第十六节:语法总结(3)(C#6.0和C#7.0新语法)
一. C# 6.0 新语法
1. 自动属性初始化可以赋值
1 /// <summary> 2 /// 自动属性初始化 3 /// </summary> 4 public class UserInfor 5 { 6 public string userId { get; set; } = "123456"; 7 8 public string userName { get; set; } = "lmr"; 9 10 } 11 { 12 Console.WriteLine("------------------------- 1. 自动属性初始化可以赋值----------------------------"); 13 UserInfor uInfor = new UserInfor(); 14 Console.WriteLine($"id={uInfor.userId},userName={uInfor.userName}"); 15 }
2. 字符串嵌入值【$配合{}使用】
特别注意:{}中如果有业务计算需要配合()使用
1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("------------------------- 2. 字符串嵌入值【$配合{}使用】----------------------------"); 3 UserInfor uInfor2 = new UserInfor(); 4 Console.WriteLine($"名字为:{uInfor2.userName}"); 5 //代表要输入一个括号{} 6 Console.WriteLine($"名字为:{{{uInfor2.userName}}}"); 7 //{}中如果有业务计算需要配合()使用 8 Console.WriteLine($"{(uInfor2.userName != "lmr" ? "小鲜肉" : "老鲜肉")}"); 9 }

3. 可以在命名空间出使用static声明静态类
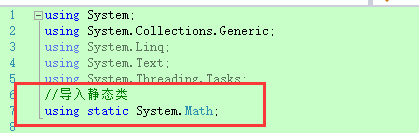
1 { 2 Console.WriteLine($"-------------------------3.可以在命名空间出使用static声明静态类-------------------------"); 3 Console.WriteLine($"之前的使用方式: {Math.Pow(4, 2)}"); 4 Console.WriteLine($"导入后可直接使用方法: {Pow(4, 2)}"); 5 }
4. 空值运算符(?)
不需要判断是否为空了.
1 { 2 Console.WriteLine($"-------------------------4. 空值运算符-------------------------"); 3 int? iValue = 10; 4 Console.WriteLine(iValue?.ToString());//不需要判断是否为空 5 string name = null; 6 Console.WriteLine(name?.ToString()); 7 }
5. 对象初始化
可以直接给字典类型通过类似“索引”的形式赋值 (原先是通过Add方法赋值)
1 { 2 Console.WriteLine($"-------------------------5. 字典对象初始化-------------------------"); 3 Dictionary<string, string> dicList = new Dictionary<string, string>() 4 { 5 ["1"] = "ypf1", 6 ["2"] = "ypf2", 7 ["3"] = "ypf3" 8 }; 9 Dictionary<string, string> dicList2 = new Dictionary<string, string>() 10 { 11 { "1","lmr1"}, 12 { "2","lmr2"}, 13 { "3","lmr3"} 14 }; 15 foreach (var item in dicList) 16 { 17 Console.WriteLine("key:{0},value:{1}", item.Key.ToString(), item.Value.ToString()); 18 } 19 foreach (var item in dicList2) 20 { 21 Console.WriteLine("key:{0},value:{1}", item.Key.ToString(), item.Value.ToString()); 22 } 23 }
6. 异常过滤器增加when判断条件
只有符合when里的条件,才能进入catch,如果不满足的话,直接代码报错,不能抛异常。
1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("-------------------------6. 异常过滤器增加when判断条件-------------------------"); 3 int epCheck = 100; 4 try 5 { 6 int.Parse("ypf"); 7 } 8 catch (Exception e) when (epCheck > 11) 9 { 10 Console.WriteLine(e.Message); 11 } 12 }
7. nameof表达式
把实例转换成同名的字符串
1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("-------------------------7. nameof表达式-------------------------"); 3 UserInfor userInfor = new UserInfor(); 4 Console.WriteLine(nameof(userInfor)); 5 }
8. 在catch和finally语句块里使用await(暂不介绍,不常用)
9. 在属性或方法上使用Lambada表达式
①:方法针对于只有一行的方法
②:属性通过Lambda的形式进行赋值
public class UserInfor { public string userId { get; set; } = "123456"; public string userName { get; set; } = "lmr"; /// <summary> /// Lambda类型的方法 /// </summary> public void LambdaPrint() => Console.WriteLine("我是Lambda类型的方法"); public string userSex => string.Format("男"); } { Console.WriteLine("-------------------------9.在属性或方法上使用Lambada表达式-------------------------"); UserInfor userInfor = new UserInfor(); userInfor.LambdaPrint(); Console.WriteLine($"userSex的值为:{userInfor.userSex}"); }
二. C# 7.0 新语法
1. out参数的改进
在C#7.0之前, out参数使用前必须先声明,然后传入方法中,在C#7.0后可以直接在传入方法的时候进行声明。
1 /// <summary> 2 /// out参数的改进 3 /// </summary> 4 /// <param name="x"></param> 5 /// <param name="y"></param> 6 public void DoNoting(out int x, out int y) 7 { 8 x = 1; 9 y = 2; 10 } 11 { 12 Console.WriteLine("--------------------1-out参数的改进------------------------"); 13 SevenEdition s = new SevenEdition(); 14 s.DoNoting(out int x, out int y); 15 Console.WriteLine(x + y); 16 }
2. 元组(Tuples)
①:需要通过nuget安装这个System.ValueTuple包
②:元组创建的三种方式:语法糖、Create静态方法、构造函数 (默认情况下是通过Item1、Item2 。。。)
③:指定元祖命名:可以通过左边指定,也可以通过右边指定
④:将元祖应用于方法中返回值,即一个方法可以返回多种不同类型的值,不需要封装实体即可以实现。
1 /// <summary> 2 /// 默认元组命名 3 /// </summary> 4 /// <returns></returns> 5 public (int, string, string) TupleWay1() 6 { 7 return (1, "ypf1", "ypf2"); 8 } 9 /// <summary> 10 /// 指定元祖命名 11 /// </summary> 12 /// <returns></returns> 13 public (int m, string n, string k) TupleWay2() 14 { 15 return (1, "ypf1", "ypf2"); 16 } 17 { 18 Console.WriteLine("--------------------2-元组(Tuples)------------------------"); 19 //1. 创建元组的三种形式 20 Console.WriteLine("--------------------1. 创建元组的三种形式------------------------"); 21 var tuple1 = (1, 2); //语法糖 22 var tuple2 = ValueTuple.Create("ypf", "lmr"); //Create静态方法 23 var tuple3 = new ValueTuple<int, string>(12, "ypf12"); //构造函数 24 Console.WriteLine($"tuple1的两个值为:{tuple1.Item1}和{tuple1.Item2}"); 25 Console.WriteLine($"tuple1的两个值为:{tuple2.Item1}和{tuple2.Item2}"); 26 Console.WriteLine($"tuple1的两个值为:{tuple3.Item1}和{tuple3.Item2}"); 27 28 //2. 指定元祖命名 29 Console.WriteLine("--------------------2. 指定元祖命名------------------------"); 30 (int m, string n) tuple4 = (100, "erp"); //左边命名 31 Console.WriteLine($"tuple4的两个值为:{tuple4.m}和{tuple4.n}"); 32 var tuple5 = (one: 250, two: "spz"); //右边命名 33 Console.WriteLine($"tuple5的两个值为:{tuple5.one}和{tuple5.two}"); 34 35 //3. 元祖应用于方法中返回值 36 Console.WriteLine("--------------------3. 元祖应用于方法中返回值------------------------"); 37 SevenEdition s = new SevenEdition(); 38 //默认命名 39 var result1 = s.TupleWay1(); 40 Console.WriteLine($"返回值有:{result1.Item1}、{result1.Item2}、{result1.Item3}"); 41 //指定命名 42 var result2 = s.TupleWay2(); 43 Console.WriteLine($"返回值有:{result2.m}、{result2.n}、{result2.k}"); 44 45 }

3. 局部函数
即在{}中声明一个函数,只有{}中能使用
1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("--------------------3-局部函数------------------------"); 3 DoSome(); 4 void DoSome() 5 { 6 Console.WriteLine("我是局部函数"); 7 } 8 }
4. 模式的比较和匹配
①:is的新模式。
首先补充一个概念:拆箱和装箱
拆箱是将引用类型→值类型 (object ,class均为引用类型)
装箱是将值类型→引用类型
案例:有一个object类型的变量a,如果它是int类型,则+10赋值给m,并输出m的值,下面看新老用法比较。
1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("--------------------4-模式比较(is)------------------------"); 3 object a = 9; 4 //老写法 5 if (a is int) 6 { 7 int b = (int)a; //拆箱 8 int c = b + 10; 9 Console.WriteLine($"老写法c的值为:{c}"); 10 } 11 //新写法 12 if (a is int m) //这里的a直接拆箱为m 13 { 14 int c = m + 10; 15 Console.WriteLine($"新写法c的值为:{c}"); 16 } 17 }
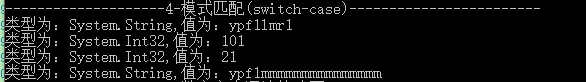
②:switch-case中可以自定义参数类型
传统情况,所有的case中必须是同类型的;而在C# 7.0 新版本中,case中可以不同类型,即Swich中可以传入任何类型,然后通过case中进行对应匹配,这就叫做模式匹配。

1 /// <summary> 2 /// 单一类型 3 /// </summary> 4 /// <param name="m"></param> 5 /// <returns></returns> 6 public dynamic SwitchWay1(string m) 7 { 8 dynamic data; 9 switch (m) 10 { 11 case "ypf1": 12 data = m + "lmr1"; 13 break; 14 case "ypf2": 15 data = m + "lmr2"; 16 break; 17 default: 18 data = "spz00000"; 19 break; 20 } 21 return data; 22 } 23 24 /// <summary> 25 /// 多种类型 26 /// </summary> 27 /// <param name="m"></param> 28 /// <returns></returns> 29 public dynamic SwitchWay2(object m) 30 { 31 dynamic data; 32 switch (m) 33 { 34 case int a when a > 10: 35 data = a + 10; 36 break; 37 case int b: 38 data = b + 100; 39 break; 40 case String c: 41 data = c + "mmmmmmmmmmmmmmm"; 42 break; 43 default: 44 data = "spz00000"; 45 break; 46 } 47 return data; 48 }
1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("--------------------4-模式匹配(switch-case)------------------------"); 3 SevenEdition sE = new SevenEdition(); 4 //老用法 5 var data1 = sE.SwitchWay1("ypf1"); 6 Console.WriteLine($"类型为:{data1.GetType()},值为:{data1}"); 7 //新用法 8 var data2 = sE.SwitchWay2(1); 9 Console.WriteLine($"类型为:{data2.GetType()},值为:{data2}"); 10 11 var data3 = sE.SwitchWay2(11); 12 Console.WriteLine($"类型为:{data3.GetType()},值为:{data3}"); 13 14 var data4 = sE.SwitchWay2("ypf1"); 15 Console.WriteLine($"类型为:{data4.GetType()},值为:{data4}"); 16 17 }
5. 数字文本语法的改写
比如10000000 可以写成10_000_000 ,方便识别。
{ Console.WriteLine("--------------------5-数字文本语法的改写------------------------"); long a = 10000000; long b = 10_000_000; Console.WriteLine($"a的值为:{a},b的值为:{b}"); }

6. 补充一些特殊地方也可以写异常表达式 (不详细测试了)
比如:条件表达式(? :)、null合并运算符(??)、一些Lambda
eg:private string _name = GetName() ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(GetName));
!
- 作 者 : Yaopengfei(姚鹏飞)
- 博客地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/
- 声 明1 : 如有错误,欢迎讨论,请勿谩骂^_^。
- 声 明2 : 原创博客请在转载时保留原文链接或在文章开头加上本人博客地址,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。




