一、异步通知机制简介
异步通知机制的意思:一旦设备准备就绪,可以主动的通知应用程序进行相应的操作,从而使得应用程序不必去查询设备的状态。
异步通知比较准确的称谓是"信号驱动的异步IO",因此其实现也是通过发送、接收信号的方式。
1.1 信号接收:
// 信号接收函数原型 void (*signal(int signum,void (*handler)(int)))(int); // 函数名:signal // 函数参数:int signum // void (*handler)(int) typedef void(*sighandler_t)(int); sighandler_t signal(int signum,sighandler_t handler);
第一个参数指定信号的值, 第二个参数指定信号的处理函数。若第二个参数为SIG_IGN,表示对该信号忽略(有两个信号不能被忽略SIGSTOP和SIGKILL)
若第二个参数为SIG_DEF,表示进程接收到该信号后执行默认的处理函数、
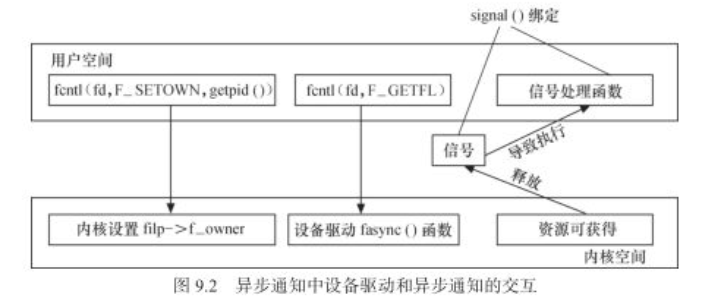
在信号接收端即应用程序中需要完成的工作:
(1)设置设备文件的拥有者为本进程,这样从设备发出的信号才能被本进程接收到
(2)设置设备文件支持fasync,即异步通知模式
(3)通过signal函数连接信号和信号处理函数
1.2 信号发送:
在设备驱动与应用程序的异步通知交互中,由设备驱动释放信号,因此需要在设备驱动中需要明确:将信号发给哪一个进程,如何发送信号到应用程序。
因此在驱动程序中涉及到3项工作:
(1)设置filp->f_owner为对应进程ID ,以支持应用程序中的工作1
(2)调用驱动程序中的fasync()函数,以支持应用程序中的工作2
(3)当设备资源可以获得的时候,调用kill_fasync()函数发出相应的信号
二、应用程序
int fd; void my_fun(int signum) // 信号处理函数 { int press_cnt[4]; int i; printf("my_fun\n"); read(fd, press_cnt, sizeof(press_cnt)); for (i = 0; i < sizeof(press_cnt)/sizeof(press_cnt[0]); i++) { if (press_cnt[i]) printf("K%d has been pressed %d times!\n", i+1, press_cnt[i]); } } int main(int argc, char **argv) { int flags; signal(SIGIO, my_fun); // 注册信号处理函数 fd = open("/dev/tiny6410_button", O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { printf("Can't open /dev/buttons\n"); return -1; } else printf("tiny6410_button open successfully!\n"); fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid()); // 设置设备文件的拥有者为本进程 flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL); // 读取设备文件的标志符 fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags|FASYNC); // 设置设备文件的标志符使设备文件支持异步通知模式 while (1) { sleep(1000); } close(fd); return 0; }
三、驱动程序
static struct fasync_struct* button_async; // 定义异步驱动结构体 static irqreturn_t buttons_interrupt(int irq, void *dev_id) { ...... kill_fasync(&button_async, SIGIO, POLL_IN); // 当有中断发生的时候会发送SIGIO信号到应用程序 ...... } int tiny6410_button_fasync (int fd, struct file *file, int on) { return fasync_helper(fd, file, on, &button_async); // } static struct file_operations tiny6410_button_fops = { ...... .fasync = tiny6410_button_fasync, ...... };
四、fcntl(...)函数的系统调用过程
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(fcntl, unsigned int, fd, unsigned int, cmd, unsigned long, arg)
do_fcntl(fd, cmd, arg, filp);
static long do_fcntl(int fd, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg, struct file *filp) { long err = -EINVAL; switch (cmd) { ...... case F_GETFL: // 得到设置的文件标志flag err = filp->f_flags; // flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL) break; case F_SETFL: // 设置文件标志flag err = setfl(fd, filp, arg); // fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags|FASYNC);--->setfl(fd, filp, flags|FASYNC) break; case F_SETOWN: // 设置将接收SIGIO和SIGURG信号的进程id或者进程组ID,进程组ID通过提供提供一个负值的arg来说明arg的绝对值是一个进程组id,负责arg被认为是进程id err = f_setown(filp, arg, 1); // fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid());--->f-setown(filp, pid, 1) break; ...... default: break; } return err; }
4.1 f_setown函数
int f_setown(struct file *filp, unsigned long arg, int force) { enum pid_type type; struct pid *pid; int who = arg; int result; type = PIDTYPE_PID; if (who < 0) { // arg < 0 说明传来的 |arg|为组ID type = PIDTYPE_PGID; // arg > 0 说明传来的arg为进程ID who = -who; } rcu_read_lock(); pid = find_vpid(who); //根据传来的arg(pid),找到pid结构体 result = __f_setown(filp, pid, type, force); // 根据应用程序的pid结构体、pid的类型、force 的值(force=1),来设置该文件所属的pid rcu_read_unlock(); return result; }
在f_setown函数中,先根据传入的pid的值找到pid结构体。这里边区分了进程ID还是进程组ID,如过传来的是进程ID,那么arg>0 ,进程ID为arg, pid类型为 PIDTYPE_PID
如果传来的是进程组ID,那么arg<0,进程组ID为|arg|,pid类型为 PIDTYPE_PGID
其次,执行__f_setown,来设置filp->f_owner下边有关pid的参数
4.2 setfl(...)函数
static int setfl(int fd, struct file * filp, unsigned long arg) { struct inode * inode = filp->f_path.dentry->d_inode; int error = 0; ...... if (((arg ^ filp->f_flags) & FASYNC) && filp->f_op && filp->f_op->fasync) { error = filp->f_op->fasync(fd, filp, (arg & FASYNC) != 0); //当FASYNC位有变化时会执行到这里,并且当filp->f_op->fasync为真时,会调用到驱动程序的fasync函数 if (error < 0) // 在本例程中就会调用到 tiny6410_button_fasync(...)函数调用fasync_helper(...) 函数 goto out; // --->tiny6410_button_fasync(fd, filp, 1) 开启fasync if (error > 0) // --->fasync_helper(fd, filp, 1, &button_async) error = 0; } spin_lock(&filp->f_lock); filp->f_flags = (arg & SETFL_MASK) | (filp->f_flags & ~SETFL_MASK); spin_unlock(&filp->f_lock); out: return error; }
可以看到用户程序调用fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags|FASYNC),当fasync位有变化时,会调用驱动程序的fasync函数,从而调用fasync_helper(...)函数
五、fasync_helper(...)函数
int fasync_helper(int fd, struct file * filp, int on, struct fasync_struct **fapp) { if (!on) return fasync_remove_entry(filp, fapp); return fasync_add_entry(fd, filp, fapp);// fasync_add_entry(fd, filp, &button_async } static int fasync_add_entry(int fd, struct file *filp, struct fasync_struct **fapp) { struct fasync_struct *new; new = fasync_alloc(); if (!new) return -ENOMEM; if (fasync_insert_entry(fd, filp, fapp, new)) { fasync_free(new); return 0; } return 1; } // fd文件描述符 filp文件描述结构体指针 fapp:fasync机构体的二级指针 new:新分配的fasync结构体的指针 struct fasync_struct *fasync_insert_entry(int fd, struct file *filp, struct fasync_struct **fapp, struct fasync_struct *new) { struct fasync_struct *fa, **fp; spin_lock(&filp->f_lock); spin_lock(&fasync_lock); for (fp = fapp; (fa = *fp) != NULL; fp = &fa->fa_next) { //这里fp = fapp fa = *fp = null 因为定义的struct fasync_struct * button_fasync = NULL if (fa->fa_file != filp) //故for循环中的内容是不会执行的 continue; spin_lock_irq(&fa->fa_lock); fa->fa_fd = fd; spin_unlock_irq(&fa->fa_lock); goto out; } spin_lock_init(&new->fa_lock); new->magic = FASYNC_MAGIC; // 这里给新分配的fasync_struct 结构体赋值 new->fa_file = filp; new->fa_fd = fd; new->fa_next = *fapp; rcu_assign_pointer(*fapp, new); filp->f_flags |= FASYNC; out: spin_unlock(&fasync_lock); spin_unlock(&filp->f_lock); return fa; }

