面向对象-反射
当调用一个类中不存在得属性或方法,类默认调用__getarrt__()方法,可以自定义
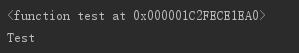
def test(): print("Test") T={"six":test} class Student(object): def __init__(self,name,age): self.name=name self.age=age def __getattr__(self, item): if item in T: return T[item] s=Student('y',18) print(s.six) s.six()
反射:通过字符串映射到对象的属性,该方法实用于对象与类
hasattr(obj,'name')
class People: def __init__(self,name,age): self.name=name self.age=age def talk(self): print("%s is talking" % self.name) obj=People('ya',22) #判断对象obj下面有没有obj.name属性 print(hasattr(obj,'name')) print(hasattr(obj,'talk'))

getattr(obj,'str','defaultstr')拿到对象属性
print(getattr(obj,'name',None)) print(getattr(obj,'talk',None))
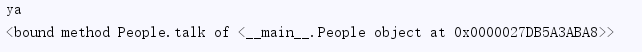
setattr(obj,'sex','male')设置对象属性
setattr(obj,'sex','male') print(obj.sex)

delattr(obj,'str')删除对象属性
print(obj.__dict__) delattr(obj,'age') print(obj.__dict__)

反射的应用
class service: def run(self): while True: inp=input(">>:").strip() cmds=inp.split() if hasattr(self,cmds[0]): func=getattr(self,cmds[0]) func(cmds) def get(self,cmds): print("get......",cmds) def put(self,cmds): print("put......",cmds) obj=service() obj.run()


