RESTful Webservice
1,REST和RESTFUL是什么?
REST ( REpresentational State Transfer ),State Transfer 为 "状态传输" 或 "状态转移 ",Representational 中文有人翻译为"表征"、"具象",合起来就是 "表征状态传输" 或 "具象状态传输" 或 "表述性状态转移"
REST是一种架构风格,REST 指的是一组架构约束条件和原则。满足这些约束条件和原则的应用程序或设计就是 RESTful。其核心是面向资源,REST专门针对网络应用设计和开发方式,以降低开发的复杂性,提高系统的可伸缩性。
REST提出设计概念和准则为:
1.网络上的所有事物都可以被抽象为资源(resource)
2.每一个资源都有唯一的资源标识(resource identifier),对资源的操作不会改变这些标识
3.所有的操作都是无状态的
REST简化开发,其架构遵循CRUD原则,该原则告诉我们对于资源(包括网络资源)只需要四种行为:创建,获取,更新和删除就可以完成相关的操作和处理。您可以通过统一资源标识符(Universal
Resource Identifier,URI)来识别和定位资源,并且针对这些资源而执行的操作是通过 HTTP
规范定义的。其核心操作只有GET,PUT,POST,DELETE。
由于REST强制所有的操作都必须是stateless的,这就没有上下文的约束,如果做分布式,集群都不需要考虑上下文和会话保持的问题。极大的提高系统的可伸缩性。
2.SOAP Webservice和RESTful Webservice
WebService是一种能够使应用程序在不同的平台使用不同的编程语言进行通讯的技术规范,而这种技术规范的实现可以用不同的方法,比如使用基于XML形式的协议(SOAP)进行通讯或者是RESTFUL形式的。
既然我们知道可以使用上面的两种形式进行通讯,那么我们就需要对上面的两种形式进行描述,规范化。而这些规范化的工作sun已经帮我们完成了,也就是JAX-WS,JAX-RS这两种规范.
JAX-WS是一种规范,而在jdk1.6之后就有了自带的实现,但是这种实现是比较简单的,基本上就只能够传递SOAP协议格式的消息。这就是为什么我们可以在没有axis2或者CXF的情况下开发WebService。 这时候我们就会想了,如果我们需要其他的服务,比如我想让JAX-WS与Spring集成。这种需求前辈都已经考虑过了,也实现了,不需要我们在去实现这样的需求。而这种需求的解决方案在JAX-WS中是采用框架。而JAX-WS的框架就有AXIS2和CXF。框架使用起来可能会更加灵活,功能更加强大。比如CXF不仅仅实现JAX-WS,也实现了JAX-RS规范。
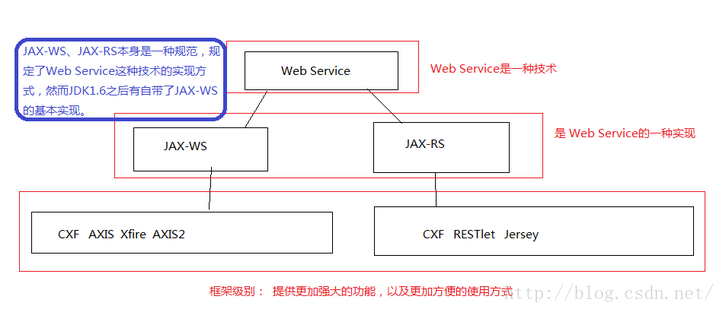
那么选择SOAP Webservice和Restful Webservice的使用,首先需要理解就是SOAP偏向于面向活动,有严格的规范和标准,包括安全,事务等各个方面的内容,同时SOAP强调操作方法和操作对象的分离,有WSDL文件规范和XSD文件分别对其定义。而REST强调面向资源,只要我们要操作的对象可以抽象为资源即可以使用REST架构风格。
3. Cxf 开发soap webservice 简单实例:
接口和实现类:
package demo2;
import javax.jws.WebParam;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService
public interface HiGirl {
String sayHi(@WebParam(name = "text") String text);
}
package demo2;
import javax.jws.WebParam;
public class HiGirlImpl implements HiGirl {
@Override
public String sayHi(@WebParam(name = "text") String text) {
return "hi," + text;
}
}
spring配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws" xmlns:cxf="http://cxf.apache.org/core"
xmlns:wsa="http://cxf.apache.org/ws/addressing"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.1.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/core http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/core.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd">
<!-- 以下三个文件在 cxf-2.7.18.jar 中定义 ,主要功能室CXF和Spring集成时,注册一些Process Bean -->
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf.xml" />
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf-extension-soap.xml" />
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf-servlet.xml" />
<!-- publish -->
<jaxws:endpoint id="hiGirl" implementor="demo2.HiGirlImpl"
address="/hiGirl" />
<!-- client 如果是通过web的方式访问,可以不用配置 该client,但是需要配置web.xml-->
<bean id="client" class="demo2.HiGirl" factory-bean="clientFactory"
factory-method="create"></bean>
<bean id="clientFactory" class="org.apache.cxf.jaxws.JaxWsProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="serviceClass" value="demo2.HiGirl"></property>
<property name="address" value="http://localhost:8080/webservice/hiGirl"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
web.xml 配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>CXFwebservice</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:demo2/applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>CxfServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>CxfServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/webservice/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <filter> <filter-name>encoding</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>forceEncoding</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>encoding</filter-name> <url-pattern>*.jsp</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>encoding</filter-name> <url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> </web-app>
客户端调用:
package demo2;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class WebServiceApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("demo2/applicationContext.xml");
HiGirl client = (HiGirl) factory.getBean("client");
System.out.println(client.sayHi("bitch!"));
}
}
4,CXF开发 restful webservice 简单实例:
package demo;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class Config {
public static List<Person> persons;
static {
persons = new LinkedList<Person>();
Person person = new Person();
person.setId("6272058");
person.setName("刘德华");
persons.add(person);
}
}
package demo;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement(name = "Person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private String id;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
package demo;
import javax.ws.rs.Consumes;
import javax.ws.rs.DELETE;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.POST;
import javax.ws.rs.PUT;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.QueryParam;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response.Status;
@Path("/PersonService")
//@Produces注释用来指定将要返回给client端的数据标识类型(MIME)。
//@Produces可以作为class注释,也可以作为方法注释,方法的@Produces注释将会覆盖class的注释。
//覆盖的意思是假如方法声明了自己的Produce,那么以方法的为准,class的仅供参考
@Produces({ "application/json", "application/xml" })
public class PersonService {
@GET
@Path("/getPerson/{dd}")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)
public Person getPerson(@PathParam("dd") String id) {
if (id != null && id.length() > 0) {
for (Person pp : Config.persons) {
if(id.equals(pp.getId())){
return pp;
}
}
Person result = new Person();
result.setId(id);
return result;
} else {
return new Person();
}
}
@POST
@Path("/regPerson")
//@Consumes与@Produces相反,用来指定可以接受client发送过来的MIME类型,
//同样可以用于class或者method,也可以指定多个MIME类型,一般用于@PUT,@POST。
@Consumes({ "application/json", "application/xml" })
public Response regPerson(Person person) {
if (Config.persons.contains(person)) {
return Response.status(Status.BAD_REQUEST).build();
} else {
Config.persons.add(person);
return Response.ok(person).build();
}
}
@DELETE
@Path("/delPerson")
@Consumes({ "application/json", "application/xml" })
public Response delPerson(@QueryParam("id") String id) {
Person person = new Person();
person.setId(id);
if (Config.persons.contains(person)) {
return Response.status(Status.BAD_REQUEST).build();
} else {
Config.persons.remove(person);
return Response.ok(person).build();
}
}
@PUT
@Path("/updatePerson")
@Consumes({ "application/json", "application/xml" })
public Response updatePerson(Person person) {
if (Config.persons.contains(person)) {
return Response.status(Status.BAD_REQUEST).build();
} else {
for (Person pp : Config.persons) {
if (pp.equals(person)) {
pp.setName(person.getName());
}
}
return Response.ok(person).build();
}
}
}
spring配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:jaxrs="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxrs"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/jaxrs
http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxrs.xsd">
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf.xml" />
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf-servlet.xml" />
<bean id="personService" class="demo.PersonService" />
<jaxrs:server id="rs_server" address="/rs">
<jaxrs:serviceBeans>
<ref bean="personService"/>
</jaxrs:serviceBeans>
</jaxrs:server>
</beans>
web.xml 配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>CxfRestWebservice</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:demo/beans.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>cxfservlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>cxfservlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/webservice/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
通过浏览器访问:注意URL和配置文件的及参数的对应关系
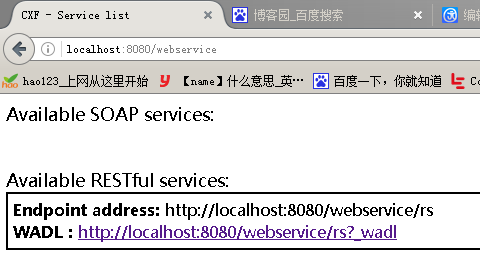

OK 本文到此结束,这只是个入门级的简单实例,更多更复杂功能都是在此基础上演化而来,跟过更复杂的配置也是以此为基础,有兴趣可以继续挖掘研究。



