在Unity(C#)下实现Lazy Theta*寻路
在上篇文章中我们介绍了Lazy Theta*。本篇中我会演示一下我实现的Lazy Theta*。
先上代码
//在一个点被expand时是否调用DebugOnExpanded事件,用于debug查看expand的范围。
#define _PATHDEBUGEVENT_
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using System.Linq;
using C5;
namespace CSPathFinding {
public interface IPFVertex<T> where T:IPFVertex<T> , IEquatable<T>{
/// <summary>
/// 检查视线
/// </summary>
/// <param name="other">另一点</param>
/// <returns>能否看到另一点</returns>
bool CheckLOS(T other);
/// <summary>
/// 该点到另一点的消耗
/// </summary>
/// <param name="other">另一点</param>
/// <returns></returns>
float Cost(T other);
/// <summary>
/// 获取该点的邻居
/// </summary>
/// <returns>邻居列表</returns>
IEnumerable<T> Neighbours();
}
public static class BasicPathFind<T> where T : IPFVertex<T>, IEquatable<T> {
public class PathFinder {
public int maxIterations = 200;
public float heuristicWeight = 1.5f;
struct _HPacker :IComparable<_HPacker>{
public _HPacker(T val,float gph) {
value = val;
this.GPH = gph;
}
public T value;
public float GPH;
public int CompareTo(_HPacker other) {
if (GPH < other.GPH) {
return -1;
}
if (GPH > other.GPH)
return 1;
return 0;
}
}
//priority queue from C5.
IntervalHeap<_HPacker> open = new IntervalHeap<_HPacker>();
System.Collections.Generic.HashSet<T> close = new System.Collections.Generic.HashSet<T>();
Dictionary<T, T> parent = new Dictionary<T, T>();
Dictionary<T, float> g = new Dictionary<T, float>();
public T start { get; private set; }
public T end{ get; private set; }
int iteration = 0;
public PathFinder(T start,T end,float heuristicWeight = 1.0f,int maxIterations = 200) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.heuristicWeight = heuristicWeight;
this.maxIterations = maxIterations;
parent[start] = start;
g[start] = 0;
open.Add(new _HPacker(start, g[start] + this.heuristicWeight * start.Cost(end)));
}
public event Action<T> DebugOnExpanded;
//the code here is basicly a translation of psuedo-code from http://aigamedev.com/wp-content/blogs.dir/5/files/2013/07/fig53-full.png
private bool InternalIterate() {
if (open.Count == 0)
return true;
var s = open.FindMin().value;
open.DeleteMin();
#if _PATHDEBUGEVENT_
if (DebugOnExpanded != null)
DebugOnExpanded(s);
#endif
if (close.Contains(s))
return false;
SetVertex(s);
close.Add(s);
if (iteration++ > maxIterations || s.Equals(end)) {
return true;
}
foreach (var sp in s.Neighbours()) {
if (!close.Contains(sp)) {
if (!g.ContainsKey(sp)) {
g[sp] = Mathf.Infinity;
parent.Remove(sp);
}
UpdateVertex(s, sp);
}
}
return false;
}
public IEnumerable<T> QuickFind() {
while (!InternalIterate()) ;
List<T> res = new List<T>();
var temp = close
.OrderBy(
v => v.Cost(end))
.FirstOrDefault();
if (temp == null)
return null;
while (!parent[temp].Equals(temp)) {
res.Add(temp);
temp = parent[temp];
}
res.Reverse();
return res;
}
void UpdateVertex(T s,T sp) {
var gold = g[sp];
ComputeCost(s, sp);
if (g[sp] < gold) {
open.Add(new _HPacker(sp,g[sp]+ heuristicWeight * sp.Cost(end)));
}
}
void ComputeCost(T s,T sp) {
if (g[parent[s]] + parent[s].Cost(sp) < g[sp]) {
parent[sp] = parent[s];
g[sp] = g[parent[s]] + parent[s].Cost(sp);
}
}
void SetVertex(T s) {
if (!parent[s].CheckLOS(s)) {
var temp = s
.Neighbours()
.Intersect(close)
.Select(sp => new { sp = sp, gpc = g[sp] + sp.Cost(s) })
.OrderBy(sppair => sppair.gpc)
.FirstOrDefault();
if (temp == null)
return;
parent[s] = temp.sp;
g[s] = temp.gpc; ;
}
}
}
public static PathFinder FindPath(T start, T end) {
return new PathFinder(start, end);
}
}
}
为了泛用性考虑,我使用了一个接口代表寻路模型中的节点。寻路时传入两个继承该接口的节点即可。如果寻路的节点时是临时生成的(在获取邻点的时候直接new出来的),那么应该实现自己的IEquatable方法来保证相等。
对自己的寻路模型实现IPFVertex
主体代码基本上是上一篇中伪代码的直接翻译。但是我把循环打开节点放在了单独的方法中,这样以后可以修改成不要求单帧内完成的寻路。
- IntervalHeap来自一个github上的集合库C5(https://github.com/sestoft/C5/),功能类似c++中的priority queue,可以加速在open里查询最优先点的过程。需要注意的是这里不能用sortedList,因为sortedList按键值存储,重复的键会抛出异常。如果不用C5的话直接换成List也可以。
- close用了HashSet,因为只需要做求交、插入两种操作。
- parent用的是Dictionary,最快的实现应该是用数组表示,但是要求节点能够返回一个唯一表示自己的正数,太麻烦了。
- g用的Dictionary,理由同上。
原文中的UpdateVertex中做的操作是查询open里是否存在sp,存在则先移除,这是防止一个节点被多次expand。我的实现里去掉了这一行,相应的在expand节点时检测该节点是否已经被close。这是考虑到PriorityQueue的检测元素的效率较低。同时考虑到:一个节点多个存在于PriorityQueue中的话,只有优先值最低的那个会先出来,被expand。而被expand之后,就会被加入到close表里去。对于之后的多个相同节点,我们只需检测是否在close里就可以知道它们是不是被expand过了。
需要注意的是在许多讨论A*的文章中这一步的具体实现都是略过的,主要是同时支持优先级、调整优先级、检测存在这三个特性并且时间复杂度过得去的容器根本不存在,上面我提到的就是一种workaround,我之前刷题写的A*都是用的这种workaround,可以保证正确性。
加入了一个maxIteration的设置,因为如果目标点不可达,而不停止的话,最终所有可达的点都会被expand一遍,然后cpu就炸了。不过如果有一个点可达但只是路程太绕的话,这个设置可能会导致一直撞墙,还是需要自己取舍。
在到达maxiteration或者到达终点之后,会在所有close的点里找一个和终点最接近的。这样就算目标点在墙里,也会走到离目标点最近的地方,而不是原地不动,更加合理。同时如果太远的话,也可以分段寻路。
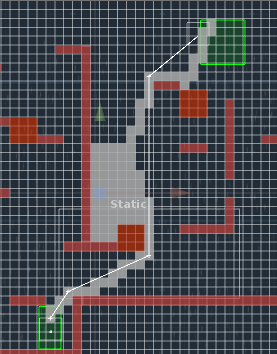
下面是一些演示:
右上角绿色是起点,左下角绿色是终点。
白色块的是进入过open的节点。
白线是最终的路径。
HeuristicWeight = 1.0f时(超过MaxIteration了,直接返回了中间的路径。)
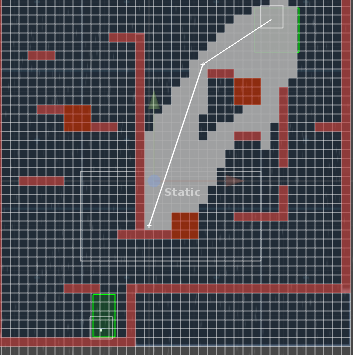
HeuristicWeight = 1.5f时