Angular之指令Directive系列
项目筹备近期开启Angular学习,指令比较难理解所以记录备案,推荐Angualr实战学习视频大漠穷秋 Angular实战
一、指令directive概述
指令可以对元素绑定事件监听或者改变DOM结构而使HTML拥有像jQuery一样效果具有交互性。不同于jQuery,Angular设计核心思想是通过数据与模板的绑定,
摆脱繁琐的DOM操作,而将注意力集中在业务逻辑上。
几种常见指令ng-app 指令用来指定ng的作用域是在那个标签以内部分(<html ng-app="myApp">标签) ng-repeat迭代器指令可以重复标记元素、
ng-show指令可以根据条件是否显示一个元素、ng-model指令具有双向数据绑定特性、ng-controller 用来声明一个需要和数据进行绑定的模板区域
二、自定义指令directive之模式匹配restrict
直接上代码体验一把,index.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | <!DOCTYPE html><html ng-app="myModule"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Angular指令--自定义标签</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="framework/1.3.0.14/angular.js"></script> </head> <body> <hello></hello> <div hello></div> <div class='hello'></div> <!-- directive:hello --> <div></div> <!--代码模板template--> <script type="text/ng-template" id="hello_Angular.html"> <p>Hello Angular</p> </script> <!--代码模板template--> </body></html> |
指令Directive.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | <script type="text/javascript"> //调用angular对象的module方法来声明一个模块,模块的名字和ng-app的值对应 var myModule = angular.module('myModule',[]); /* restrict 属性值说明 <推荐使用EA> * E--element元素 <hello></hello> * A--attribute 属性 <div hello></div> * C-class 样式类 <div class="hello"></div> * M 注释 <!-- directive:hello --> */ //指令--对元素绑定事件监听或者改变DOM myModule.directive('hello', function(){ return { restrict: 'EACM', templateUrl:'hello_Angular.html', /*template : '<p>Hello Angular</p>',*/ replace: true } })</script> |
代码在线编辑 请点击这里哦
===================================================================================
restrict---匹配模式说明, 英文意思是"限制;约束;限定",这里指的是匹配我自定义的标签
===================================================================================
- E 元素(element) <hello></hello>
- A 属性(attribute) <div hello></div>
- C 样式类(class) <div class="hello"></div>
- M 注释 <!-- directive:hello --> 注意!!!空格(不常用)
温馨tips: 推荐使用EC或EA匹配模式
replace 是否替换元素的模式 replace:true浏览器DOM结构如下
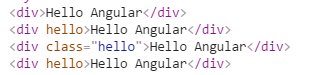
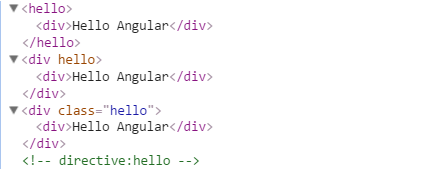
replace:false 或没有replace属性时浏览器DOM结构如下
三、指令之嵌套变换transclude
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | <!DOCTYPE html><html ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>transclude 嵌套变换</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="framework/1.3.0.14/angular.js"></script> </head> <body> <hello>这里是内容哦.....</hello> <div hello>这里是内容哦hello....</div> <script type="text/javascript"> var myApp = angular.module('myApp', []); myApp.directive('hello',function(){ return { restrict: 'EA', template: '<p>Hello World!!!<b ng-transclude></b></p>', transclude: true, /*嵌套变换*/ replace: true /*替换*/ } }) </script> </body></html> |
四、指令directive运行原理

五、指令配置参数说明
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | myModule.directive('namespaceDirectiveName', function factory(injectables) { var directiveDefinitionObject = { restrict: string,//指令的使用方式,包括标签,属性,类,注释 priority: number,//指令执行的优先级 template: string,//指令使用的模板,用HTML字符串的形式表示 templateUrl: string,//从指定的url地址加载模板或<script type="text/ng-template" id="string"></script> replace: bool,//是否用模板替换当前元素,若为false,则append在当前元素上 transclude: bool,//是否将当前元素的内容转移到模板中 scope: bool or object,//指定指令的作用域 controller: function controllerConstructor($scope, $element, $attrs, $transclude){...},//定义与其他指令进行交互的接口函数 require: string,//指定需要依赖的其他指令 link: function postLink(scope, iElement, iAttrs) {...},//以编程的方式操作DOM,包括添加监听器等 compile: function compile(tElement, tAttrs, transclude){ return: { pre: function preLink(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller){...}, post: function postLink(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller){...} } }//编程的方式修改DOM模板的副本,可以返回链接函数 }; return directiveDefinitionObject;}); |
六、指令与控制器的交互
index.html 如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | <!DOCTYPE html><html ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Directive指令与Controller控制器交互</title> <!--引入js库anglarjs--> <script type="text/javascript" src="framework/1.3.0.14/angular.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/Directive&Controller.js"></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="myAppCtrl"> <loader hello howToLoad="loadData()">数据加载......</loader> </div> <div ng-controller="myAppCtrl2"> <loader hello howToLoad="loadData2()">数据加载2......</loader> </div> </body></html> |
Directive&Controller.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | var myApp = angular.module('myApp', []);myApp.controller('myAppCtrl', ['$scope', function($scope){ console.log($scope); $scope.loadData = function(){ console.log('数据加载中.....'); }}]);myApp.controller('myAppCtrl2', ['$scope', function($scope){ console.log($scope); $scope.loadData2 = function(){ console.log('数据加载中2.....'); }}]);//指令与控制器之间交互myApp.directive('loader', function(){ return { restrict: 'EA', template: '<div ng-transclude></div>', transclude: true, replace: true, /*scope: {}, 独立scope*/ link: function(scope, element, attrs){ element.bind('mouseenter', function(){ /*这里调用controller中的方法三种方式*/ /*(1) scope.loadData(); (2) scope.$apply('loadData()'); (3) attrs.howtoload === 属性上绑定的函数名称*/ //属性方式 注意坑!!! howtoload 得小写 scope.$apply(attrs.howtoload); }) } }}) |
实现的效果是当鼠标滑过div元素时,调用一个加载数据的方法。
七、指令与指令的交互
代码过长开始折叠 index.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | <!DOCTYPE html><html ng-app="myModule"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>directive指令与directive指令之间的交互</title> <!--引入第三方样式库bootstrap.min.css--> <link rel="stylesheet" href="framework/bootstrap-3.0.0/css/bootstrap.min.css" /> <!--引入js库anglarjs--> <script type="text/javascript" src="framework/1.3.0.14/angular.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/Directive&Directive.js"></script> </head> <body> <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-3"> <superman strength>动感超人---力量</superman> </div> </div> <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-3"> <superman strength speed>动感超人2---力量+敏捷</superman> </div> </div> <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-3"> <superman strength speed light>动感超人3---力量+敏捷+发光</superman> </div> </div> </body></html> |
Directive&Directive.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 | var myModule = angular.module('myModule',[]); //指令与指令之间交互myModule.directive('superman', function(){ return { scope: {},/*独立作用域*/ restrict: 'AE', template: '<button class="btn btn-primary" ng-transclude></button>', transclude: true, controller: function($scope){ /*暴露controller里面方法*/ $scope.abilities = []; this.addStrength = function(){ $scope.abilities.push('strength'); }; this.addSpeed = function(){ $scope.abilities.push('speed'); }; this.addLight = function(){ $scope.abilities.push('light'); }; }, link: function(scope, element, attrs, supermanCtr){ element.addClass = "btn btn-primary"; element.bind('mouseenter', function(){ console.log(scope.abilities); }) } }})myModule.directive('strength', function(){ return { require: "^superman",/*require参数指明需要依赖的指令*/ link: function(scope, element, attrs, supermanCtr){ supermanCtr.addStrength(); } }});myModule.directive('speed', function(){ return { require: "^superman", link: function(scope, element, attrs, supermanCtr){ supermanCtr.addSpeed(); } }});myModule.directive('light', function(){ return { require: "^superman", link: function(scope, element, attrs, supermanCtr){ supermanCtr.addLight(); } }}); |
*require参数指明需要依赖的指令
*指令中的controller相当于暴露里面方法,便于指令复用
八、scope作用域绑定策略

scope “@” 把当前属性作为字符串传值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | <!DOCTYPE html><html ng-app="myModule"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>scope绑值策略一.'@'把当前属性作为字符串传值</title> <!--引入js库anglarjs--> <script type="text/javascript" src="framework/1.3.0.14/angular.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/Scope@.js"></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="myAppCtrl"> <drink flavor="{{ctrFlavor}}"></drink> </div> </body></html> |
Scope@.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | var myModule = angular.module('myModule', []);myModule.controller('myAppCtrl',['$scope', function($scope){ console.log($scope); $scope.ctrFlavor = "百事可乐";}]);myModule.directive('drink', function(){ return { restrict: 'AE', scope: { /*独立scope作用域*/ flavor: '@' }, replace:true, template: '<p>{{flavor}}</p>' //使用link进行指令和控制器两个作用域中数据的绑定。 //如果用scope中@的话,就不需要link这么麻烦了,angularJS会自动进行绑定 /*, link:function(scope,element,attrs){ element.bind('mouseenter', function(){ }) scope.flavor = attrs.flavor; }*/ }}) |
scope “=” 与父scope属性进行双向绑定
index.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | <!DOCTYPE html><html ng-app="myModule"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>scope绑值策略二.'='与父scope中的属性进行双向绑定</title> <!--引入第三方样式库bootstrap.min.css--> <link rel="stylesheet" href="framework/bootstrap-3.0.0/css/bootstrap.min.css" /> <!--引入js库anglarjs--> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/scope=.js"></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="myModuleCtrl" class="col-sm-6"> <p>{{describe}}</p> Ctrl--控制器:<br /> <input type="text" ng-model="ctrFlavor" class="form-control" /> <br /> <p>{{ctrFlavor}}</p> Directive--指令:<br /> <drink flavor="ctrFlavor"></drink> <p>{{flavor}}</p> </div> </body></html> |
scope=.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | var myModule = angular.module('myModule', []);myModule.controller('myModuleCtrl',['$scope', function($scope){ $scope.describe = "scope绑值策略二.=与父scope中的属性进行双向绑定"; $scope.ctrFlavor = "可口可乐";}]);//=与父scope中的属性进行双向绑定myModule.directive('drink',function(){ return { restrict: 'EA', scope: { /*ng-isolate-scope 隔离作用域*/ flavor : '=' }, template: '<input type="text" class="form-control" ng-model="flavor" />' /*replace:true*/ }}); |
这个例子中有两个输入框,第一个绑定了myModuleCtrl控制器中的scope对象的ctrlFlavor 属性。
第二个绑定的是指令中的flavor属性。但是在drink 指令中 scope对象的flavor 属性 用了 ”=“ ,
与父scope中的属性进行双向数据绑定。所以两个值有一个改动,另一个属性值也会改动。 简单理解为把两个存放数据仓库给相等 A1 == B1
scope& '&'传递一个来自父scope的函数,稍后调用
index.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | <!DOCTYPE html><html ng-app="myModule"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>scope绑值策略三.'&'传递一个来自父scope的函数,稍后调用</title> <!--引入第三方样式库bootstrap.min.css--> <link rel="stylesheet" href="framework/bootstrap-3.0.0/css/bootstrap.min.css" /> <!--引入js库anglarjs--> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/scope&.js"></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="myModuleCtrl"> <greeting greet="sayHello(name)"></greeting> <greeting greet="sayHello(name)"></greeting> <greeting greet="sayHello(name)"></greeting> </div> <!--代码模板template--> <script type="text/ng-template" id="sayHello.html"> <div class="col-sm-12 container"> <form role = "form"> <div class = "form-group"> <input type="text" class="form-control" ng-model="userName" /> <button class="btn btn-primary" ng-click="greet({name:userName})">Greeting</button> </div> </form> </div> </script> <!--代码模板template--> </body></html> |
scope&.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | var myModule = angular.module('myModule', []);myModule.controller('myModuleCtrl',['$scope', function($scope){ $scope.sayHello = function(name){ console.log('Hello'+name); }}]);myModule.directive('greeting', function(){ return { restrict: 'EA', scope: { /*'&'传递一个来自父scope的函数,稍后调用*/ greet : '&' }, templateUrl: 'sayHello.html' }}); |
以上所有代码汇总下载请点击
【资料参考】
http://www.cnblogs.com/lvdabao/tag/AngularJs/
http://angularjs.cn/T001


【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步