django-from
构建一个表单
这是一个非常简单的表单。实际应用中,一个表单可能包含几十上百个字段,其中大部分需要预填充,而且我们预料到用户将来回编辑-提交几次才能完成操作。
我们可能需要在表单提交之前,在浏览器端作一些验证。我们可能想使用非常复杂的字段,以允许用户做类似从日历中挑选日期这样的事情,等等。
这个时候,让Django 来为我们完成大部分工作是很容易的。
在Django 中构建一个表单
Form 类
我们已经计划好了我们的 HTML 表单应该呈现的样子。在Django 中,我们的起始点是这里:form模块
from django.forms import Form #继承Form类
from django.forms import fields #验证字段
from django.forms import widgets #通过widgets来更改form表单中的样式
xxxxxxxxxxform模块from django.forms import Form #继承Form类from django.forms import fields #验证字段from django.forms import widgets #通过widgets来更改form表单中的样式from django.forms import Form #继承Form类
from django.forms import fields #验证字段
from django.forms import widgets #通过widgets来更改form表单中的样式
class TeacherForm(Form)
username = fields.CharField(
required=True, #True字段不能为空,false字段可以为空
error_messages={'required':'用户名不能为空'}, #报错信息可以指定添加报错信息,不指定的话就是默认的报错信息
widget=widgets.TextInput(attrs={'placeholder':'用户名','class':'form-control'}) #可以给表单添加样式然后在前端页面渲染出来
) # 不能为空
password = fields.CharField(required=True,
error_messages={'required':'密码不能为空'},
widget=widgets.TextInput(attrs={'placeholder':'密码','class':'form-control'})) # 不能为空
email = fields.EmailField(required=True,
error_messages={'required':'邮箱不能为空','invalid':'邮箱格式错误'}, # 不能为空,且邮箱格式
widget=widgets.EmailInput(attrs={'placeholder':'邮箱','class':'form-control'}))
xxxxxxxxxxfrom django.forms import Form #继承Form类from django.forms import fields #验证字段from django.forms import widgets #通过widgets来更改form表单中的样式class TeacherForm(Form) username = fields.CharField( required=True, #True字段不能为空,false字段可以为空 error_messages={'required':'用户名不能为空'}, #报错信息可以指定添加报错信息,不指定的话就是默认的报错信息 widget=widgets.TextInput(attrs={'placeholder':'用户名','class':'form-control'}) #可以给表单添加样式然后在前端页面渲染出来 ) # 不能为空 password = fields.CharField(required=True, error_messages={'required':'密码不能为空'}, widget=widgets.TextInput(attrs={'placeholder':'密码','class':'form-control'})) # 不能为空 email = fields.EmailField(required=True, error_messages={'required':'邮箱不能为空','invalid':'邮箱格式错误'}, # 不能为空,且邮箱格式 widget=widgets.EmailInput(attrs={'placeholder':'邮箱','class':'form-control'})) 视图
发送给Django 网站的表单数据通过一个视图处理,一般和发布这个表单的是同一个视图。这允许我们重用一些相同的逻辑。
当处理表单时,我们需要在视图中实例化它:
def add_teacher(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
form = TeacherForm()
return render(request,'add_teacher.html',{'form':form})
else:
"""
1. 用户请求数据验证
2. 自动生成错误信息
3. 打包用户提交正确信息
4. 错误:保留上次输入内容
5. 定制页面上显示的HTML标签
Django Form组件
1. 创建规则(类,字段)
class Foo:
username = xxx
password = xxx
email = xxx
2. 数据和规则进行匹配
"""
form = TeacherForm(data=request.POST) # 数据和规则放置一起
if form.is_valid(): # 开始校验,并获取校验结果
# print('执行成功',form.cleaned_data) # 所有匹配成功,字典
# {'username': 'asd', 'password': 'sdf', 'email': 'sadf@live.com','ut_id':1}
form.cleaned_data['ut_id'] = 1
models.UserInfo.objects.create(**form.cleaned_data)
return redirect('/teachers/')
return render(request, 'add_teacher.html',{'form':form})xxxxxxxxxxdef add_teacher(request): if request.method == 'GET': form = TeacherForm() return render(request,'add_teacher.html',{'form':form}) else: """ 1. 用户请求数据验证 2. 自动生成错误信息 3. 打包用户提交正确信息 4. 错误:保留上次输入内容 5. 定制页面上显示的HTML标签 Django Form组件 1. 创建规则(类,字段) class Foo: username = xxx password = xxx email = xxx 2. 数据和规则进行匹配 """ form = TeacherForm(data=request.POST) # 数据和规则放置一起 if form.is_valid(): # 开始校验,并获取校验结果 # print('执行成功',form.cleaned_data) # 所有匹配成功,字典 # {'username': 'asd', 'password': 'sdf', 'email': 'sadf@live.com','ut_id':1} form.cleaned_data['ut_id'] = 1 models.UserInfo.objects.create(**form.cleaned_data) return redirect('/teachers/') return render(request, 'add_teacher.html',{'form':form})如果访问视图的是一个GET 请求,它将创建一个空的表单实例并将它放置到要渲染的模板的上下文中。这是我们在第一个访问该URL 时预期发生的情况。
如果表单的提交使用POST 请求,那么视图将再次创建一个表单实例并使用请求中的数据填充它:form = NameForm(request.POST)。这叫做”绑定数据至表单“(它现在是一个绑定的表单)。
我们调用表单的is_valid()方法;如果它不为True,我们将带着这个表单返回到模板。这时表单不再为空(未绑定),所以HTML 表单将用之前提交的数据填充,然后可以根据要求编辑并改正它。
如果is_valid()为True,我们将能够在cleaned_data 属性中找到所有合法的表单数据。在发送HTTP 重定向给浏览器告诉它下一步的去向之前,我们可以用这个数据来更新数据库或者做其它处理。
模板
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>添加老师</h1>
<form method="POST" novalidate>
{% csrf_token %}
<p>{{ form.username }} {{ form.errors.username.0 }} </p> #直接通过后端上下文对应调用名字,通过form.errors.username.0来调用错误信息
<p>{{ form.email }} {{ form.errors.email.0 }} </p>
<p>{{ form.password }} {{ form.errors.password.0 }} </p>
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
</form>
</body>
</html>xxxxxxxxxx<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Title</title></head><body> <h1>添加老师</h1><form method="POST" novalidate> {% csrf_token %} <p>{{ form.username }} {{ form.errors.username.0 }} </p> #直接通过后端上下文对应调用名字,通过form.errors.username.0来调用错误信息 <p>{{ form.email }} {{ form.errors.email.0 }} </p> <p>{{ form.password }} {{ form.errors.password.0 }} </p> <input type="submit" value="提交" /></form></body></html> 根据{{ form }},所有的表单字段和它们的属性将通过Django 的模板语言拆分成HTML 标记 。
注:Django 原生支持一个简单易用的跨站请求伪造的防护。当提交一个启用CSRF 防护的POST 表单时,你必须使用上面例子中的csrf_token 模板标签。
现在我们有了一个可以工作的网页表单,它通过Django Form 描述、通过视图处理并渲染成一个HTML <form>。
Django Form 类详解
form字段参数
#密码验证
- max_length
- min_length
- validators = [RegexValidator('xxx')] #正则表达式 通过正则表达式来进行验证
xxxxxxxxxx #密码验证 - max_length - min_length - validators = [RegexValidator('xxx')] #正则表达式 通过正则表达式来进行验证 password = fields.CharField(
required=True,
min_length=3,
max_length=18,
error_messages={
'required': '密码不能为空',
'min_length': '密码长度不能小于3',
'max_length': '密码长度不能大于18',
'invalid': '密码格式错误', #如果加上xxx的话invalid也要改xxx要相同的名字
},
validators=[RegexValidator('\d+','只能是数字','xxxx') ] #****注意当两个相同的判断都生效时,上面的优先级更高
)xxxxxxxxxx password = fields.CharField( required=True, min_length=3, max_length=18, error_messages={ 'required': '密码不能为空', 'min_length': '密码长度不能小于3', 'max_length': '密码长度不能大于18', 'invalid': '密码格式错误', #如果加上xxx的话invalid也要改xxx要相同的名字 }, validators=[RegexValidator('\d+','只能是数字','xxxx') ] #****注意当两个相同的判断都生效时,上面的优先级更高 )from django.shortcuts import render,redirect,HttpResponse
from django.conf import settings
# Create your views here.
from django.forms import Form
from django.forms import fields
from django.forms import widgets
from app01 import models
from django.core.validators import RegexValidator
from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError
class LoginForm(Form):
username = fields.CharField(
required=True,
min_length=3,
max_length=18,
error_messages={
'required': '用户不能为空',
'min_length': '用户长度不能小于3',
'max_length': '用户长度不能大于18',
}
)
password = fields.CharField(
required=True,
min_length=3,
max_length=18,
error_messages={
'required': '密码不能为空',
'min_length': '密码长度不能小于3',
'max_length': '密码长度不能大于18',
'invalid': '密码格式错误', #如果加上xxx的话invalid也要改xxx要相同的名字
},
validators=[RegexValidator('\d+','只能是数字') ] #****注意当两个相同的判断都生效时,上面的优先级更高
)
''' 之前的方法
# def clean_username(self):
# # ...
# user = self.cleaned_data['username']
# is_exsit = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user).count()
# if not is_exsit:
# raise ValidationError('用户名不存在')
# return user
#
# def clean_password(self):
# user = self.cleaned_data['username']
# return user
'''
def login(request): #现在用form进行验证
if request.method == "GET":
form = LoginForm()
return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form})
elif request.method == "POST":
form = LoginForm(data=request.POST)
# <tr><th><label for="id_password">Password:</label></th><td><input type="text" name="password" value="123" maxlength="18" minlength="3" requir 这里form拿到的是前端页面上的所有input框中的代码
ed id="id_password" /></td></tr>
if form.is_valid(): #先进行form验证
# 验证成功
user = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(**form.cleaned_data).first() #这里接收的话需要加上**form表单验证成功在进行数据库验证
if not user:
# 如果验证错误用户名或密码错误
# form.add_error('password','用户名或密码错误')
form.add_error('password', ValidationError('用户名或密码错误')) #则主动抛出错误
return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form})
else:
request.session[settings.SJF] = {'id': user.id, 'username': user.username}
return redirect('/index/')
else:
# 验证失败
return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form})
else:
return HttpResponse('滚')
xxxxxxxxxxfrom django.shortcuts import render,redirect,HttpResponsefrom django.conf import settings# Create your views here.from django.forms import Formfrom django.forms import fieldsfrom django.forms import widgetsfrom app01 import modelsfrom django.core.validators import RegexValidatorfrom django.core.exceptions import ValidationErrorclass LoginForm(Form): username = fields.CharField( required=True, min_length=3, max_length=18, error_messages={ 'required': '用户不能为空', 'min_length': '用户长度不能小于3', 'max_length': '用户长度不能大于18', } ) password = fields.CharField( required=True, min_length=3, max_length=18, error_messages={ 'required': '密码不能为空', 'min_length': '密码长度不能小于3', 'max_length': '密码长度不能大于18', 'invalid': '密码格式错误', #如果加上xxx的话invalid也要改xxx要相同的名字 }, validators=[RegexValidator('\d+','只能是数字') ] #****注意当两个相同的判断都生效时,上面的优先级更高 )''' 之前的方法 # def clean_username(self): # # ... # user = self.cleaned_data['username'] # is_exsit = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user).count() # if not is_exsit: # raise ValidationError('用户名不存在') # return user # # def clean_password(self): # user = self.cleaned_data['username'] # return user'''def login(request): #现在用form进行验证 if request.method == "GET": form = LoginForm() return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form}) elif request.method == "POST": form = LoginForm(data=request.POST) # <tr><th><label for="id_password">Password:</label></th><td><input type="text" name="password" value="123" maxlength="18" minlength="3" requir 这里form拿到的是前端页面上的所有input框中的代码ed id="id_password" /></td></tr> if form.is_valid(): #先进行form验证 # 验证成功 user = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(**form.cleaned_data).first() #这里接收的话需要加上**form表单验证成功在进行数据库验证 if not user: # 如果验证错误用户名或密码错误 # form.add_error('password','用户名或密码错误') form.add_error('password', ValidationError('用户名或密码错误')) #则主动抛出错误 return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form}) else: request.session[settings.SJF] = {'id': user.id, 'username': user.username} return redirect('/index/') else: # 验证失败 return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form}) else: return HttpResponse('滚')Django Form 扩展
钩子函数
当用户进行验证时,会有两个值username,password,拿到两个值后,会进行一个循环验证是否有这两个,
@property #2 #当视图函数调用时,@property不需要()就可以调用
def errors(self):
"Returns an ErrorDict for the data provided for the form"
if self._errors is None:
self.full_clean() #3 #通过full_clean()拿到全部的值之后调用
return self._errors
def is_valid(self): #1 #可以看到iv_valid验证,
"""
Returns True if the form has no errors. Otherwise, False. If errors are
being ignored, returns False.
"""
return self.is_bound and not self.errors
def full_clean(self): #4
"""
Cleans all of self.data and populates self._errors and
self.cleaned_data.
"""
self._errors = ErrorDict()
if not self.is_bound: # Stop further processing.
return
self.cleaned_data = {}
# If the form is permitted to be empty, and none of the form data has
# changed from the initial data, short circuit any validation.
if self.empty_permitted and not self.has_changed():
return
self._clean_fields()
self._clean_form()
self._post_clean()
def _clean_fields(self): #执行里面的方法
for name, field in self.fields.items(): #进行一个循环,把用户传过来的值进行循环验证
# value_from_datadict() gets the data from the data dictionaries.
# Each widget type knows how to retrieve its own data, because some
# widgets split data over several HTML fields.
if field.disabled:
value = self.get_initial_for_field(field, name)
else:
value = field.widget.value_from_datadict(self.data, self.files, self.add_prefix(name))
try:
if isinstance(field, FileField):
initial = self.get_initial_for_field(field, name)
value = field.clean(value, initial)
else:
value = field.clean(value)
self.cleaned_data[name] = value
if hasattr(self, 'clean_%s' % name):
value = getattr(self, 'clean_%s' % name)()
self.cleaned_data[name] = value
except ValidationError as e:
self.add_error(name, e)
xxxxxxxxxx当用户进行验证时,会有两个值username,password,拿到两个值后,会进行一个循环验证是否有这两个, #2 #当视图函数调用时,@property不需要()就可以调用 def errors(self): "Returns an ErrorDict for the data provided for the form" if self._errors is None: self.full_clean() #3 #通过full_clean()拿到全部的值之后调用 return self._errors def is_valid(self): #1 #可以看到iv_valid验证, """ Returns True if the form has no errors. Otherwise, False. If errors are being ignored, returns False. """ return self.is_bound and not self.errors def full_clean(self): #4 """ Cleans all of self.data and populates self._errors and self.cleaned_data. """ self._errors = ErrorDict() if not self.is_bound: # Stop further processing. return self.cleaned_data = {} # If the form is permitted to be empty, and none of the form data has # changed from the initial data, short circuit any validation. if self.empty_permitted and not self.has_changed(): return self._clean_fields() self._clean_form() self._post_clean() def _clean_fields(self): #执行里面的方法 for name, field in self.fields.items(): #进行一个循环,把用户传过来的值进行循环验证 # value_from_datadict() gets the data from the data dictionaries. # Each widget type knows how to retrieve its own data, because some # widgets split data over several HTML fields. if field.disabled: value = self.get_initial_for_field(field, name) else: value = field.widget.value_from_datadict(self.data, self.files, self.add_prefix(name)) try: if isinstance(field, FileField): initial = self.get_initial_for_field(field, name) value = field.clean(value, initial) else: value = field.clean(value) self.cleaned_data[name] = value if hasattr(self, 'clean_%s' % name): value = getattr(self, 'clean_%s' % name)() self.cleaned_data[name] = value except ValidationError as e: self.add_error(name, e)from django.shortcuts import render,redirect,HttpResponse
from django.conf import settings
# Create your views here.
from django.forms import Form
from django.forms import fields
from django.forms import widgets
from app01 import models
from django.core.validators import RegexValidator
from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError
class LoginForm(Form):
username = fields.CharField( #每一个进来的值,先进行正则,在进行钩子函数
required=True,
min_length=3,
max_length=18,
error_messages={
'required': '用户不能为空',
'min_length': '用户长度不能小于3',
'max_length': '用户长度不能大于18',
}
)
password = fields.CharField( #在进来一个值,先进行正则,在执行钩子函数
required=True,
min_length=3,
max_length=18,
error_messages={
'required': '密码不能为空',
'min_length': '密码长度不能小于3',
'max_length': '密码长度不能大于18',
'invalid': '密码格式错误',
},
validators=[RegexValidator('\d+','只能是数字') ]
)
#自定义函数
def clean_username(self):
# ...
user = self.cleaned_data['username'] #这样拿到用户的值
is_exsit = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user).count() #通过models进行用户的验证
if not is_exsit: #如果没有值
raise ValidationError('用户名不存在') #则抛出错误,用户名不存在
return user #在返回回去,如果没返回的话会一直拿到的是空值
def clean_password(self): #注意,这里只能拿自己的字段不能拿别人的字段,用户拿过来的值是字典,字典是无序的,不知道是先执行的username,还是password,
user = self.cleaned_data['username']
return user
def login(request):
if request.method == "GET":
form = LoginForm()
return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form})
elif request.method == "POST":
form = LoginForm(data=request.POST)
print(form)
if form.is_valid():
# 验证成功
user = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(**form.cleaned_data).first()
if not user:
# 用户名或密码错误
# form.add_error('password','用户名或密码错误')
# form.add_error('username',ValidationError('用户名错误'))
form.add_error('password', ValidationError('用户名密码错误'))
return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form})
else:
request.session[settings.SJF] = {'id': user.id, 'username': user.username}
return redirect('/index/')
else:
# 验证失败
return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form})
else:
return HttpResponse('滚')
xxxxxxxxxxfrom django.shortcuts import render,redirect,HttpResponsefrom django.conf import settings# Create your views here.from django.forms import Formfrom django.forms import fieldsfrom django.forms import widgetsfrom app01 import modelsfrom django.core.validators import RegexValidatorfrom django.core.exceptions import ValidationErrorclass LoginForm(Form): username = fields.CharField( #每一个进来的值,先进行正则,在进行钩子函数 required=True, min_length=3, max_length=18, error_messages={ 'required': '用户不能为空', 'min_length': '用户长度不能小于3', 'max_length': '用户长度不能大于18', } ) password = fields.CharField( #在进来一个值,先进行正则,在执行钩子函数 required=True, min_length=3, max_length=18, error_messages={ 'required': '密码不能为空', 'min_length': '密码长度不能小于3', 'max_length': '密码长度不能大于18', 'invalid': '密码格式错误', }, validators=[RegexValidator('\d+','只能是数字') ] ) #自定义函数 def clean_username(self): # ... user = self.cleaned_data['username'] #这样拿到用户的值 is_exsit = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user).count() #通过models进行用户的验证 if not is_exsit: #如果没有值 raise ValidationError('用户名不存在') #则抛出错误,用户名不存在 return user #在返回回去,如果没返回的话会一直拿到的是空值 def clean_password(self): #注意,这里只能拿自己的字段不能拿别人的字段,用户拿过来的值是字典,字典是无序的,不知道是先执行的username,还是password, user = self.cleaned_data['username'] return userdef login(request): if request.method == "GET": form = LoginForm() return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form}) elif request.method == "POST": form = LoginForm(data=request.POST) print(form) if form.is_valid(): # 验证成功 user = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(**form.cleaned_data).first() if not user: # 用户名或密码错误 # form.add_error('password','用户名或密码错误') # form.add_error('username',ValidationError('用户名错误')) form.add_error('password', ValidationError('用户名密码错误')) return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form}) else: request.session[settings.SJF] = {'id': user.id, 'username': user.username} return redirect('/index/') else: # 验证失败 return render(request, 'login.html', {'form': form}) else: return HttpResponse('滚')中间件
def auth(func):
def inner(request,*args,**kwargs):
user_info = request.session.get(settings.SJF)
if not user_info:
return redirect('/login/')
return func(request,*args,**kwargs)
return inner
@auth #当进入index页面验证是否带有session
def index(request):
username = request.session[settings.SJF]['username']
return render(request,'index.html',{'username':username})
@auth
def teachers(request):
# models.UserInfo.objects.filter(ut__title='讲师')
teacher_list = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(ut_id=1)
return render(request,'teachers.html',{'teacher_list':teacher_list})
xxxxxxxxxxdef auth(func): def inner(request,*args,**kwargs): user_info = request.session.get(settings.SJF) if not user_info: return redirect('/login/') return func(request,*args,**kwargs) return inner #当进入index页面验证是否带有sessiondef index(request): username = request.session[settings.SJF]['username'] return render(request,'index.html',{'username':username})def teachers(request): # models.UserInfo.objects.filter(ut__title='讲师') teacher_list = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(ut_id=1) return render(request,'teachers.html',{'teacher_list':teacher_list})
from django.conf import settings
from django.shortcuts import redirect
class MiddlewareMixin(object):
def __init__(self, get_response=None):
self.get_response = get_response
super(MiddlewareMixin, self).__init__()
def __call__(self, request): #call方法让子类继承
response = None
if hasattr(self, 'process_request'):
response = self.process_request(request)
if not response:
response = self.get_response(request)
if hasattr(self, 'process_response'):
response = self.process_response(request, response)
return response
class M1(MiddlewareMixin): #里面继承类
def process_request(self,request):
# 无返回值:继续执行后续中间件和视图函数
# 有返回值:执行自己的process_response和上面的response
# request.xxxx= 888
# request.path_info # /login/
if request.path_info == "/login/": #取路径,需要login页面一直是放开的,所以不对login做验证
return None
user_info = request.session.get(settings.SJF) #取session,有session值的话是true,
if not user_info: #没有session的话则直接返回login
return redirect('/login/')
def process_response(self,request,response):
print('m1.process_response')
return response
class M2(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self,request):
print('m2.process_request')
def process_response(self,request,response):
print('m2.process_response')
return responsexxxxxxxxxxfrom django.conf import settingsfrom django.shortcuts import redirectclass MiddlewareMixin(object): def __init__(self, get_response=None): self.get_response = get_response super(MiddlewareMixin, self).__init__() def __call__(self, request): #call方法让子类继承 response = None if hasattr(self, 'process_request'): response = self.process_request(request) if not response: response = self.get_response(request) if hasattr(self, 'process_response'): response = self.process_response(request, response) return responseclass M1(MiddlewareMixin): #里面继承类 def process_request(self,request): # 无返回值:继续执行后续中间件和视图函数 # 有返回值:执行自己的process_response和上面的response # request.xxxx= 888 # request.path_info # /login/ if request.path_info == "/login/": #取路径,需要login页面一直是放开的,所以不对login做验证 return None user_info = request.session.get(settings.SJF) #取session,有session值的话是true, if not user_info: #没有session的话则直接返回login return redirect('/login/') def process_response(self,request,response): print('m1.process_response') return responseclass M2(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self,request): print('m2.process_request') def process_response(self,request,response): print('m2.process_response') return response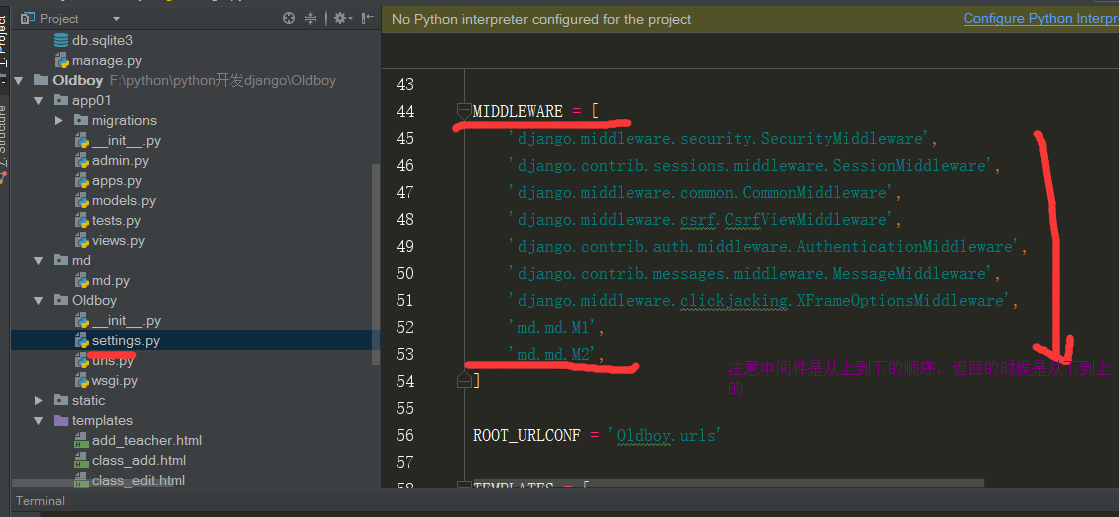
django中间件做过什么
- 用户登录
- 日志记录
- csrf
- session
- 权限管理***xxxxxxxxxx - 用户登录 - 日志记录 - csrf - session - 权限管理***数据源无法实时更新
1. headmaster_id
2. 数据源无法实施更新,重写构造方法
方式一(推荐):
class ClassForm(Form):
caption = fields.CharField(error_messages={'required':'班级名称不能为空'})
# headmaster = fields.ChoiceField(choices=[(1,'娜娜',)])
headmaster_id = fields.ChoiceField(choices=[])
def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs):
super().__init__(*args,**kwargs)
self.fields['headmaster_id'].choices =models.UserInfo.objects.filter(ut_id=2).values_list('id','username')
方式二:
from django.forms.models import ModelChoiceField
class ClassForm(Form):
caption = fields.CharField(error_messages={'required':'班级名称不能为空'})
# headmaster = fields.ChoiceField(choices=[(1,'娜娜',)])
headmaster_id = ModelChoiceField(queryset=models.UserInfo.objects.filter(ut_id=2)) 1. headmaster_id 2. 数据源无法实施更新,重写构造方法 方式一(推荐): class ClassForm(Form): caption = fields.CharField(error_messages={'required':'班级名称不能为空'}) # headmaster = fields.ChoiceField(choices=[(1,'娜娜',)]) headmaster_id = fields.ChoiceField(choices=[]) def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs): super().__init__(*args,**kwargs) self.fields['headmaster_id'].choices =models.UserInfo.objects.filter(ut_id=2).values_list('id','username') 方式二: from django.forms.models import ModelChoiceField class ClassForm(Form): caption = fields.CharField(error_messages={'required':'班级名称不能为空'}) # headmaster = fields.ChoiceField(choices=[(1,'娜娜',)]) headmaster_id = ModelChoiceField(queryset=models.UserInfo.objects.filter(ut_id=2))

