java 集合系列目录:
Java 集合系列 03 ArrayList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 04 LinkedList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 05 Vector详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 06 Stack详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 07 List总结(LinkedList, ArrayList等使用场景和性能分析)
Java 集合系列 09 HashMap详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 10 Hashtable详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 11 hashmap 和 hashtable 的区别
概述
第1部分 WeakHashMap介绍
WeakHashMap简介
WeakHashMap 继承于AbstractMap,实现了Map接口。
和HashMap一样,WeakHashMap 也是一个散列表,它存储的内容也是键值对(key-value)映射,而且键和值都可以是null。
不过WeakHashMap的键是“弱键”。在 WeakHashMap 中,当某个键不再正常使用时,会被从WeakHashMap中被自动移除。更精确地说,对于一个给定的键,其映射的存在并不阻止垃圾回收器对该键的丢弃,这就使该键成为可终止的,被终止,然后被回收。某个键被终止时,它对应的键值对也就从映射中有效地移除了。
这个“弱键”的原理呢?大致上就是,通过WeakReference和ReferenceQueue实现的。 WeakHashMap的key是“弱键”,即是WeakReference类型的;ReferenceQueue是一个队列,它会保存被GC回收的“弱键”。实现步骤是:
(01) 新建WeakHashMap,将“键值对”添加到WeakHashMap中。
实际上,WeakHashMap是通过数组table保存Entry(键值对);每一个Entry实际上是一个单向链表,即Entry是键值对链表。
(02) 当某“弱键”不再被其它对象引用,并被GC回收时。在GC回收该“弱键”时,这个“弱键”也同时会被添加到ReferenceQueue(queue)队列中。
(03) 当下一次我们需要操作WeakHashMap时,会先同步table和queue。table中保存了全部的键值对,而queue中保存被GC回收的键值对;同步它们,就是删除table中被GC回收的键值对。
这就是“弱键”如何被自动从WeakHashMap中删除的步骤了。
和HashMap一样,WeakHashMap是不同步的。可以使用 Collections.synchronizedMap 方法来构造同步的 WeakHashMap。
WeakHashMap的构造函数
WeakHashMap共有4个构造函数,如下:
// 构造具有默认初始容量 (16) 和加载因子 (0.75) 的新的空 WeakHashMap() // 构造具有给定初始容量和默认加载因子 (0.75) 的新的空 WeakHashMap WeakHashMap(int capacity) // 用给定的初始容量和加载因子构造一个新的空 WeakHashMap WeakHashMap(int capacity, float loadFactor) // 包含“子Map”的构造函数 WeakHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)
WeakHashMap的API
void clear() 从此映射中移除所有映射关系。 boolean containsKey(Object key) 如果此映射对于指定的键包含映射关系,则返回 true。 boolean containsValue(Object value) 如果此映射将一个或多个键映射到指定值,则返回 true。 Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() 返回此映射所包含的映射关系的 Set 视图。 V get(Object key) 返回指定键所映射的值,如果对于该键来说,此映射不包含任何映射关系,则返回 null。 boolean isEmpty() 如果此映射不包含键-值映射关系,则返回 true。 Set<K> keySet() 返回此映射所包含的键的 Set 视图。 V put(K key, V value) 关联此映射中的指定值与指定键。 void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) 将指定映射的全部映射关系复制到此映射。 V remove(Object key) 从此弱哈希映射中移除键的映射关系(如果存在)。 int size() 返回该映射中的键-值映射关系的数目。 Collection<V> values() 返回此映射所包含的值的 Collection 视图。
第2部分 WeakHashMap数据结构
WeakHashMap的继承关系如下
java.lang.Object ↳ java.util.AbstractMap<K, V> ↳ java.util.WeakHashMap<K, V> public class WeakHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> {}
WeakHashMap与Map关系如下图:
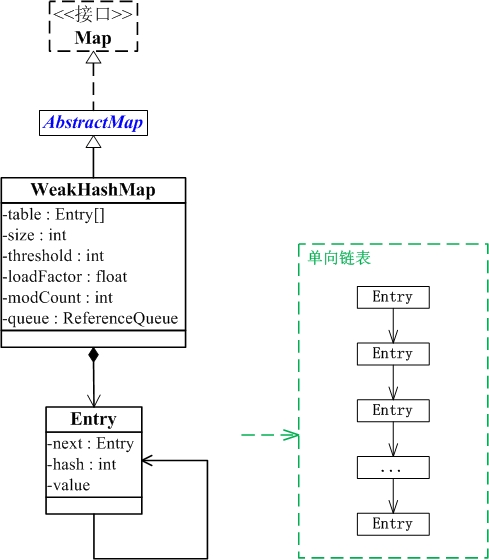
从图中可以看出:
(01) WeakHashMap继承于AbstractMap,并且实现了Map接口。
(02) WeakHashMap是哈希表,但是它的键是"弱键"。WeakHashMap中保护几个重要的成员变量:table, size, threshold, loadFactor,modCount, queue。
table是一个Entry[]数组类型,而Entry实际上就是一个单向链表。哈希表的"key-value键值对"都是存储在Entry数组中的。
size是Hashtable的大小,它是Hashtable保存的键值对的数量。
threshold是Hashtable的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整Hashtable的容量。threshold的值="容量*加载因子"。
loadFactor就是加载因子。
modCount是用来实现fail-fast机制的
queue保存的是“已被GC清除”的“弱引用的键”。
第3部分 WeakHashMap源码解析(基于JDK1.7.0_45)
1 public class WeakHashMap<K,V> 2 extends AbstractMap<K,V> 3 implements Map<K,V> { 4 5 // 默认的初始容量是16,必须是2的幂。 6 private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; 7 8 // 最大容量(必须是2的幂且小于2的30次方,传入容量过大将被这个值替换) 9 private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; 10 11 // 默认加载因子 12 private static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; 13 14 // 存储数据的Entry数组,长度是2的幂。 15 // WeakHashMap是采用拉链法实现的,每一个Entry本质上是一个单向链表 16 private Entry[] table; 17 18 // WeakHashMap的大小,它是WeakHashMap保存的键值对的数量 19 private int size; 20 21 // WeakHashMap的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整WeakHashMap的容量(threshold = 容量*加载因子) 22 private int threshold; 23 24 // 加载因子实际大小 25 private final float loadFactor; 26 27 // queue保存的是“已被GC清除”的“弱引用的键”。 28 // 弱引用和ReferenceQueue 是联合使用的:如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中 29 private final ReferenceQueue<K> queue = new ReferenceQueue<K>(); 30 31 // WeakHashMap被改变的次数 32 private volatile int modCount; 33 34 // 指定“容量大小”和“加载因子”的构造函数 35 public WeakHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { 36 if (initialCapacity < 0) 37 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Initial Capacity: "+ 38 initialCapacity); 39 // WeakHashMap的最大容量只能是MAXIMUM_CAPACITY 40 if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) 41 initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; 42 43 if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) 44 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load factor: "+ 45 loadFactor); 46 // 找出“大于initialCapacity”的最小的2的幂 47 int capacity = 1; 48 while (capacity < initialCapacity) 49 capacity <<= 1; 50 // 创建Entry数组,用来保存数据 51 table = new Entry[capacity]; 52 // 设置“加载因子” 53 this.loadFactor = loadFactor; 54 // 设置“WeakHashMap阈值”,当WeakHashMap中存储数据的数量达到threshold时,就需要将WeakHashMap的容量加倍。 55 threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor); 56 useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() && 57 (capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD); 58 } 59 60 // 指定“容量大小”的构造函数 61 public WeakHashMap(int initialCapacity) { 62 this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); 63 } 64 65 // 默认构造函数。 66 public WeakHashMap() { 67 this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; 68 threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); 69 table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY]; 70 } 71 72 // 包含“子Map”的构造函数 73 public WeakHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { 74 this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1, 16), 75 DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); 76 // 将m中的全部元素逐个添加到WeakHashMap中 77 putAll(m); 78 } 79 80 // 键为null的mask值。 81 // 因为WeakReference中允许“null的key”,若直接插入“null的key”,将其当作弱引用时,会被删除。 82 // 因此,这里对于“key为null”的清空,都统一替换为“key为NULL_KEY”,“NULL_KEY”是“静态的final常量”。 83 private static final Object NULL_KEY = new Object(); 84 85 // 对“null的key”进行特殊处理 86 private static Object maskNull(Object key) { 87 return (key == null ? NULL_KEY : key); 88 } 89 90 // 还原对“null的key”的特殊处理 91 private static <K> K unmaskNull(Object key) { 92 return (K) (key == NULL_KEY ? null : key); 93 } 94 95 // 判断“x”和“y”是否相等 96 static boolean eq(Object x, Object y) { 97 return x == y || x.equals(y); 98 } 99 100 // 返回索引值 101 // h & (length-1)保证返回值的小于length 102 static int indexFor(int h, int length) { 103 return h & (length-1); 104 } 105 106 // 清空table中无用键值对。原理如下: 107 // (01) 当WeakHashMap中某个“弱引用的key”由于没有再被引用而被GC收回时, 108 // 被回收的“该弱引用key”也被会被添加到"ReferenceQueue(queue)"中。 109 // (02) 当我们执行expungeStaleEntries时, 110 // 就遍历"ReferenceQueue(queue)"中的所有key 111 // 然后就在“WeakReference的table”中删除与“ReferenceQueue(queue)中key”对应的键值对 112 private void expungeStaleEntries() { 113 Entry<K,V> e; 114 while ( (e = (Entry<K,V>) queue.poll()) != null) { 115 int h = e.hash; 116 int i = indexFor(h, table.length); 117 118 Entry<K,V> prev = table[i]; 119 Entry<K,V> p = prev; 120 while (p != null) { 121 Entry<K,V> next = p.next; 122 if (p == e) { 123 if (prev == e) 124 table[i] = next; 125 else 126 prev.next = next; 127 e.next = null; // Help GC 128 e.value = null; // " " 129 size--; 130 break; 131 } 132 prev = p; 133 p = next; 134 } 135 } 136 } 137 138 // 获取WeakHashMap的table(存放键值对的数组) 139 private Entry[] getTable() { 140 // 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对” 141 expungeStaleEntries(); 142 return table; 143 } 144 145 // 获取WeakHashMap的实际大小 146 public int size() { 147 if (size == 0) 148 return 0; 149 // 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对” 150 expungeStaleEntries(); 151 return size; 152 } 153 154 public boolean isEmpty() { 155 return size() == 0; 156 } 157 158 // 获取key对应的value 159 public V get(Object key) { 160 Object k = maskNull(key); 161 // 获取key的hash值。 162 int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode()); 163 Entry[] tab = getTable(); 164 int index = indexFor(h, tab.length); 165 Entry<K,V> e = tab[index]; 166 // 在“该hash值对应的链表”上查找“键值等于key”的元素 167 while (e != null) { 168 if (e.hash == h && eq(k, e.get())) 169 return e.value; 170 e = e.next; 171 } 172 return null; 173 } 174 175 // WeakHashMap是否包含key 176 public boolean containsKey(Object key) { 177 return getEntry(key) != null; 178 } 179 180 // 返回“键为key”的键值对 181 Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { 182 Object k = maskNull(key); 183 int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode()); 184 Entry[] tab = getTable(); 185 int index = indexFor(h, tab.length); 186 Entry<K,V> e = tab[index]; 187 while (e != null && !(e.hash == h && eq(k, e.get()))) 188 e = e.next; 189 return e; 190 } 191 192 // 将“key-value”添加到WeakHashMap中 193 public V put(K key, V value) { 194 K k = (K) maskNull(key); 195 int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode()); 196 Entry[] tab = getTable(); 197 int i = indexFor(h, tab.length); 198 199 for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { 200 // 若“该key”对应的键值对已经存在,则用新的value取代旧的value。然后退出! 201 if (h == e.hash && eq(k, e.get())) { 202 V oldValue = e.value; 203 if (value != oldValue) 204 e.value = value; 205 return oldValue; 206 } 207 } 208 209 // 若“该key”对应的键值对不存在于WeakHashMap中,则将“key-value”添加到table中 210 modCount++; 211 Entry<K,V> e = tab[i]; 212 tab[i] = new Entry<K,V>(k, value, queue, h, e); 213 if (++size >= threshold) 214 resize(tab.length * 2); 215 return null; 216 } 217 218 // 重新调整WeakHashMap的大小,newCapacity是调整后的单位 219 void resize(int newCapacity) { 220 Entry[] oldTable = getTable(); 221 int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; 222 if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { 223 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 224 return; 225 } 226 227 // 新建一个newTable,将“旧的table”的全部元素添加到“新的newTable”中, 228 // 然后,将“新的newTable”赋值给“旧的table”。 229 Entry<K,V>[] newTable = newTable(newCapacity); 230 boolean oldAltHashing = useAltHashing; 231 useAltHashing |= sun.misc.VM.isBooted() && 232 (newCapacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD); 233 boolean rehash = oldAltHashing ^ useAltHashing; 234 transfer(oldTable, newTable, rehash); 235 table = newTable; 236 237 if (size >= threshold / 2) { 238 threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor); 239 } else { 240 // 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对” 241 expungeStaleEntries(); 242 transfer(newTable, oldTable); 243 table = oldTable; 244 } 245 } 246 247 // 将WeakHashMap中的全部元素都添加到newTable中 248 private void transfer(Entry[] src, Entry[] dest) { 249 for (int j = 0; j < src.length; ++j) { 250 Entry<K,V> e = src[j]; 251 src[j] = null; 252 while (e != null) { 253 Entry<K,V> next = e.next; 254 Object key = e.get(); 255 if (key == null) { 256 e.next = null; // Help GC 257 e.value = null; // " " 258 size--; 259 } else { 260 int i = indexFor(e.hash, dest.length); 261 e.next = dest[i]; 262 dest[i] = e; 263 } 264 e = next; 265 } 266 } 267 } 268 269 // 将"m"的全部元素都添加到WeakHashMap中 270 public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { 271 int numKeysToBeAdded = m.size(); 272 if (numKeysToBeAdded == 0) 273 return; 274 275 // 计算容量是否足够, 276 // 若“当前实际容量 < 需要的容量”,则将容量x2。 277 if (numKeysToBeAdded > threshold) { 278 int targetCapacity = (int)(numKeysToBeAdded / loadFactor + 1); 279 if (targetCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) 280 targetCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; 281 int newCapacity = table.length; 282 while (newCapacity < targetCapacity) 283 newCapacity <<= 1; 284 if (newCapacity > table.length) 285 resize(newCapacity); 286 } 287 288 // 将“m”中的元素逐个添加到WeakHashMap中。 289 for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) 290 put(e.getKey(), e.getValue()); 291 } 292 293 // 删除“键为key”元素 294 public V remove(Object key) { 295 Object k = maskNull(key); 296 // 获取哈希值。 297 int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode()); 298 Entry[] tab = getTable(); 299 int i = indexFor(h, tab.length); 300 Entry<K,V> prev = tab[i]; 301 Entry<K,V> e = prev; 302 303 // 删除链表中“键为key”的元素 304 // 本质是“删除单向链表中的节点” 305 while (e != null) { 306 Entry<K,V> next = e.next; 307 if (h == e.hash && eq(k, e.get())) { 308 modCount++; 309 size--; 310 if (prev == e) 311 tab[i] = next; 312 else 313 prev.next = next; 314 return e.value; 315 } 316 prev = e; 317 e = next; 318 } 319 320 return null; 321 } 322 323 // 删除“键值对” 324 Entry<K,V> removeMapping(Object o) { 325 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) 326 return null; 327 Entry[] tab = getTable(); 328 Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)o; 329 Object k = maskNull(entry.getKey()); 330 int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode()); 331 int i = indexFor(h, tab.length); 332 Entry<K,V> prev = tab[i]; 333 Entry<K,V> e = prev; 334 335 // 删除链表中的“键值对e” 336 // 本质是“删除单向链表中的节点” 337 while (e != null) { 338 Entry<K,V> next = e.next; 339 if (h == e.hash && e.equals(entry)) { 340 modCount++; 341 size--; 342 if (prev == e) 343 tab[i] = next; 344 else 345 prev.next = next; 346 return e; 347 } 348 prev = e; 349 e = next; 350 } 351 352 return null; 353 } 354 355 // 清空WeakHashMap,将所有的元素设为null 356 public void clear() { 357 while (queue.poll() != null) 358 ; 359 360 modCount++; 361 Entry[] tab = table; 362 for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) 363 tab[i] = null; 364 size = 0; 365 366 while (queue.poll() != null) 367 ; 368 } 369 370 // 是否包含“值为value”的元素 371 public boolean containsValue(Object value) { 372 // 若“value为null”,则调用containsNullValue()查找 373 if (value==null) 374 return containsNullValue(); 375 376 // 若“value不为null”,则查找WeakHashMap中是否有值为value的节点。 377 Entry[] tab = getTable(); 378 for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;) 379 for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next) 380 if (value.equals(e.value)) 381 return true; 382 return false; 383 } 384 385 // 是否包含null值 386 private boolean containsNullValue() { 387 Entry[] tab = getTable(); 388 for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;) 389 for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next) 390 if (e.value==null) 391 return true; 392 return false; 393 } 394 395 // Entry是单向链表。 396 // 它是 “WeakHashMap链式存储法”对应的链表。 397 // 它实现了Map.Entry 接口,即实现getKey(), getValue(), setValue(V value), equals(Object o), hashCode()这些函数 398 private static class Entry<K,V> extends WeakReference<K> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { 399 private V value; 400 private final int hash; 401 // 指向下一个节点 402 private Entry<K,V> next; 403 404 // 构造函数。 405 Entry(K key, V value, 406 ReferenceQueue<K> queue, 407 int hash, Entry<K,V> next) { 408 super(key, queue); 409 this.value = value; 410 this.hash = hash; 411 this.next = next; 412 } 413 414 public K getKey() { 415 return WeakHashMap.<K>unmaskNull(get()); 416 } 417 418 public V getValue() { 419 return value; 420 } 421 422 public V setValue(V newValue) { 423 V oldValue = value; 424 value = newValue; 425 return oldValue; 426 } 427 428 // 判断两个Entry是否相等 429 // 若两个Entry的“key”和“value”都相等,则返回true。 430 // 否则,返回false 431 public boolean equals(Object o) { 432 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) 433 return false; 434 Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o; 435 Object k1 = getKey(); 436 Object k2 = e.getKey(); 437 if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) { 438 Object v1 = getValue(); 439 Object v2 = e.getValue(); 440 if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2))) 441 return true; 442 } 443 return false; 444 } 445 446 // 实现hashCode() 447 public int hashCode() { 448 Object k = getKey(); 449 Object v = getValue(); 450 return ((k==null ? 0 : k.hashCode()) ^ 451 (v==null ? 0 : v.hashCode())); 452 } 453 454 public String toString() { 455 return getKey() + "=" + getValue(); 456 } 457 } 458 459 // HashIterator是WeakHashMap迭代器的抽象出来的父类,实现了公共了函数。 460 // 它包含“key迭代器(KeyIterator)”、“Value迭代器(ValueIterator)”和“Entry迭代器(EntryIterator)”3个子类。 461 private abstract class HashIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> { 462 // 当前索引 463 int index; 464 // 当前元素 465 Entry<K,V> entry = null; 466 // 上一次返回元素 467 Entry<K,V> lastReturned = null; 468 // expectedModCount用于实现fast-fail机制。 469 int expectedModCount = modCount; 470 471 // 下一个键(强引用) 472 Object nextKey = null; 473 474 // 当前键(强引用) 475 Object currentKey = null; 476 477 // 构造函数 478 HashIterator() { 479 index = (size() != 0 ? table.length : 0); 480 } 481 482 // 是否存在下一个元素 483 public boolean hasNext() { 484 Entry[] t = table; 485 486 // 一个Entry就是一个单向链表 487 // 若该Entry的下一个节点不为空,就将next指向下一个节点; 488 // 否则,将next指向下一个链表(也是下一个Entry)的不为null的节点。 489 while (nextKey == null) { 490 Entry<K,V> e = entry; 491 int i = index; 492 while (e == null && i > 0) 493 e = t[--i]; 494 entry = e; 495 index = i; 496 if (e == null) { 497 currentKey = null; 498 return false; 499 } 500 nextKey = e.get(); // hold on to key in strong ref 501 if (nextKey == null) 502 entry = entry.next; 503 } 504 return true; 505 } 506 507 // 获取下一个元素 508 protected Entry<K,V> nextEntry() { 509 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 510 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 511 if (nextKey == null && !hasNext()) 512 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 513 514 lastReturned = entry; 515 entry = entry.next; 516 currentKey = nextKey; 517 nextKey = null; 518 return lastReturned; 519 } 520 521 // 删除当前元素 522 public void remove() { 523 if (lastReturned == null) 524 throw new IllegalStateException(); 525 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 526 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 527 528 WeakHashMap.this.remove(currentKey); 529 expectedModCount = modCount; 530 lastReturned = null; 531 currentKey = null; 532 } 533 534 } 535 536 // value的迭代器 537 private class ValueIterator extends HashIterator<V> { 538 public V next() { 539 return nextEntry().value; 540 } 541 } 542 543 // key的迭代器 544 private class KeyIterator extends HashIterator<K> { 545 public K next() { 546 return nextEntry().getKey(); 547 } 548 } 549 550 // Entry的迭代器 551 private class EntryIterator extends HashIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> { 552 public Map.Entry<K,V> next() { 553 return nextEntry(); 554 } 555 } 556 557 // WeakHashMap的Entry对应的集合 558 private transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet = null; 559 560 // 返回“key的集合”,实际上返回一个“KeySet对象” 561 public Set<K> keySet() { 562 Set<K> ks = keySet; 563 return (ks != null ? ks : (keySet = new KeySet())); 564 } 565 566 // Key对应的集合 567 // KeySet继承于AbstractSet,说明该集合中没有重复的Key。 568 private class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> { 569 public Iterator<K> iterator() { 570 return new KeyIterator(); 571 } 572 573 public int size() { 574 return WeakHashMap.this.size(); 575 } 576 577 public boolean contains(Object o) { 578 return containsKey(o); 579 } 580 581 public boolean remove(Object o) { 582 if (containsKey(o)) { 583 WeakHashMap.this.remove(o); 584 return true; 585 } 586 else 587 return false; 588 } 589 590 public void clear() { 591 WeakHashMap.this.clear(); 592 } 593 } 594 595 // 返回“value集合”,实际上返回的是一个Values对象 596 public Collection<V> values() { 597 Collection<V> vs = values; 598 return (vs != null ? vs : (values = new Values())); 599 } 600 601 // “value集合” 602 // Values继承于AbstractCollection,不同于“KeySet继承于AbstractSet”, 603 // Values中的元素能够重复。因为不同的key可以指向相同的value。 604 private class Values extends AbstractCollection<V> { 605 public Iterator<V> iterator() { 606 return new ValueIterator(); 607 } 608 609 public int size() { 610 return WeakHashMap.this.size(); 611 } 612 613 public boolean contains(Object o) { 614 return containsValue(o); 615 } 616 617 public void clear() { 618 WeakHashMap.this.clear(); 619 } 620 } 621 622 // 返回“WeakHashMap的Entry集合” 623 // 它实际是返回一个EntrySet对象 624 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { 625 Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es = entrySet; 626 return es != null ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet()); 627 } 628 629 // EntrySet对应的集合 630 // EntrySet继承于AbstractSet,说明该集合中没有重复的EntrySet。 631 private class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> { 632 public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() { 633 return new EntryIterator(); 634 } 635 636 // 是否包含“值(o)” 637 public boolean contains(Object o) { 638 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) 639 return false; 640 Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o; 641 Object k = e.getKey(); 642 Entry candidate = getEntry(e.getKey()); 643 return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e); 644 } 645 646 // 删除“值(o)” 647 public boolean remove(Object o) { 648 return removeMapping(o) != null; 649 } 650 651 // 返回WeakHashMap的大小 652 public int size() { 653 return WeakHashMap.this.size(); 654 } 655 656 // 清空WeakHashMap 657 public void clear() { 658 WeakHashMap.this.clear(); 659 } 660 661 // 拷贝函数。将WeakHashMap中的全部元素都拷贝到List中 662 private List<Map.Entry<K,V>> deepCopy() { 663 List<Map.Entry<K,V>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<K,V>>(size()); 664 for (Map.Entry<K,V> e : this) 665 list.add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<K,V>(e)); 666 return list; 667 } 668 669 // 返回Entry对应的Object[]数组 670 public Object[] toArray() { 671 return deepCopy().toArray(); 672 } 673 674 // 返回Entry对应的T[]数组(T[]我们新建数组时,定义的数组类型) 675 public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { 676 return deepCopy().toArray(a); 677 } 678 } 679 }
说明:WeakHashMap和HashMap都是通过"拉链法"实现的散列表。它们的源码绝大部分内容都一样,这里就只是对它们不同的部分就是说明。
WeakReference是“弱键”实现的哈希表。它这个“弱键”的目的就是:实现对“键值对”的动态回收。当“弱键”不再被使用到时,GC会回收它,WeakReference也会将“弱键”对应的键值对删除。
“弱键”是一个“弱引用(WeakReference)”,在Java中,WeakReference和ReferenceQueue 是联合使用的。在WeakHashMap中亦是如此:如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。 接着,WeakHashMap会根据“引用队列”,来删除“WeakHashMap中已被GC回收的‘弱键’对应的键值对”。
另外,理解上面思想的重点是通过 expungeStaleEntries() 函数去理解。
关于WeakHashMap怎么实现Weak,以及如何清理key和Entry,参考 深入WeakHashMap。
WeakHashMap自动释放失效的弱引用,是通过私有的expungeStaleEntries()方法,这个方法在大部分共有方法中被调用,参考 Java中的WeakHashMap实现分析




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步