1.异常
/// 1 try catch旨在上端使用,保证对用户的展示
/// 2 下端不要吞掉异常,隐藏错误是没有意义的,抓住再throw也没意义
/// 3 除非这个异常对流程没有影响或者你要单独处理这个异常
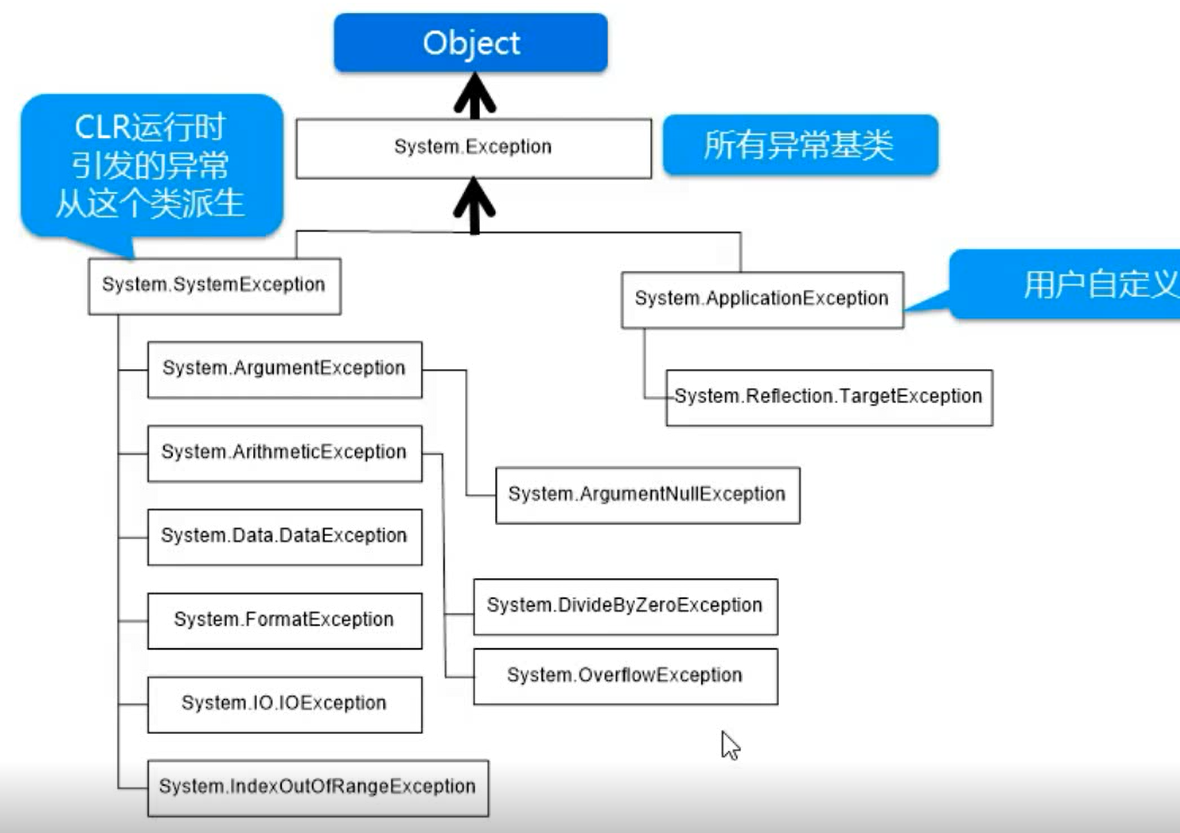
2.常用的异常
2.1与参数有关的异常类:派生自SystemException,用于方法成员传递参数时发生异常
ArgumentException类:用于处理参数无效的异常。ArgumentNullException类:参数为空。
FormatException类:用于处理参数格式错误的异常。
2.2与数组有关的异常:继承自SystemException
IndexOutOfException类:用于处理下标超出了数组长度所引发的异常。
ArrayTypeMismatchException类:用于处理在数组中存储了数据类型不正确的元素所引发的异常。
2.3与IO有关的异常:继承自SystemException
IOException类:用于处理进行文件输入输出操作时所引发的异常。
2.4内存溢出有关的异常
OverFlowException类:用于处理程序逻辑错误造成的死循环异常。
2.5与算术有关的异常
ArithmeticException类:用于处理与算术有关的异常,比如0做除数。DivideByZeroException类。
2.6数据库操作异常类
DbException类:用于处理所有数据源操作异常类的基类。
SqlException类:用于处理针对sql数据源的异常,比如数据库链接错误。
3.异常处理
3.1“底层方法”将第一次捕获的异常传递给上级调用者进一步详细处理

1 public static int Update(string sql)
2 {
3 SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(connString);
4 SqlCommand cmd= new SqlCommand(sql,conn);
5 try
6 {
7 conn.Open();
8 return cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
9 }
10 catch(Exception ex)
11 {
12 //此处可以添加日志
13 throw ex;
14 }
15 finally
16 {
17 conn.Close();
18 }
19 }
20
21 try catch throw finally
3.2"中层调用者"可以使用多路捕获异常并封装详细异常信息
添加具体异常对象,通过判断错误号决定异常的类型。
1.多路捕获异常不是必须的,只有需要的时候才使用。
2.可以添加多个catch块。
3.一定要把Exception类放在最后。
ex.Number的使用,throw new Exception("********"+ex.Message);
throw ex;这种未经包装
throw new Exception("******"+ex.Message);这种稍微包装了一下
异常一般放在业务逻辑里面,不需要放在界面里面,这样界面捕获后就直接显示。
3.3异常处理的建议
3.3.1在代码底层出现问题,不要隐瞒,第一时间终止运行
3.3.2 UI层直接把异常catch住,底层尽量不要catch异常,有问题直接throw异常
3.3.3除非能容忍某个异常,那么自己try catch,然后日志,剩下的继续
如果代码有问题,尽量早可能报错,早可能解决
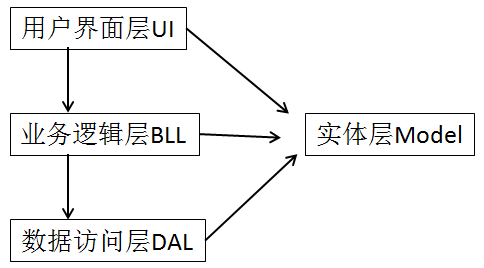
4.系统功能较多并且业务复杂时,可以使用三层架构设计项目
表示UI:界面层
业务逻辑层BLL:将界面层或数据访问层的部分职责(逻辑代码)分离出来
数据访问层DAL:主要负责连接读写数据库
表示层UI、业务逻辑层BLL、数据访问层都需要访问实体层(Models)。
5.项目命名的一般规范
解决方案 项目名称+Pro
用户界面层 项目名称
业务逻辑层 项目名称+BLL 业务逻辑类:实体类名+Manager
数据访问层 项目名称+DAL 数据访问类:实体类名+Service
实体对象 一般和数据库实体相同
6.理解框架
作用:支撑、主导
7.典型两层架构设计原理
分表示层和数据访问层,表示层由前台开发人员夫负责,主要是和用户交互的界面;数据访问层由后台开发人员负责,主要完成数据库的操作。表示层和数据访问层由实体层连接,分层与实体类无必然联系,实体类只是数据传递的载体,什么时候都可以使用。
8.关于类库项目
类库项目专门提供软件的功能模块
类库项目最终生成的是一个dll文件
通过封装,类库项目能够很好的与外界协作,安全性高
9.两层架构项目之间的引用
数据访问层DAL需引用实体层Models,表示层From需引用数据访问层DAL和实体层Models。
10.实体对象的可序列化
10.1实体对象在程序中不断的被传递
表示层(UI)<——>实体对象Models<——>数据访问层DAL
10.2序列化与反序列
序列化:将对象状态转换为可保持或传输的格式的过程,在序列化过程中,对象的公有字段和私有字段以及类的名称(包括包含该类的程序集)都被转化为字节流,然后写入数据流。
反序列化:将流转化为对象,与序列化结合可轻松地存储和传输数据。
10.3对象序列化的意义
10.3.1将对的状态保持在存储媒体中,以便可以在以后重新创建精确的副本。
10.3.2将对象从一个应用程序域发送到另一个应用程序域,对象序列化以后保证数据传输的稳定和安全。
实体类Models的前面加 [Serializable]
11.接口
接口又叫接口类,接口也是类
使用关键字interface定义,接口类名称通常使用I开头
接口中的属性、方法等,只是做一个声明,没有任何实现
接口中的属性、方法等,默认都是public。
方法声明类似于抽象方法
11.1接口具有强制性,实现接口的类必须实现接口的所有成员
11.2一个类既可以实现多个接口,也可以同时继承其他类
通常把父类写在接口的前面,继承了一个类,实现了一个接口
class Student:Person,IStudent,IComparable{...}

1 //定义接口
2 interface IMultiPrinter
3 {
4 void Print(string content);
5 void Copy(string content);
6 bool Fax(string content);
7 }
8
9 //类实现接口
10 class HPMultiPrinter:IMultiPrinter
11 {
12 public void Print(string content)
13 {
14 Console.WriteLine("惠普打印机正在打印..." + content);
15 }
16
17 public void Copy(string content)
18 {
19 Console.WriteLine("惠普打印机正在复印..." + content);
20 }
21
22 public bool Fax(string content)
23 {
24 Console.WriteLine("惠普打印机正在传真..." + content);
25 return true;
26 }
27 }
28
29 //调用接口
30 static void Main(string[] args)
31 {
32 //使用接口定义,类实现该对象
33 IMultiPrinter objPrinter = new HPMultiPrinter();
34 objPrinter.Print("学生成绩表");
35 objPrinter.Copy("学生信息表");
36 objPrinter.Fax("老师信息表");
37 Console.ReadKey();
38 }
12.接口的实践
12.1提高团队成员并行开发项目的效率
接口使用者只关心接口的应用功能,不必关心接口的内部实现
接口实现者只关心如何实现接口的内部实现,不关心谁使用
12.2提高系统的可维护性
当用户的需求改变时,只需要修改接口的实现,系统即可更新
13.接口总结
接口的应用场合
如果某一个功能点需求变化较多,应使用接口保证系统的可扩展性
如果想实现团队成员的并行开发,可以使用接口来规范对象的使用
接口编写规范
接口成员只能是一个声明
实现接口的类必须全部实现接口中规定的属性、方法
特别说明
接口的使用不是必须的,要根据用户的需求来决定
14.继承多态
多态的应用大大提高了程序的可扩展性
继承多态实现的条件:1、父类中必须有抽象方法和虚方法
2、子类必须重写父类中的抽象方法或虚方法
3、子类对象必须转换成父类类型去使用
父类类型作为方法的参数类型,调用时实际传递的是子类的对象
15.接口多态
实现接口多态的条件:1、一个接口必须被两个或两个以上类实现
2、接口实现类必须转换成接口类型去使用
接口作为方法参数类型,调用时实际传递的是接口实现类的对象
接口多态在实践中应用最广泛
通俗来说,同样一个方法(方法声明的是接口类对象),因为传递的对象(传递的是接口的派生类)不一样,执行的过程和结果也不一样,这就是接口多态

1 //定义接口
2 interface IMultiPrinter
3 {
4 void Print(string content);
5 void Copy(string content);
6 bool Fax(string content);
7 }
8
9 //惠普类
10 class HPMultiPrinter : IMultiPrinter
11 {
12 public void Print(string content)
13 {
14 Console.WriteLine("惠普打印机正在打印..." + content);
15 }
16
17 public void Copy(string content)
18 {
19 Console.WriteLine("惠普打印机正在复印..." + content);
20 }
21
22 public bool Fax(string content)
23 {
24 Console.WriteLine("惠普打印机正在传真..." + content);
25 return true;
26 }
27 }
28
29 //佳能类
30 class JNMultiPrinter : IMultiPrinter
31 {
32 public void Print(string content)
33 {
34 Console.WriteLine("佳能打印机正在打印..." + content);
35 }
36
37 public void Copy(string content)
38 {
39 Console.WriteLine("佳能打印机正在复印..." + content);
40 }
41
42 public bool Fax(string content)
43 {
44 Console.WriteLine("佳能打印机正在传真..." + content);
45 return true;
46 }
47 }
48
49 //实现多态
50 class Program
51 {
52 static void Main(string[] args)
53 {
54 Print(new HPMultiPrinter());
55 Print(new JNMultiPrinter());
56 Console.ReadLine();
57 }
58
59 static void Print(IMultiPrinter objPrinter)
60 {
61 objPrinter.Print("学生成绩表");
62 objPrinter.Copy("学生信息表");
63 objPrinter.Fax("老师信息表");
64 }
65 }
16.接口与抽象类
| 抽象类 | 接口 | |
| 不同点 | 用abstract定义 | 用interface定义 |
| 只能继承一个类 | 可以实现多个接口 | |
| 非抽象派生类必须实现抽象方法 | 实现接口的类必须实现所有成员 | |
| 需要override实现抽象方法 | 直接实现 | |
| 相似点 | 都不能直接实例化 | |
| 都包含未实现的方法 | ||
| 子类或“接口实现类”必须实现未实现的方法 | ||
17.设计模式与简单工厂
简单工厂是设计模式中的一种。
什么是设计模式?设计模式是人们在开发中遇到的共性问题而提出的一个解决方案
程序开发中的设计模式只是一种参考,而不是一成不变的
简单工厂:典型应用是解决单一对象创建的扩展问题
抽象工厂:典型应用是解决多种类型数据库访问问题或不同业务逻辑
单例模式:典型应用是在开发中设计购物车的时候需使用
18.简单工厂

实现原理:工厂通过“选择”的方法来指定应该创建哪个“接口实现类的对象”
“工厂”其实就是一个对象创建的方法,让对象“延迟创建”
简单工厂创建步骤:
1、添加接口。
2、添加需要实现接口的类并实现接口。
3、添加工厂(建议使用静态类)。
<1>定义接口变量。
<2>读取配置文件。
<3>使用反射创建接口实现类的对象。
<4>返回接口变量(实际返回的是一个接口实现类的对象)
4、添加配置文件并配置相应的节点。
5、调用工厂方法并实现功能。

1 //接口
2 /// <summary>
3 /// 打印接口(产品原型)
4 /// </summary>
5 public interface IReport
6 {
7 void StartPrint();
8 }
9
10 //实现接口的类1
11 public class ExcelReport:Factory.IReport
12 {
13 public void StartPrint()
14 {
15 System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show("...正在调用Excel报表程序");
16 }
17 }
18
19 //实现接口的类2
20 public class WordExport:Factory.IReport
21 {
22 public void StartPrint()
23 {
24 System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show("...正在调用Word报表程序");
25 }
26 }
27
28 //工厂类
29 public class Factory
30 {
31 //【1】定义接口变量
32 static IReport objReport = null;
33 //【2】读取配置文件
34 static string reportType = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["ReportType"].ToString();
35 //【3】根据配置文件初始化接口变量
36 public static IReport Choose()
37 {
38 switch (reportType)
39 {
40 case "ExcelReport":
41 objReport = new ExcelReport();
42 break;
43 case "WordReport":
44 objReport = new WordExport();
45 break;
46 default:
47 break;
48 }
49 return objReport;
50 }
51 }
52
53 //实现调用代码
54 private void btn_Print_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
55 {
56 //IReport objReport = new ExcelReport();//new WordReport
57 //根据工厂提供的具体产品来使用
58 //这种设计方法,使得调用者和后台实现方法完全脱离,大大增加了系统的可扩展性
59 IReport objReport = Factory.Factory.Choose();
60 objReport.StartPrint();
61 }
19.反射 Reflection
反射的概念
反射是.NET中的一个重要技术。通过反射,可以在运行时获得某个类型的各种信息,包括方法、属性、事件、及构造函数等,还可以获得每个成员的名称等信息。
反射的特点
在程序运行时,动态创建对象、调用方法、设置属性和激励事件,而不是在编译的时候完成。
反射的应用
在VS中的智能提示、使用MSIL反汇编工具查看IL代码用的都是反射技术。
Java开发工具Eclipse中的插件使用,也是用反射技术。
开发中的应用
系统需要基于插件开发的时候,必须要用反射。
在简单工厂和抽象工厂设计模式中将使用反射技术。
使用反射一般都要配合接口使用。
反射技术使得系统性能一定程度降低,除非必要情况,反射不宜过多使用。

1 //1、创建接口类
2 namespace ICal
3 {
4 public interface ICalculator
5 {
6 int Add(int a, int b);
7 int Sub(int a, int b);
8 }
9 }
10
11 //2、创建计算器类实现接口
12 namespace CalDll
13 {
14 public class Calculator : ICal.ICalculator
15 {
16 public int Add(int a, int b)
17 {
18 return a + b;
19 }
20
21 public int Sub(int a, int b)
22 {
23 return a - b;
24 }
25 }
26 }
27
28 //3、使用反射技术应用接口
29 using System.Reflection;//【1】引入反射命名空间
30 using ICal;//【2】引入接口类库
31
32 private void btn_Cal_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
33 {
34 //动态加载程序集并创建对象
35 ICalculator objCal = (ICalculator)Assembly.LoadFrom("CalDll.dll").CreateInstance("CalDll.Calculator");
36 //通过接口完成运算
37 int result = objCal.Add(Convert.ToInt16(this.tb_Num1.Text.Trim()), Convert.ToInt16(this.tb_Num2.Text.Trim()));
38 this.lbl_Result.Text = result.ToString();
39 }
反射:System.Reflection .Net框架提供帮助类库,可以读取并使用metadata。程序可配置可扩展,不需要修改代码,首次运行时读取的。Assembly.Load(Path)这里的path是Debug这个路径下的dll文件名,通过这样并不需要重新引用。IOC,依赖抽象接口,Reflection+Factory+Config

Console.WriteLine("************************Reflection*****************");
//【1】 加载dll
//方式1:dll名称无后缀,从当前目录即Debug加载
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load("Ruanmou.DB.MySql");
//方式2:完整路径的加载 可以是别的目录 加载不会错,但是如果没有依赖项,使用的时候会错
Assembly assembly1 = Assembly.LoadFile(@"D:\MyReflection\bin\Debug\Ruanmou.DB.MySql.dll");
//方式3://带后缀或者完整路径
Assembly assembly2 = Assembly.LoadFrom("Ruanmou.DB.MySql.dll");
foreach (var item in assembly.GetModules())
{
Console.WriteLine(item.FullyQualifiedName);
}
foreach (var item in assembly.GetTypes())
{
Console.WriteLine(item.FullName);
}
//【2】获取类
Type type = assembly.GetType("Ruanmou.DB.MySql.MySqlHelper");//2 获取类型信息
//【3】创建对象
object oDBHelper = Activator.CreateInstance(type);
//oDBHelper.Query();//oDBHelper是objec不能调用,但实际上方法是有的 因为编译器不认可所以这句会报错
//【4】类型转换
IDBHelper iDBHelper = (IDBHelper)oDBHelper;
//【5】方法调用
iDBHelper.Query();

Console.WriteLine("************************Reflection+Factory+Config*****************");
IDBHelper iDBHeler = Factory.CreateHelper();//1/2
iDBHeler.Query();//可配置可扩展 反射是动态的 依赖的是字符串
Console.WriteLine("************************Common*****************");
IDBHelper iDBHelper = new SqlServerHelper();
iDBHelper.Query();

public class ReflectionTest
{
#region Identity
/// <summary>
/// 无参构造函数
/// </summary>
public ReflectionTest()
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0}无参数构造函数", this.GetType());
}
/// <summary>
/// 带参数构造函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
public ReflectionTest(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0} 有参数构造函数", this.GetType());
}
public ReflectionTest(int id)
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0} 有参数构造函数", this.GetType());
}
#endregion
}
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load("Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer");
Type type = assembly.GetType("Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer.ReflectionTest");
object oReflectionTest1 = Activator.CreateInstance(type);//调用无参数构造函数
object oReflectionTest2 = Activator.CreateInstance(type, new object[] { 123 });//调用int型构造函数
object oReflectionTest3 = Activator.CreateInstance(type, new object[] { "123" });//调用string型构造函数

public class GenericClass<T, W, X>
{
public void Show(T t, W w, X x)
{
Console.WriteLine("t.type={0},w.type={1},x.type={2}", t.GetType().Name, w.GetType().Name, x.GetType().Name);
}
}
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load("Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer");
Type type = assembly.GetType("Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer.GenericClass`3");//有几个参数,就占位符+几
//object oGeneric = Activator.CreateInstance(type);
Type newType = type.MakeGenericType(new Type[] { typeof(int), typeof(string), typeof(DateTime) });
object oGeneric = Activator.CreateInstance(newType);

/// <summary>
/// 反射测试类
/// </summary>
public class ReflectionTest
{
#region Method
/// <summary>
/// 无参方法
/// </summary>
public void Show1()
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0}的Show1", this.GetType());
}
/// <summary>
/// 有参数方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
public void Show2(int id)
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0}的Show2", this.GetType());
}
/// <summary>
/// 重载方法之一
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
/// <param name="name"></param>
public void Show3(int id, string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0}的Show3", this.GetType());
}
/// <summary>
/// 重载方法之二
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
/// <param name="id"></param>
public void Show3(string name, int id)
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0}的Show3_2", this.GetType());
}
/// <summary>
/// 重载方法之三
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
public void Show3(int id)
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0}的Show3_3", this.GetType());
}
/// <summary>
/// 重载方法之四
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
public void Show3(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0}的Show3_4", this.GetType());
}
/// <summary>
/// 重载方法之五
/// </summary>
public void Show3()
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0}的Show3_1", this.GetType());
}
/// <summary>
/// 私有方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
private void Show4(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0}的Show4", this.GetType());
}
/// <summary>
/// 静态方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
public static void Show5(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是{0}的Show5", typeof(ReflectionTest));
}
#endregion
}
Console.WriteLine("************************Reflection+Method*****************");
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load("Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer");
Type type = assembly.GetType("Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer.ReflectionTest");
object oReflectionTest = Activator.CreateInstance(type);
foreach (var item in type.GetMethods())
{//遍历所有的方法名
Console.WriteLine(item.Name);
}
//oReflectionTest.Show1();//object不能直接调用方法
{
//调用Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer命名空间下ReflectionTest类中void Show1()方法
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Show1");
method.Invoke(oReflectionTest, null);
}
{
//调用Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer命名空间下ReflectionTest类中void Show2(int id)方法
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Show2");
method.Invoke(oReflectionTest, new object[] { 123 });
}
{
//调用Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer命名空间下ReflectionTest类中static void Show5(string name)
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Show5");
//使用Reflection调用静态方法,实例那里可以指定为null,因为static是全局唯一的
method.Invoke(oReflectionTest, new object[] { "麦田的稻草人" });
method.Invoke(null, new object[] { "果然" });//等同上句
}
{
//void Show3()
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Show3", new Type[] { });
method.Invoke(oReflectionTest, new object[] { });
}
{
//void Show3(int id)
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Show3", new Type[] { typeof(int) });
method.Invoke(oReflectionTest, new object[] { 123 });
}
{
//void Show3(string name)
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Show3", new Type[] { typeof(string) });
method.Invoke(oReflectionTest, new object[] { "Ant" });
}
{
//void Show3(int id, string name)
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Show3", new Type[] { typeof(int), typeof(string) });
method.Invoke(oReflectionTest, new object[] { 234, "W" });
}
{
//void Show3(string name, int id)
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Show3", new Type[] { typeof(string), typeof(int) });
method.Invoke(oReflectionTest, new object[] { "W", 234 });
}
{
//用Reflection调用私有方法private void Show4(string name)
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Show4", BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
method.Invoke(oReflectionTest, new object[] { "天空之上" });
}

namespace Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer
{
public class GenericDouble<T>
{
public void Show<W, X>(T t, W w, X x)
{
Console.WriteLine("t.type={0},w.type={1},x.type={2}", t.GetType().Name, w.GetType().Name, x.GetType().Name);
}
}
}
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load("Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer");
Type typeGenericDouble = assembly.GetType("Ruanmou.DB.SqlServer.GenericDouble`1");//泛型类有一个参数<T>
Type newType = typeGenericDouble.MakeGenericType(new Type[] { typeof(int) });
object oGeneric = Activator.CreateInstance(newType);
MethodInfo method = newType.GetMethod("Show");
MethodInfo methodNew = method.MakeGenericMethod(new Type[] { typeof(string), typeof(DateTime) });//泛型方法后两个参数<W,X>
methodNew.Invoke(oGeneric, new object[] { 123, "流浪诗人", DateTime.Now });//<int,string,Datetime>

namespace Ruanmou.Model
{
/// <summary>
/// 实体
/// </summary>
public class People
{
public People()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}被创建", this.GetType().FullName);
}
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Description;
}
}
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load("Ruanmou.Model");
Type type = assembly.GetType("Ruanmou.Model.People");
//以上两句也可以用这句代替 Type type = typeof(People);
object oPeople = Activator.CreateInstance(type);
foreach (var prop in type.GetProperties())
{//遍历所有的属性
Console.WriteLine(type.Name);
Console.WriteLine(prop.Name);
Console.WriteLine(prop.GetValue(oPeople));
if (prop.Name.Equals("Id"))
{
prop.SetValue(oPeople, 234);
}
else if (prop.Name.Equals("Name"))
{
prop.SetValue(oPeople, "风潇潇");
}
Console.WriteLine($"{type.Name}.{prop.Name}={prop.GetValue(oPeople)}");
}
foreach (var field in type.GetFields())
{//遍历所有的字段
Console.WriteLine(type.Name);
Console.WriteLine(field.Name);
Console.WriteLine(field.GetValue(oPeople));
if (field.Name.Equals("Description"))
{
field.SetValue(oPeople, "高级班的新学员");
}
Console.WriteLine($"{type.Name}.{field.Name}={field.GetValue(oPeople)}");
}

namespace Ruanmou.Model
{
/// <summary>
/// 实体
/// </summary>
public class People
{
public People()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}被创建", this.GetType().FullName);
}
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Description;
}
public class PeopleDTO
{
public PeopleDTO()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}被创建", this.GetType().FullName);
}
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }//ShortName 特性
public string Description;
}
}
//【1】先声明初始化一个people对象
People people = new People();
people.Id = 123;
people.Name = "Lutte";
people.Description = "高级班的新学员";
PeopleDTO peopleDTO_1 = new PeopleDTO()
{
Id = people.Id,
Name = people.Name,
Description = people.Description
};//通常可以这样声明一个PeopleDTO硬编码
//【2】利用反射根据Dll和了类名创建类型
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load("Ruanmou.Model");
Type typePeople = assembly.GetType("Ruanmou.Model.People");
Type typePeopleDTO = assembly.GetType("Ruanmou.Model.People");
//以上三句可以用下面两句代替
//Type typePeople = typeof(People);
//Type typePeopleDTO = typeof(PeopleDTO);
//【3】创建一个DTO实例
object peopleDTO = Activator.CreateInstance(typePeopleDTO);
foreach (var prop in typePeopleDTO.GetProperties())
{//【4】遍历属性
object value = typePeople.GetProperty(prop.Name).GetValue(people);
prop.SetValue(peopleDTO, value);
}
foreach (var filed in typePeopleDTO.GetFields())
{//【5】遍历字段
object value = typePeople.GetField(filed.Name).GetValue(people);
filed.SetValue(peopleDTO, value);
}
反射优点:动态。面向对象语言是静态的,相对安全的,但很多是写死的。
反射缺点:写起来复杂、避开编译器的检查(有时有异常)、反射性能差一点(性能优化,空间换时间) 、MVC和EF第一次访问很慢,后面很快
所有的访问修饰符对于反射都是没用的。

//需要把YKMDLL.dll放到执行目录Debug下
namespace YKMDLL
{
public class CalaAdd
{
/// <summary>
/// 共有字段
/// </summary>
public int addResult;
/// <summary>
/// 共有属性
/// </summary>
public int FirstNum { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 共有属性
/// </summary>
public int SecondNum { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 共有方法
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public int Add()
{
return FirstNum + SecondNum;
}
}
}
//【1】加载程序集
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load("YKMDLL");
//【2】遍历程序集下所有类型的所有共有成员(属性、字段、方法)
foreach (Type type in assembly.GetTypes())
{
Console.WriteLine($"**当前类型是{type.Name}");
foreach (PropertyInfo propInfo in type.GetProperties())
{//仅遍历共有属性
Console.WriteLine($" 属性类型:{propInfo.PropertyType} 属性名:{propInfo.Name}");
}
foreach (FieldInfo fieldInfo in type.GetFields())
{//仅遍历共有字段
Console.WriteLine($" 字段类型:{fieldInfo.FieldType} 字段名:{fieldInfo.Name}");
}
foreach (MethodInfo methodInfo in type.GetMethods())
{//仅遍历共有方法
Console.WriteLine($" 方法返回值类型:{methodInfo.ReturnType} 方法名:{methodInfo.Name}");
}
}
//【3】获取指定类类型
Type type_Add = assembly.GetType("YKMDLL.CalaAdd");
//【4】创建实例
object obj_Add = Activator.CreateInstance(type_Add);
//【5】设置属性值
PropertyInfo prop_AddFirst = type_Add.GetProperty("FirstNum");
prop_AddFirst.SetValue(obj_Add, 123);
PropertyInfo prop_AddSecond = type_Add.GetProperty("SecondNum");
prop_AddSecond.SetValue(obj_Add, 2);
//【6】执行方法
MethodInfo method_Add = type_Add.GetMethod("Add");
int result = Convert.ToInt32(method_Add.Invoke(obj_Add, null));
Console.WriteLine($"反射方法计算的结果:{prop_AddFirst.GetValue(obj_Add)}+{prop_AddSecond.GetValue(obj_Add)}={result}");

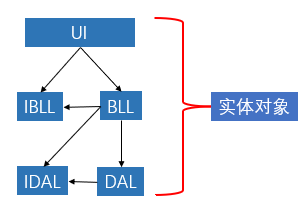
20.基于接口设计三层架构
开发团队协作的保障——指定项目开发规范
项目命名、模块命名、类编写规范、注释要求...
数据库设计规范:表的命名、实体属性命名、约束...
项目开发中协作的形式:垂直分工、并行开发
垂直分工协作
任务分工:按功能模块
技术要求:要求开发人员必须熟悉项目各模块(DAL、BLL、UI)编写方法
应用场合:中小型项目,且开发团队力量较小
现实比较:类似于小企业的“作坊式”生产
人员特点:开发人员的工作贯穿整个项目
并行开发协作
任务分工:按层(BLL、DAL、UI)划分
技术要求:只要求开发人员熟悉项目其中一层(BLL、DAL、UI)的业务和编写方法
应用场合:大中型项目,且开发团队力量强
现实比较:类似于大企业的“专业化、流水线”生产
人员特点:熟悉系统业务的开发人员设计BLL业务层
熟悉数据库开发的人员设计DAL数据层
善于设计用户界面的开发人员设计UI
21.特性
特性:就是一个类,直接或间接继承自Attribute,一般以Attribute结尾,声明时候可以省略Attribute。特性可以影响程序的运行。使用方法是用中括号,感觉上每一个特性都可以带来对应的功能,例如在一个类前加【Serializable】就表明给可以序列化和反序列化,其实这是一种错觉,实际上特性添加后,编译会在元素内部产生IL,但是无法直接使用,仅会在metadata里面有记录。

//修饰特性 AttributeTargets指该特性用在哪里,All表示全部;AllowMultiple表示特性是否是多重修饰;Inherited表示使用该特性是否可以被继承下去
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.All, AllowMultiple = false, Inherited = true)]

//修饰特性 AttributeTargets指该特性用在哪里,All表示全部;AllowMultiple表示特性是否是多重修饰;Inherited表示使用该特性是否可以被继承下去
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.All, AllowMultiple = false, Inherited = true)]
public class CustomAttribute : Attribute
{
public CustomAttribute()
{ }
public CustomAttribute(int id)
{
Console.WriteLine("********************");
}
public string Description { get; set; }
public string Remark = null;
public void Show()
{
Console.WriteLine($"This is {nameof(CustomAttribute)}");
}
//委托 事件 都没问题
}

[Custom(123, Description = "1234", Remark = "2345")]//方法不行
public class Student
{
[CustomAttribute]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Leng(5,10)]//还有各种检查
public string Name { get; set; }
[Leng(20, 50)]
public string Accont { get; set; }
[Custom()]//给【该方法】添加特性
[return: Custom()]//给【该方法返回值】添加特性
public string Answer([Custom]string name)//给【该方法参数】添加特性
{
return $"This is {name}";
}
}

public class Manager
{
public static void Show(Student student)
{
//特性本身是没用的,只有通过反射创建特性类,才可以执行特性类中的方法,获取特性类中的属性、字段
//【1】类特性
Type type = typeof(Student); //student.GetType();
if (type.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))//创建特性实例前应先检查有没有,而不是直接创建实例,这样性能高
{
//Attribute attribute0 = type.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
//CustomAttribute attribute = (CustomAttribute)attribute0;
//上面两句等同于下面一句
CustomAttribute attribute = (CustomAttribute)type.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
Console.WriteLine($"{attribute.Description}_{attribute.Remark}");
attribute.Show();
}
//【2】属性特性
PropertyInfo property = type.GetProperty("Id");
if (property.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
CustomAttribute attribute = (CustomAttribute)property.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
Console.WriteLine($"{attribute.Description}_{attribute.Remark}");
attribute.Show();
}
//【3】方法特性
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Answer");
if (method.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
CustomAttribute attribute = (CustomAttribute)method.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
Console.WriteLine($"{attribute.Description}_{attribute.Remark}");
attribute.Show();
}
//【4】方法参数特性
ParameterInfo parameter = method.GetParameters()[0];
if (parameter.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
CustomAttribute attribute = (CustomAttribute)parameter.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
Console.WriteLine($"{attribute.Description}_{attribute.Remark}");
attribute.Show();
}
//【5】方返回值数特性
ParameterInfo returnParameter = method.ReturnParameter;
if (returnParameter.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
CustomAttribute attribute = (CustomAttribute)returnParameter.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
Console.WriteLine($"{attribute.Description}_{attribute.Remark}");
attribute.Show();
}
}
}
小结:特性本身是没用的,程序运行的过程中找到特性并加以利用,也就是说没有破坏类型封装的前提下,可以加点额外的信息与行为。不反射就使用不了特性,也就是说特性必须结合反射来使用。任何一个可以生效的特性,都是因为有地方主动使用了的。类使用特性的时候,那个类必须先写好调用特性的代码。

//第一部分【Demo部分】
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace YKMAttribute
{
// 枚举类型
public enum UserState
{
[Remark("正常")]
Normal = 0,
[Remark("冻结")]
Frozen = 1,
[Remark("删除")]
Deleted = 2
}
//特性类
public class RemarkAttribute : Attribute
{
public RemarkAttribute(string remark)
{//特性类构造函数
_remark = remark;
}
private string _remark = null;
public string GetAttributeRemark()
{//特性类返回remark方法
return _remark;
}
}
//Remark特性管理类
public static class RemarkManager
{
//根据枚举值得到中文含义
public static string GetRemark(this Enum value)
{
Type type = value.GetType();
FieldInfo filedInfo = type.GetField(value.ToString());
if (filedInfo.IsDefined(typeof(RemarkAttribute), true))
{
RemarkAttribute attribute = (RemarkAttribute)filedInfo.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(RemarkAttribute), true);
//上面这句是下面这两句的合写版
//Attribute attribute0 = filedInfo.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(RemarkAttribute), true);
//RemarkAttribute attribute1 = (RemarkAttribute)attribute0;
return attribute.GetAttributeRemark();
}
else
{
return value.ToString();
}
}
}
}
//第二部分【测试部分】
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//正常应该这样写,静态类静态方法传入一个枚举值
Console.WriteLine(RemarkManager.GetRemark(UserState.Normal));
//以下两种用到了扩展方法,注意该方法声明GetRemark(this Enum value)中的this
Console.WriteLine(UserState.Frozen.GetRemark());
Console.WriteLine(UserState.Deleted.GetRemark());
Console.ReadKey();
}


/* 定义一个Syudent类,三个属性
* 要求1:Name属性长度在5~10
* 要求2:Address属性长度在20~50
* 要求3:QQ范围为1001~999999999999
*/
public class Student
{
[Length(5,10)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Length(20, 50)]
public string Address { get; set; }
[Long(10001, 999999999999)]
public long QQ { get; set; }
}
/* 抽象特性类
* 两个特性子类
* 特性验证管理类(其中包含特性验证方法)
*/
namespace YKMAttribute
{
/* 分析可知Name和Address都是验证长度,QQ是验证范围
* Name和Address可以共用一个特性指定不同的上下限长度
* QQ可以用另一个特性指定上下限范围
* 分析结果:【用一个抽象泛型类,和两个子类泛型类】
*/
//抽象特性类
public abstract class AbstractValidateAttribute : Attribute
{
//抽象特性类的抽象方法
public abstract bool Validate(object value);
}
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property|AttributeTargets.Field)]
public class LengthAttribute : AbstractValidateAttribute
{
private int _min = 0;
private int _max = 0;
public LengthAttribute(int min, int max)
{
_min = min;
_max = max;
}
public override bool Validate(object value)
{
if (value != null && !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value.ToString()))
{
int length = value.ToString().Length;
if (length >= _min && length <= _max)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property | AttributeTargets.Field)]
public class LongAttribute : AbstractValidateAttribute
{
private long _min = 0;
private long _max = 0;
public LongAttribute(long min, long max)
{
_min = min;
_max = max;
}
public override bool Validate(object value)
{
if (value != null && !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value.ToString()))
{
long result = 0;
if (long.TryParse(value.ToString(), out result))
{
if (result >= _min && result <= _max)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
//特性验证管理类
public static class ValidateExtension
{
public static bool Validate(this object o)//注意这里有this,扩展方法
{
Type type = o.GetType();
foreach (PropertyInfo info in type.GetProperties())
{//通过反射遍历所有的属性
if (info.IsDefined(typeof(AbstractValidateAttribute), true))
{//判断是否有配置该特性的属性
//如果有配置该特性的属性,得到该属性所有的AbstractValidateAttribute特性
object[] attributeArray = info.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AbstractValidateAttribute), true);
foreach (AbstractValidateAttribute attribute in attributeArray)//在这一步转换的
{//遍历所有的特性
if (!attribute.Validate(info.GetValue(o)))
{//检测该方法,判断该值
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
}
//测试
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student()
{
Name = "MeTrun",
Address="银河系太阳系地球村江苏省苏州市昆山市开发区世贸东一号13栋1367室",
QQ=521256
};
Console.WriteLine($"stu合格结果:{stu.Validate()}");
stu.Name = "唐三";
Console.WriteLine($"stu修改Name后结果:{stu.Validate()}");
stu.Name = "MeTrun";
stu.Address = "水帘洞";
Console.WriteLine($"stu修改Address后结果:{stu.Validate()}");
stu.Address = "银河系太阳系地球村江苏省苏州市昆山市开发区世贸东一号13栋1367室";
stu.QQ = 1119;
Console.WriteLine($"stu修改QQ后结果:{stu.Validate()}");
Console.ReadKey();
}

22.反射、特性、泛型作业

//(数据库)实体类基类 public class BaseModel { public int Id { get; set; } } //用户类 public class User : BaseModel { [ChinaName("姓名"),Length(5,10)] public string Name { get; set; } public string Account { get; set; } [ChinaName("密码")] public string Password { get; set; } [ChinaName("邮箱")] public string Email { get; set; } public string Mobile { get; set; } public int CompanyId { get; set; } public string CompanyName { get; set; } //public int State { get; set; } [Column("State"),ChinaName("状态")] public int Status { get; set; } public int UserType { get; set; } public DateTime? LastLoginTime { get; set; } public DateTime CreateTime { get; set; } public int CreatorId { get; set; } public int LastModifierId { get; set; } public DateTime LastModifyTime { get; set; } } //公司类 public class Company : BaseModel { public string Name { get; set; } public DateTime CreateTime { get; set; } public int CreatorId { get; set; } public int? LastModifierId { get; set; }//可空 public DateTime LastModifyTime { get; set; } }

/// <summary> /// 静态常量类 /// </summary> public class StaticConstant { /// <summary> /// sqlServer数据库连接字符串 /// </summary> public static string SqlServerConnString = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["Customers"].ConnectionString; private static string DALTypeDll = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["DALTypeDLL"]; /// <summary> /// Dll名称(命名空间) /// </summary> public static string DAlDllName = DALTypeDll.Split(',')[0]; /// <summary> /// 类型名称 /// </summary> public static string DALTypeName = DALTypeDll.Split(',')[1]; }

/// <summary> /// 仅修饰属性的特性:列名 /// </summary> [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property)] public class ColumnAttribute:Attribute { public ColumnAttribute(string name) { _name = name; } private string _name = null; public string GetColumnName() { return _name; } } //中文名特性 public class ChinaNameAttribute:Attribute { public ChinaNameAttribute(string name) { _name = name; } private string _name = null; public string GetChinaName() { return _name; } }

//抽象特性类 public abstract class AbstractValidateAttribute : Attribute { //抽象特性类的抽象方法 public abstract bool Validate(object value); } //Email验证特性 [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property | AttributeTargets.Field)] public class EmailAttribute : AbstractValidateAttribute { public override bool Validate(object oValue) { return oValue != null && Regex.IsMatch(oValue.ToString(), @"^\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*$"); } } //长度验证特性 [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property | AttributeTargets.Field)] public class LengthAttribute : AbstractValidateAttribute { private int _min = 0; private int _max = 0; public LengthAttribute(int min, int max) { _min = min; _max = max; } public override bool Validate(object value) { if (value != null && !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value.ToString())) { int length = value.ToString().Length; if (length >= _min && length <= _max) { return true; } } return false; } } //数值范围验证特性 [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property | AttributeTargets.Field)] public class LongAttribute : AbstractValidateAttribute { private long _min = 0; private long _max = 0; public LongAttribute(long min, long max) { _min = min; _max = max; } public override bool Validate(object value) { if (value != null && !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value.ToString())) { long result = 0; if (long.TryParse(value.ToString(), out result)) { if (result >= _min && result <= _max) { return true; } } } return false; } } //电话验证特性 [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property | AttributeTargets.Field)] public class MobileAttribute : AbstractValidateAttribute { public override bool Validate(object oValue) { return oValue != null && Regex.IsMatch(oValue.ToString(), @"^[1]+[3,5]+\d{9}"); } } //正则表达式验证特性 [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property | AttributeTargets.Field)] public class RegexAttribute : AbstractValidateAttribute { private string _RegexExpression = string.Empty; public RegexAttribute(string regex) { this._RegexExpression = regex; } public override bool Validate(object oValue) { return oValue != null && Regex.IsMatch(oValue.ToString(), _RegexExpression); } }

public static class AttributeHelper { /// <summary> /// 判断该属性是否使用Column特性,如果使用Column特性,就返回特性指定的列名,如果未使用,就直接返回列名 /// </summary> /// <param name="prop"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static string GetColumnName(this PropertyInfo prop) { if (prop.IsDefined(typeof(ColumnAttribute), true)) { ColumnAttribute attribute = (ColumnAttribute)prop.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(ColumnAttribute), true); return attribute.GetColumnName(); } else { return prop.Name; } } //中文名 public static string GetChinaName(this PropertyInfo prop) { if (prop.IsDefined(typeof(ChinaNameAttribute), true)) { ChinaNameAttribute attribute = (ChinaNameAttribute)prop.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(ChinaNameAttribute), true); return attribute.GetChinaName(); } else { return prop.Name; } } public static bool Validate<T>(this T t) where T : BaseModel { Type type = t.GetType(); foreach (PropertyInfo info in type.GetProperties()) {//通过反射遍历所有的属性 if (info.IsDefined(typeof(AbstractValidateAttribute), true)) {//判断是否有配置该特性的属性 //如果有配置该特性的属性,得到该属性所有的AbstractValidateAttribute特性 object[] attributeArray = info.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AbstractValidateAttribute), true); foreach (AbstractValidateAttribute attribute in attributeArray)//在这一步转换的 {//遍历所有的特性 if (!attribute.Validate(info.GetValue(t))) {//检测该方法,判断该值 return false; //throw new Exception($"{info.Name}的值{info.GetValue(t)}设置不正确");//throw与return二选一 } } } } return true; } }

public interface IBaseDAL { //查询Id T Find<T>(int id) where T : BaseModel; //查询列表 List<T> FindAll<T>() where T : BaseModel; //更新实体 void Update<T>(T t) where T : BaseModel; //实体删除 void Delete<T>(T t) where T : BaseModel; //Id删除 void Delete<T>(int id) where T : BaseModel; //插入实体 void Insert<T>(T t) where T : BaseModel; }

//实现接口的类 public class BaseDAL: IBaseDAL { // 泛型访问数据库的方法,用BaseModel约束 // 用id去查询单个实体 public T Find<T>(int id) where T : BaseModel { string sql = $"{TSqlHelper<T>._findSql}{id}"; List<T> listT = new List<T>(); using (SqlConnection conn=new SqlConnection(StaticConstant.SqlServerConnString)) { SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, conn); conn.Open(); SqlDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader(); listT = ReaderToList<T>(reader); } return listT.FirstOrDefault(); } // 泛型访问数据库的方法,用BaseModel约束 // 查询出所有数据表的全部数据列表 public List<T> FindAll<T>() where T : BaseModel { string sql = $"{TSqlHelper<T>._findAllSql}"; List<T> listT = new List<T>(); using (SqlConnection conn=new SqlConnection(StaticConstant.SqlServerConnString)) { SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, conn); conn.Open(); SqlDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader(); listT = ReaderToList<T>(reader); } return listT; } /// <summary> /// 显示中文名 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> public static void ShowChinaName<T>() { Type type = typeof(T); foreach (PropertyInfo prop in type.GetProperties()) { if (prop.IsDefined(typeof(ChinaNameAttribute), true)) { ChinaNameAttribute attribute = (ChinaNameAttribute)prop.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(ChinaNameAttribute), true); Console.WriteLine($"属性:[{prop.Name}] 中文名:[{attribute.GetChinaName()}]"); } else { Console.WriteLine($"属性:[{prop.Name}] 中文名:[null]"); } } } //更新实体 public void Update<T>(T t) where T : BaseModel { if (!t.Validate<T>())//在这里使用特性进行验证 { throw new Exception("数据不正确"); } Type type = typeof(T); var props = type.GetProperties().Where(p => !p.Name.Equals("Id")); string columns = string.Join(",", props.Select(p => $"[{p.GetColumnName()}]=@{p.GetColumnName()}")); var paras = props.Select(p => new SqlParameter($"@{p.GetColumnName()}", p.GetValue(t) ?? DBNull.Value)).ToArray(); //必须参数化 否则引号? 或者值里面还有引号 string sql = $"update [{type.Name}] set {columns} where Id={t.Id}"; using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(StaticConstant.SqlServerConnString)) { SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, conn); cmd.Parameters.AddRange(paras); conn.Open(); int result = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery(); if (result==0) { throw new Exception("更新失败,Update数据不存在"); } } } //实体删除 public void Delete<T>(T t) where T : BaseModel { string sql = $"{TSqlHelper<T>._deleteSql}{t.Id}"; using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(StaticConstant.SqlServerConnString)) { SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, conn); conn.Open(); int result = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery(); if (result == 0) { throw new Exception("删除失败,Delete数据不存在"); } } } //Id删除 public void Delete<T>(int id) where T : BaseModel { string sql = $"{TSqlHelper<T>._deleteSql}{id}"; using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(StaticConstant.SqlServerConnString)) { SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, conn); conn.Open(); int result = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery(); if (result == 0) { throw new Exception("删除失败,Delete数据不存在"); } } } //插入实体 public void Insert<T>(T t) where T : BaseModel { Type type = typeof(T); var props = type.GetProperties().Where(p => !p.Name.Equals("Id")); string columns = string.Join(",", props.Select(p => $"[{p.GetColumnName()}]")); string values = string.Join(",", props.Select(p => $"@{p.GetColumnName()}")); var paras = props.Select(p => new SqlParameter($"@{p.GetColumnName()}", p.GetValue(t) ?? DBNull.Value)).ToArray(); //必须参数化 否则引号? 或者值里面还有引号 string sql = $"insert into [{type.Name}] ({columns}) values ({values})"; using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(StaticConstant.SqlServerConnString)) { SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, conn); cmd.Parameters.AddRange(paras); conn.Open(); int result = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery(); if (result == 0) { throw new Exception("插入失败,Insert数据不存在"); } } } #region 封装的方法 // 查询一个SqlDataReaser的List集 private List<T> ReaderToList<T>(SqlDataReader reader) where T : BaseModel { Type type = typeof(T); List<T> listT = new List<T>(); while (reader.Read()) { //这里得t必须声明在while{}中,如果不是,相当于只声明了一个t,后面每一个t都是对前一个重新赋值。 T t = (T)Activator.CreateInstance(type); foreach (PropertyInfo prop in type.GetProperties()) { object obj = reader[prop.GetColumnName()]; if (obj is DBNull) { obj = null; } prop.SetValue(t, obj); } listT.Add(t); } return listT; } #endregion }

//泛型静态缓存 //可以理解这个类就是管理Sql语句的,因为发现sql语句有很多类似的地方,所以在此利用泛型进行了一些封装 //但是在实际封装之后发现封装的并不尽人意,查询和更新与插入是不一样的,更新与插入需要参数化 //即使这里封装了,但在引用的时候还是要再次使用type.GetProperties(); //最终决定能缓存就缓存,不能缓存就算了,所以就果断删除_insertSql和_updateSql public class TSqlHelper<T> where T : BaseModel { public static string _findSql = null; public static string _findAllSql = null; public static string _deleteSql = null; //public static string _updateSql = null; //public static string _insertSql = null; static TSqlHelper() { Type type = typeof(T); //删除仅需要类型 _deleteSql = $"delete from {type.Name} where Id="; //查询需要Id var props = type.GetProperties(); string columns = string.Join(",", props.Select(p => $"[{p.GetColumnName()}]")); _findSql = $"select {columns} from [{type.Name}] where Id="; _findAllSql= $"select {columns} from [{type.Name}]"; //更新与插入不需要Id //var propsNonId = type.GetProperties().Where(p => !p.Name.Equals("Id")); //string columns0 = string.Join(",", propsNonId.Select(p => $"[{p.GetColumnName()}]=@{p.GetColumnName()}")); //string columns1 = string.Join(",", propsNonId.Select(p => $"[{p.GetColumnName()}]")); //string values = string.Join(",", propsNonId.Select(p => $"@{p.GetColumnName()}")); //_updateSql = $"update [{type.Name}] set {columns0} where Id="; //_insertSql = $"insert into [{type.Name}] ({columns1}) values ({values})"; } }

//简单工厂+配置文件+反射 public class DALFactory { static DALFactory() { Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load(StaticConstant.DAlDllName); DALType = assembly.GetType(StaticConstant.DALTypeName); } private static Type DALType = null; public static IBaseDAL CreateInstance() { return (IBaseDAL)Activator.CreateInstance(DALType); } }

/* 仔细分析增删改查方法,发现有很多重复代码,步骤细分如下 * 【1】连接对象【2】Command对象【3】打开连接【4】个别需要添加参数【5】执行增删改方法【6】返回一个结果 * 考虑使用泛型解耦,先说不同的地方,每个Command对象的sql语句不同,增删改方法不同,返回结果不同 * 返回结果不同考虑使用泛型,带返回值的委托,微软已经给我们定义好了——>>Func * 代码如下:需要注意的一个地方Command对象 */ public T ExecSQL<T>(string sql, Func<SqlCommand, T> func) { using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(StaticConstant.SqlServerConnString)) { using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, conn)) { try { conn.Open(); T t = func.Invoke(cmd); return t; } catch (Exception) { throw; } } } } private T ExcuteSql<T>(string sql, Func<SqlCommand, T> func) { using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(StaticConstant.SqlServerConnString)) { using (SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(sql, conn)) { conn.Open(); SqlTransaction sqlTransaction = conn.BeginTransaction(); try { command.Transaction = sqlTransaction; T tResult = func.Invoke(command); sqlTransaction.Commit(); return tResult; } catch (Exception ex) { sqlTransaction.Rollback(); throw ex; } } } } public T Find<T>(int id) where T : BaseModel { Type type = typeof(T); string sql = $"{TSqlHelper<T>.FindSql}{id};"; Func<SqlCommand, T> func = new Func<SqlCommand, T>(command => { SqlDataReader reader = command.ExecuteReader(); List<T> list = this.ReaderToList<T>(reader); T tnew = list.FirstOrDefault(); return tnew; }); T t = ExecSQL<T>(sql, func); return t; } public List<T> FindAll<T>() where T : BaseModel { Type type = typeof(T); string sql = TSqlHelper<T>.FindAllSql; List<T> list = new List<T>(); Func<SqlCommand, List<T>> func = (command => { SqlDataReader reader = command.ExecuteReader(); list = this.ReaderToList<T>(reader); return list; }); list = ExecSQL<List<T>>(sql, func); return list; } public void Update<T>(T t) where T : BaseModel { Type type = typeof(T); var propArray = type.GetProperties().Where(p => !p.Name.Equals("Id")); string columnString = string.Join(",", propArray.Select(p => $"[{p.GetColumnName()}]=@{p.GetColumnName()}")); var parameters = propArray.Select(p => new SqlParameter($"@{p.GetColumnName()}", p.GetValue(t) ?? DBNull.Value)).ToArray(); string sql = $"UPDATE [{type.Name}] SET {columnString} WHERE Id={t.Id}"; Func<SqlCommand, int> func = (command => { command.Parameters.AddRange(parameters); int iResult = command.ExecuteNonQuery(); return iResult; }); int result = ExecSQL<int>(sql, func); if (result==0) { throw new Exception("Update数据不存在"); } }




