42. 接雨水(dp or 双指针)
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
For example,
Given [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1], return 6.

class Solution { public: int trap(vector<int>& height) { int n = height.size(); vector<int>l_max(n); vector<int>r_max(n); l_max[0] = height[0]; r_max[n-1] = height[n-1]; for(int i = 1; i <n ;i++) { l_max[i] = max(l_max[i-1],height[i]); } for(int i = n-2; i>=0; i--) { r_max[i] = max(r_max[i+1],height[i]); } int res = 0; for(int i = 0; i <n;i++) { res += min(l_max[i],r_max[i]) - height[i]; } return res; } };
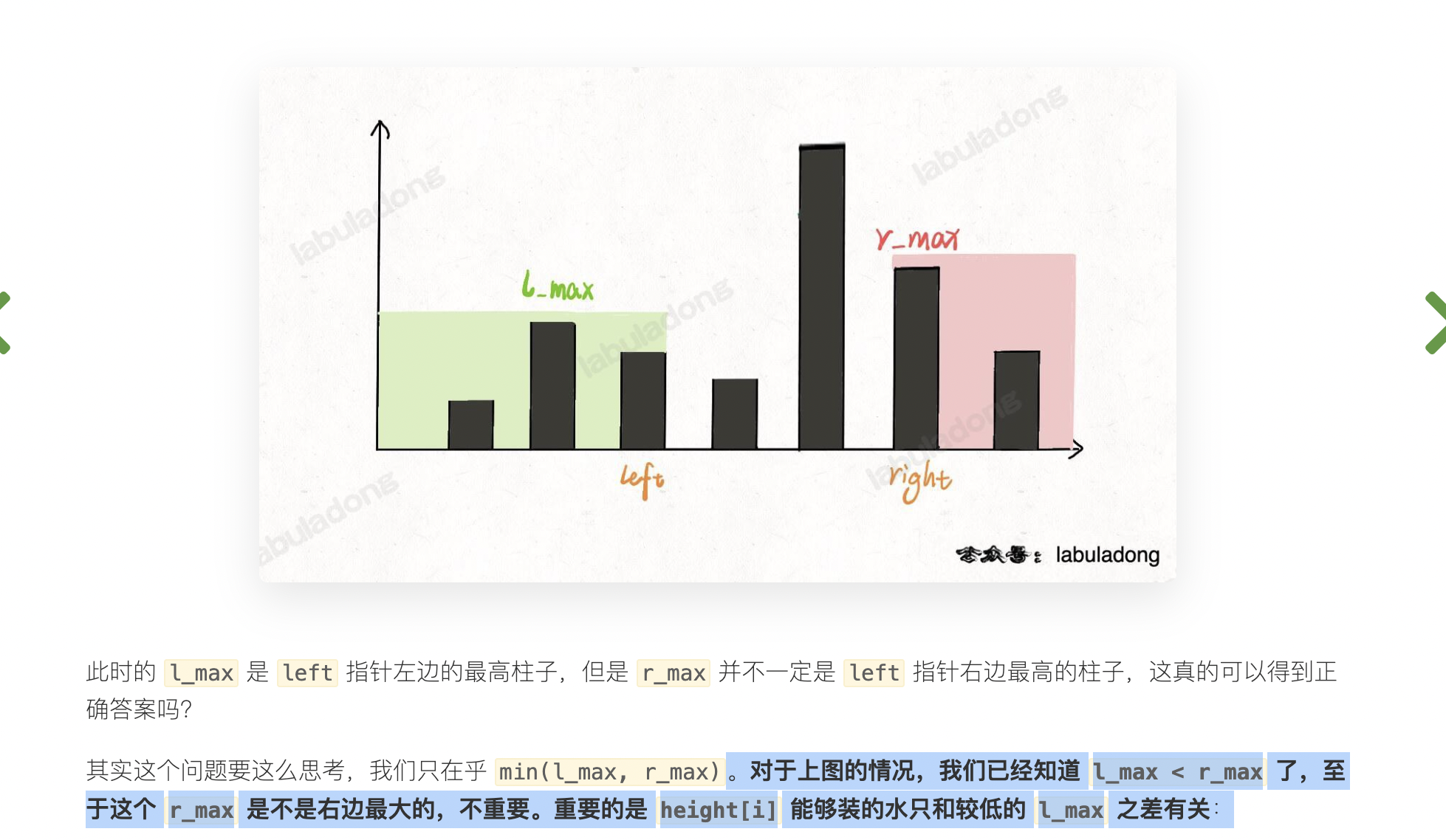
。对于上图的情况,我们已经知道 l_max < r_max 了,至于这个 r_max 是不是右边最大的,不重要。重要的是 height[i] 能够装的水只和较低的 l_max 之差有关:
class Solution: def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int: n = len(height) l = 0 r = len(height) -1 l_max = height[0] r_max = height[-1] res = 0 while l<=r: l_max = max(l_max,height[l]) r_max = max(r_max,height[r]) cur_rea = 0 if l_max < r_max: res+=(l_max-height[l]) l+=1 else: res+=(r_max-height[r]) r-=1 return res
单调栈:
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
stack<int> stk;
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < height.size();i++) {
while(!stk.empty() && height[i] > height[stk.top()]) {
int top = stk.top();
stk.pop();
if (!stk.empty()) {
int w = i - stk.top()-1;
int h = min(height[i],height[stk.top()]) - height[top];
res += w*h;
}
}
stk.push(i);
}
return res;
}
};





