瀑布流的实现
1.什么是瀑布流?
手机应用界面多数是矩阵排列的,比如掌阅的书架

每一个方格子宽高相等,整整齐齐.据说此种布局容易造成视觉疲劳,于是希望将方格子的位置摆放不要这样整整齐齐,希望每一行的方格子看起来参差不齐,于是就有了瀑布流.如图:

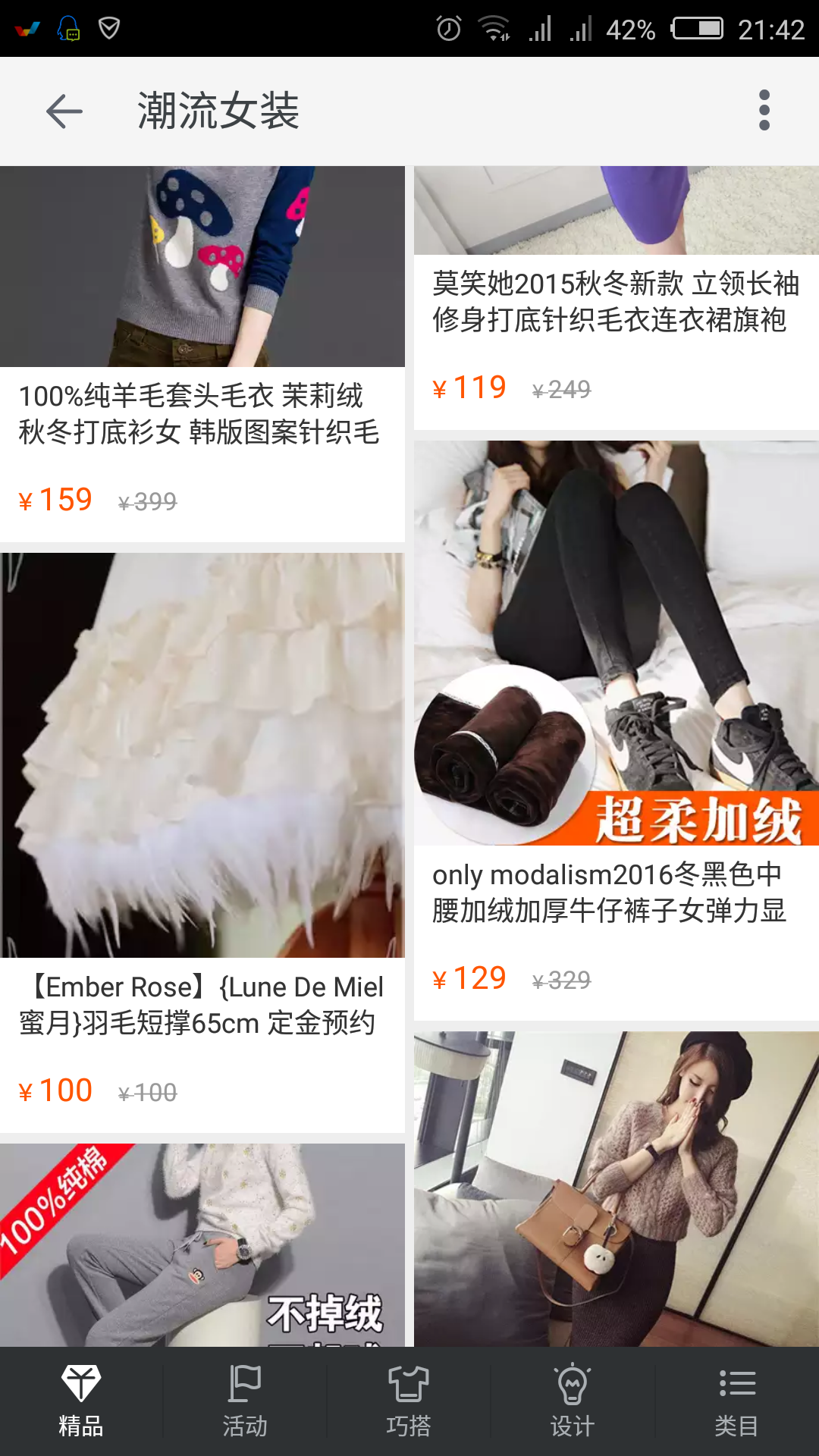
简单的说就是一种摆放控件的样式.
2.如何实现?
可以滚动,可以用Scrollview,tableView,collectionView实现,此处用collectionView,据说collectionView更强大,但是因为初学习,还没能充分体会到.
collectioView的用法大致和tableview相同.不同在于
- (UICollectionViewCell *)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView cellForItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
1>此方法中,初次加载此方法在缓存池中找不到可重用单元格,需要注册单元格,不赘述
2>collectionView的frame的设置全部交给一个类来处理了-----UICollectionViewLayout.
这个类专门用来处理UICollectionView的大小,frame等属性.
因为瀑布流实际上就是设置控件的frame,大小等属性,所以需要自定义布局,也就是需要自己写一个类继承自UICollectionViewLayout即可.苹果还封装了一个继承自UICollectionViewLayout的布局,叫做UICollectionViewFlowLayout,这个类新增了处理每一个item的大小,行间距,列间距等属性,但是此处可以不用继承这个类,直接继承UICollectionViewLayout即可,因为我们要用到的方法UICollectionViewLayout都具备.
四个方法
1>- (NSArray<UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *> *)layoutAttributesForElementsInRect:(CGRect)rect 此方法用于设置rect范围中所有item的属性 2>- (UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *)layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath 此方法用于设置indexpath对应的item的属性 3>- (BOOL)shouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange:(CGRect)newBounds 返回YES,表示当界面的位置发生改变,自动更新布局,调用第一个方法. 4>- (CGSize)collectionViewContentSize 此方法用于设置可滚动范围.
1)在方法2中计算每一个item的frame;
具体实现如下:
//返回一个属性 //计算item的frame /** * 获取indexpath对应的cell的属性 */ UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attr = [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes layoutAttributesForCellWithIndexPath:indexPath]; //自定义item的frame UIEdgeInsets inset = self.sectionInset = UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10); CGFloat screenW = [UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.width; NSInteger column = 3; CGFloat padding = 10; //宽 CGFloat attrW = (screenW - inset.left - inset.right - padding * (column - 1)) / column; //高 // CGFloat attrH = arc4random_uniform(100); NSArray *modelArray = [GoodModel goods]; GoodModel *goodModel = modelArray[indexPath.item]; CGFloat attrH = attrW * goodModel.height / goodModel.width; //x //y CGFloat tempMaxY = MAXFLOAT; NSInteger lie = 0; for (NSInteger i = 0; i < 3; i ++) { CGFloat maxY = [self.maxY[i] doubleValue]; if (maxY < tempMaxY) { tempMaxY = maxY; lie = i; } } CGFloat attrX = inset.left + (attrW + padding) * lie; CGFloat attrY = tempMaxY + padding; attr.frame = CGRectMake(attrX, attrY, attrW, attrH); //将最大Y值累加 self.maxY[lie] = @(attrY + attrH); return attr;
主要困难是计算X,Y,要计算X,实际上就是九宫格算法,X = 左边距 + 列数 * (item宽+间距);左边距,间距通常是给定的,因而关键在于求item对应的列数.当一行摆满以后,第二行从最短的那个开始摆放,这样不至于最后每一列的item总的宽高相差太大导致的不美观.因此需要获得最短的item(也就是获得最小的最大Y值)对应列数,首先要计算出最小的最大Y值,因而需要遍历每一行的item的最小的最大Y值,因而需要有一个数组存储每一个item的最大Y值,
通过懒加载实现:
- (NSMutableArray *)maxY { if (_maxY == nil) { _maxY = [NSMutableArray array]; } return _maxY; }
初始化为三个元素,值为0.问题是为什么用懒加载?不用行不行?初始化又在哪里初始化?为什么要在此处初始化?
2)当计算好每一个item的属性后,在方法1中返回可见范围属性的集合,实际上就是获取方法2中设置好的每一个item的属性,并添加到数组中,
方法1配合方法3实现滚动自动更新布局,我学习的这种做法很笨,因为在第二个方法中,返回的并不是rect范围内的所有item的属性的结合,而是plist文件中全部item(而不仅仅是界面上的),代码如下:
//返回属性的数组 // [self.maxY removeAllObjects]; //初始化最大Y值的数组 for (NSInteger i = 0; i < 3; ++ i) { self.maxY[i] = @0; } //设置属性 //获取item个数 NSInteger count = [self.collectionView numberOfItemsInSection:0]; //创建属性数组 NSMutableArray *attrs = [NSMutableArray array]; for (NSInteger i = 0; i < count; ++ i) { NSIndexPath *indexPath = [NSIndexPath indexPathForItem:i inSection:0]; UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attr = [self layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath:indexPath]; [attrs addObject:attr]; } //返回属性的集合 return attrs;
3)最后,需要重写方法四,设置可滚动范围即可.
3>这些方法的执行顺序:
collectionViewContentSize(第1次)----layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(1)----layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(1-100共100次)----collectionViewContentSize(第2次)----layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(2)----layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(101-200)----
collectionViewContentSize(3)
轻轻滚动界面,
shouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange(1)----
collectionViewContentSize(4)----layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(3)----layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(201-300)
collectionViewContentSize(5)----layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(4)----layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(301-400)
collectionViewContentSize(6)----
shouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange(2)----
collectionViewContentSize(7)----layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(5)----layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(401-500)
collectionViewContentSize(8)----layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(6)----layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(501-600)
collectionViewContentSize(9)
shouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange(3)----
collectionViewContentSize(10)----layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(7)----layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(601-700)
collectionViewContentSize(11)----layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(8)----layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(701-800)
collectionViewContentSize(12)
4>因而可以知道
当初始化的时候方法调用顺序是:
collectionViewContentSize(第1次)---- layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(1)---- layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(1-100共100次)---- collectionViewContentSize(第2次)---- layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(2)----layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(101-200)----
collectionViewContentSize(3)
当滚动界面是调用顺序是:
shouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange----初始化时候的顺序.
然而为什么以这样的顺序调用呢?
由于在方法一中直接返回全部item属性,故而每次调用方法一就会调用很多次(item的个数)方法二,故而此种实现方法效率极低.




