linux 下c语言的pwd 实现
20155211实现mypwd
关于pwd
在Linux层次结构中,用户可以在被授权的任意目录下利用mkdir命令创建新目录,也可以利用cd命令从一个目录转换到另一个目录。然而,没有提示符来告知用户目前处于哪一个目录中。想要知道当前所处的目录,可以用pwd命令,该命令显示整个路径名。
- -L
如果 PWD 环境变量包含了不包含文件名 .(点)或 ..(点点)的当前目录的绝对路径名,则显示 PWD 环境变量的值。否则,-L 标志与 -P 标志一样运行。 - -P
显示当前目录的绝对路径名。与 -P 标志一起显示的绝对路径不包含在路径名的绝对路径中涉及到符号链接类型的文件的名称。
退出状态 - 该命令返回以下出口值:
0 成功完成。 >0 发生错误。

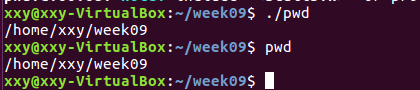
pwd实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <pwd.h>
ino_t get_inode(char *);
void printpathto(ino_t);
void inum_to_name(ino_t, char *, int);
int main() {
printpathto(get_inode(".")); /* print path to here */
putchar('\n'); /* then add newline */
return 0;
}
/*
* prints path leading down to an object with this inode
* kind of recursive
*/
void printpathto(ino_t this_inode) {
ino_t my_inode;
char its_name[BUFSIZ];
if (get_inode("..") != this_inode) {
chdir(".."); /* up one dir */
inum_to_name(this_inode, its_name, BUFSIZ);/* get its name*/
my_inode = get_inode("."); /* print head */
printpathto(my_inode); /* recursively */
printf("/%s", its_name); /* now print name of this */
}
}
void inum_to_name(ino_t inode_to_find, char *namebuf, int buflen) {
DIR *dir_ptr; /* the directory */
struct dirent *direntp; /* each entry */
dir_ptr = opendir(".");
if (dir_ptr == NULL) {
perror(".");
exit(1);
}/* search directory for a file with specified inum */
while ((direntp = readdir(dir_ptr)) != NULL)
if (direntp->d_ino == inode_to_find) {
strncpy(namebuf, direntp->d_name, buflen);
namebuf[buflen - 1] = '\0'; /* just in case */
closedir(dir_ptr);
return;
}
fprintf(stderr, "error looking for inum %d\n", inode_to_find);
exit(1);
}
/*
* returns inode number of the file
*/
ino_t get_inode(char *fname) {
struct stat info;
if (stat(fname, &info) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot stat ");
perror(fname);
return 1;
}
return info.st_ino;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步