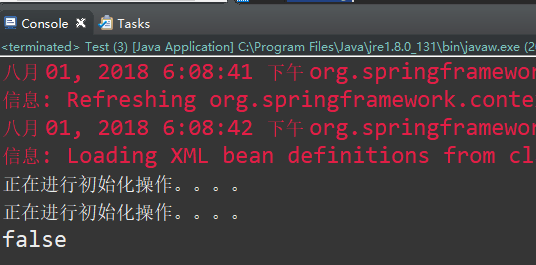
(2)指定某个方法作为初始化方法,例如我们在ExampleBean中新增一个init方法进行初始化操作
public class ExampleBean { public ExampleBean() { System.out.println("正在进行初始化操作。。。。"); } public void execute() { System.out.println("调用了execute方法"); } public void init() { System.out.println("正在执行初始化方法中的操作。。。。"); } }
在xml文件中我们指定其初始化方法。
<!-- 创建一个ExampleBean对象 --> <bean id ="example" class="com.zlc.test.ExampleBean" scope="prototype" init-method = "init"></bean>
运行以上代码,结果如下:
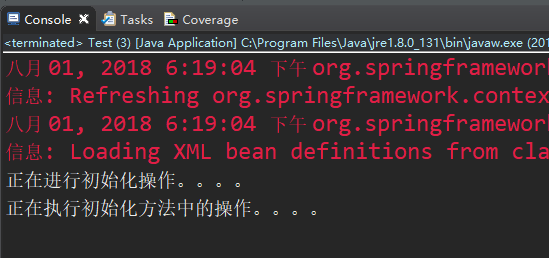
由此可以看出:spring容器创建完对象后,将会执行xml文件中指定的初始化方法,单例模式中初始化方法只会执行一次
3、指定对象(组件)的销毁方法
在xml文件中,我们为其指定一个属性destroy-method,它指定对象的销毁方法。
<!-- 创建一个ExampleBean对象 --> <bean id ="example" class="com.zlc.test.ExampleBean" init-method = "init" destroy-method="destroy"> </bean>
我们试着关闭spring容器对象以触发该单例对象的destroy方法:
public static void main(String[] args) { String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; //创建容器对象 AbstractApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); //得到Example对象 ExampleBean e1 = ac.getBean("example",ExampleBean.class); ExampleBean e2= ac.getBean("example",ExampleBean.class); ac.close();//释放spring容器对象,它会自动调用单例的destroy方法。 }
运行结果如下:

由此我们可以看出,spring容器在销毁单例对象前,先会去调用该对象指定的destroy方法
注意:只有在销毁单例对象时,才会调用该对象的destroy方法,若其scope设置为:prototype,则不会调用该方法
总结:指定对象的销毁方法,使用<bean destroy-method=""></bean>,在满足以下条件时触发其产生作用:
1、组件对象为单例模式
2、调用AbstractApplicationContext对象的close()方法



