前端学PHP之文件操作

前面的话
在程序运行时,程序本身和数据一般都存在内存中,当程序运行结束后,存放在内存中的数据被释放。如果需要长期保存程序运行所需的原始数据,或程序运行产生的结果,就需要把数据存储在文件或数据库。一般地,小型数据存储在文件中,海量数据存储在数据库中。本文主要介绍php中目录和文件的基本操作
文件类型
文件一般指存储在外部介质上具有名字(文件名)的一组相关数据集合。用文件可长期保存数据,并实现数据共享
PHP是以UNIX的文件系统为模型的。因此在Windows系统中我们只能获得”file”、”dir”或者“unknown”三种文件类型。而在UNIX系统中,我们可以获得block、char、dir、fifo、file、link和unknown七种类型
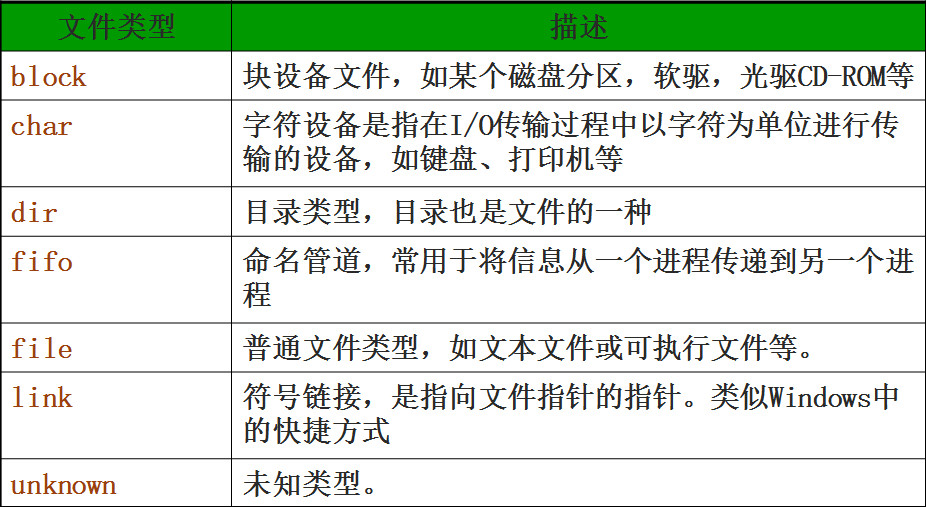
可以使用函数filetype()获取文件的具体类型,可能的值有fifo,char,dir,block,link,file 和 unknown
string filetype ( string filename )
如果出错则返回 FALSE。如果调用失败或者文件类型未知的话 filetype() 还会产生一个 E_NOTICE 消息
在服务器中新建一个目录test,并在目录中新建一个文件a.txt
<?php echo filetype('test/a.txt'); // file echo filetype('test/'); // dir echo filetype('test/b.txt'); // Warning: filetype(): Lstat failed for test/b.txt ?>
在这7种文件类型中,window系统常用的是'file'和'dir'这两种,它们配套的类型检测函数分别是is_dir( )和is_file( )
is_dir( )
判断给定文件名是否是一个目录。如果文件名存在并且是一个目录则返回 true,否则返回 false
bool is_dir(_name)
is_file( )
判断给定文件名是否为一个正常的文件,如果文件存在且为正常的文件则返回 true
bool is_file(_name)
<?php var_dump (is_file('test/a.txt')); //boolean true var_dump (is_dir('test/')); //boolean true ?>
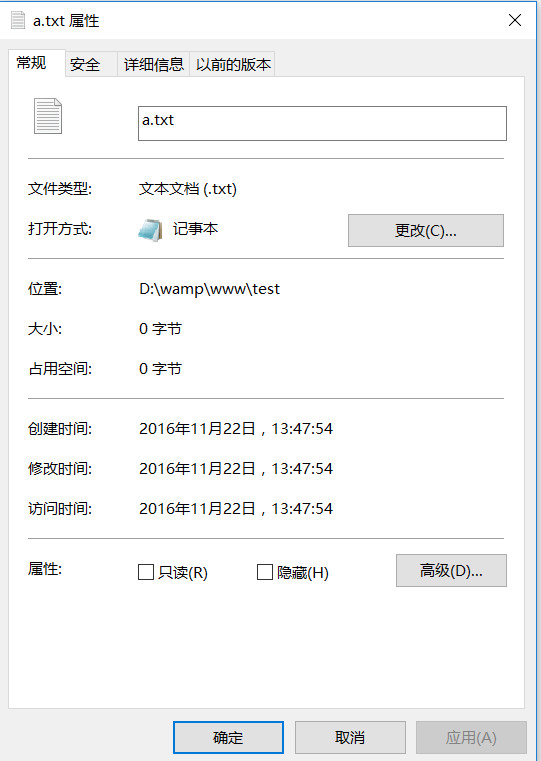
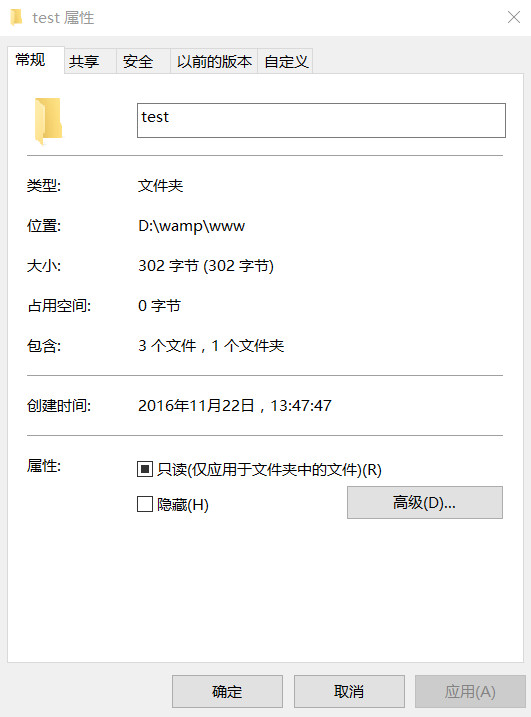
文件属性
一般地,在文件或目录右键菜单中,选择属性,即可查看文件的属性
下表中列出了php中关于文件属性的常用函数

<?php var_dump (file_exists('test/a.txt')); //boolean true var_dump (filesize('test/a.txt')); // int 0 var_dump (is_readable('test/a.txt')); //boolean true var_dump (is_writeable('test/a.txt')); //boolean true var_dump (is_executable('test/a.txt')); //boolean false var_dump (date("Y-m-d H:i:s",(filectime('test/a.txt'))));//string '2016-11-22 06:47:54' (length=19) var_dump (date("Y-m-d H:i:s",(filemtime('test/a.txt'))));//string '2016-11-22 06:47:54' (length=19) var_dump (date("Y-m-d H:i:s",(fileatime('test/a.txt'))));//string '2016-11-22 06:47:54' (length=19) ?>
目录路径
windows下的目录路径使用是正斜杠(\),而unix下的目录路径使用是反斜杠(/)
$unixPath="/var/www/html/index.php"; //在UNIX系统中的绝对路径,必须使用"/"分隔 $winPath="C:\\Appserv\\www\\index.php"; //在Windows系统的绝对路径,默认使用"\"分隔 $winPath2="C:/Appserv/www/index.php"; //在Windows系统中也可使用“/”分隔
因为在Windows系统中也可使用(/)分隔。所以,在PHP中,不论是什么操作系统,全部都使用反斜杠(/)代表路径分隔符号
在PHP中,还提供了一个常量DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR,以此来代表目录分隔符,但写起来较麻烦
<?php echo "c:".DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR."a".DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR."b".DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR."c"; //c:\a\b\c ?>
在windows下多个路径的分隔符使用分号(;)分隔,而unix下使用冒号(:)分隔
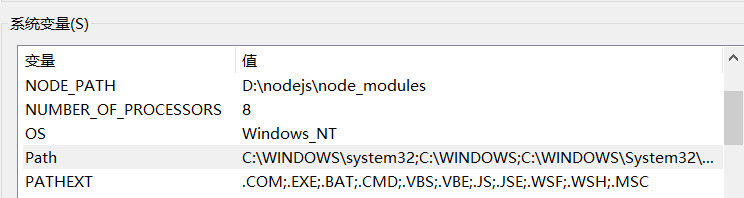
在PHP中,提供了一个常量PATH_SEPARATOR,用来在跨平台的情况下,表示多个路径之间的分隔符
<?php echo "aaa/ccc/ddd".PATH_SEPARATOR."/www/yyyy";//aaa/ccc/ddd;/www/yyyy ?>
换行
在window下,换行是\r\n,而在unix下,换行是\n。通常在写程序中,换行就以unix为准,写作\n
同样地,PHP提供了一个常量PHP_EOL,用来在跨平台的情况下,表示换行
.和..
在PHP中,.表示当前目录,..表示上一级目录
<?php var_dump (file_exists('test/a.txt'));//boolean true var_dump (file_exists('./test/a.txt'));//boolean true var_dump (file_exists('../www/test/a.txt'));//boolean true ?>
根路径
有两种根路径需要进行区分,一种是客户端根路径,一种是服务器根路径
以我自己在d盘安装的wamp为例,客户端根路径指'd:\wamp\www\',而服务器根路径为为'd:\'
<?php echo '<img src="/a.jpg">';//客户端根路径,相当于d:\wamp\www\a.jpg mkdir('/hello');//服务器根路径,相当于d:\hello ?>
路径解析函数
【basename()】
basename()函数用于返回路径中的文件名部分
<?php echo "1) ".basename("/etc/sudoers.d", ".d");//1) sudoers echo "2) ".basename("/etc/passwd").PHP_EOL;//2) passwd echo "3) ".basename("/etc/").PHP_EOL;//3) etc echo "4) ".basename(".").PHP_EOL;//4) . echo "5) ".basename("/");//5) ?>
【dirname()】
dirname()函数用于返回路径中的目录部分
<?php echo "1) " . dirname("/etc/passwd") . PHP_EOL; // 1) /etc echo "2) " . dirname("/etc/") . PHP_EOL; // 2) \ echo "3) " . dirname("."); // 3) . ?>
【pathinfo()】
pathinfo()函数用于返回文件路径的信息
<?php $path_parts = pathinfo('/www/htdocs/inc/lib.inc.php'); echo $path_parts['dirname'], "\n";// '/www/htdocs/inc' 目录名 echo $path_parts['basename'], "\n";// 'lib.inc.php' 文件名 echo $path_parts['extension'], "\n";// 'php' 文件后缀 echo $path_parts['filename'], "\n"; // 'lib.inc' 文件名不带后缀 ?>
【realpath()】
realpath()函数用于返回规范化的绝对路径名
在Windows上,realpath()会将unix风格的路径改成Windows风格的
<?php echo realpath('/wamp');// 'D:\wamp' ?>
目录遍历
glob()
glob()函数用于寻找与模式匹配的文件路径
array glob ( string $pattern [, int $flags = 0 ] )
在www目录下新建a.txt和b.txt文件
<?php foreach (glob("*.txt") as $filename) { //a.txt size 1050 b.txt size 73 echo "$filename size " . filesize($filename) . "\n"; } ?>
opendir()
opendir()函数用于打开目录句柄。如果成功则返回目录句柄的resource,失败则返回 FALSE
resource opendir ( string $path [, resource $context ] )
<?php var_dump(opendir('test'))//resource(3, stream) ?>
closedir()
closedir()函数用于关闭目录句柄
void closedir ([ resource $dir_handle ] )
参数dir_handle表示目录句柄的 resource,之前由 opendir()所打开的。如果目录句柄没有指定,那么会假定为是opendir()所打开的最后一个句柄
<?php $dir = opendir('test'); closedir($dir); ?>
readdir()
readdir()函数用于从目录句柄中读取条目,返回目录中下一个文件的文件名。文件名以在文件系统中的排序返回,失败时返回 FALSE
string readdir ([ resource $dir_handle ] )
在www目录下新建目录test,并在目录test下新建a.txt和b.txt文件
<?php $dir = opendir('test'); echo readdir($dir)."<br>";//. echo readdir($dir)."<br>";//.. echo readdir($dir)."<br>";//a.txt echo readdir($dir)."<br>";//b.txt echo readdir($dir)."<br>";// closedir($dir); ?>
在遍历目录时,每个目录的前两个返回值都是.和..,.代表当前目录,..代表上一级目录
所以,一般地,列出当前目录的所有文件并去掉 . 和 ..,常采用下面的代码
<?php if ($handle = opendir('test')) { while (false !== ($file = readdir($handle))) { if ($file != "." && $file != "..") { echo "$file\n"; } } closedir($handle); } ?>
接下来,在test目录下,新建一个目录in,并在in目录中新建文件c.txt。然后,目录和文件区分显示
[注意]通过is_dir()函数判断目录时,需要加入路径
<?php if ($handle = opendir('test')) { while (false !== ($file = readdir($handle))) { if ($file != "." && $file != "..") { $file = "test/".$file; if(is_dir($file)){ echo "目录:".$file."<br>"; }else{ echo "文件:".$file."<br>"; } } } closedir($handle); } /* 文件:test/a.txt 文件:test/b.txt 目录:test/in */ ?>
rewinddir()
rewinddir()函数用于倒回目录句柄,将参数dir_handle指定的目录流重置到目录的开头
void rewinddir ( resource $dir_handle )
如果不使用rewinddir()函数,则文件只能遍历一次
<?php if ($handle = opendir('test')) { while (false !== ($file = readdir($handle))) { if ($file != "." && $file != "..") { $file = "test/".$file; if(is_dir($file)){ echo "目录:".$file."<br>"; }else{ echo "文件:".$file."<br>"; } } } while (false !== ($file = readdir($handle))) { if ($file != "." && $file != "..") { $file = "test/".$file; if(is_dir($file)){ echo "目录:".$file."<br>"; }else{ echo "文件:".$file."<br>"; } } } closedir($handle); } /* 文件:test/a.txt 文件:test/b.txt 目录:test/in */ ?>
使用rewinddir()函数,可以把目录句柄返回到第一个文件,从而实现重新遍历
<?php if ($handle = opendir('test')) { while (false !== ($file = readdir($handle))) { if ($file != "." && $file != "..") { $file = "test/".$file; if(is_dir($file)){ echo "目录:".$file."<br>"; }else{ echo "文件:".$file."<br>"; } } } rewinddir($handle); while (false !== ($file = readdir($handle))) { if ($file != "." && $file != "..") { $file = "test/".$file; if(is_dir($file)){ echo "目录:".$file."<br>"; }else{ echo "文件:".$file."<br>"; } } } closedir($handle); } /* 文件:test/a.txt 文件:test/b.txt 目录:test/in 文件:test/a.txt 文件:test/b.txt 目录:test/in */ ?>
目录统计
disk_total_space()
disk_total_space()函数返回一个目录的磁盘总大小
float disk_total_space ( string $directory )
<?php $ds = disk_total_space("C:"); echo $ds."<br>";//126652637184 $ds = disk_total_space("D:"); echo $ds;//1000202240000 ?>
disk_free_space()
disk_free_space()函数返回目录中的可用空间
float disk_free_space ( string $directory )
<?php $ds = disk_free_space("C:"); echo $ds."<br>";//86087041024 $ds = disk_free_space("D:"); echo $ds;//481647472640 ?>
下面来统计在www文件夹下新建的test目录的个数
<?php $dirn = 0; //目录数 $filen = 0; //文件数 //统计一个目录下的文件和目录的个数 function getdirnum($file) { global $dirn; global $filen; $dir = opendir($file); while (false !== ($filename = readdir($dir))) { if($filename!="." && $filename !="..") { $filename = $file."/".$filename; //更新路径 if(is_dir($filename)) { $dirn++; getdirnum($filename); //递归,就可以查看所有子目录 } else { $filen++; } } } closedir($dir); } getdirnum("test"); echo "目录数为:{$dirn}<br>";//目录数为:1 echo "文件数为:{$filen}<br>";//文件数为:3 ?>
下面来统计在www文件夹下新建的test目录的大小
<?php //统计目录大小 function dirsize($file) { $size = 0; $dir = opendir($file); while(false !== ($filename = readdir($dir))) { if($filename!="." && $filename !="..") { $filename = $file."/".$filename; if(is_dir($filename)) { $size += dirsize($filename);//使用递归 } else { $size += filesize($filename); } } } closedir($dir); return $size; } echo "test目录大小为:".dirsize("test")."<br>";//test目录大小为:302 ?>
目录增删
mkdir()
mkdir()函数用于新建目录
bool mkdir ( string $pathname [, int $mode = 0777 [, bool $recursive = false [, resource $context ]]] )
rmdir()
rmdir()函数用于删除目录
bool rmdir ( string $dirname [, resource $context ] )
[注意]该目录必须是空的,而且要有相应的权限。失败时会产生一个 E_WARNING 级别的错误
unlink()
unlink()函数用于删除文件
bool unlink ( string $filename [, resource $context ] )
下面来清空test目录
<?php function deldir($dirname) { //如果是文件,直接删除即可 if(is_file($dirname)) { unlink($dirname); } $dir = opendir($dirname); while(FALSE !== ($filename = readdir($dir))) { if($filename !="." && $filename!="..") { $filename = $dirname."/".$filename; if(is_dir($filename)) { deldir($filename);//递归 }else { unlink($filename);//删除文件 } } } closedir($dir); if($dirname != 'test'){ rmdir($dirname);//删除目录 } } deldir("test"); ?>
目录复制
copy()
copy()函数用于拷贝文件
bool copy ( string $source , string $dest [, resource $context ] )
[注意]copy()函数不能用于复制目录
<?php $file = 'a.txt'; $newfile = 'a.bak'; copy($file, $newfile); ?>
rename()
rename()函数用于重命名一个文件或目录
bool rename ( string $oldname , string $newname [, resource $context ] )
[注意]rename()函数具有移动文件或目录的功能
下面把www目录下的test目录剪贴,命名为t,并移动到d盘目录下
<?php rename("test", "d:/t"); ?>
使用rename()只能实现剪切的操作,使用copy()只能复制文件。如果要复制目录,则需要使用循环和遍历
<?php /** * $dirsrc 原目录 * $dirto 目标目录 */ function copydir($dirsrc, $dirto) { //如果目录不存在,则新建一个目录 if(!file_exists($dirto)) { mkdir($dirto); } $dir = opendir($dirsrc); while(FALSE !== ($filename = readdir($dir))) { if($filename != "." && $filename !="..") { $srcfile = $dirsrc."/".$filename; //原文件 $tofile = $dirto."/".$filename; //目标文件 if(is_dir($srcfile)) { copydir($srcfile, $tofile); //递归处理所有子目录 }else{ copy($srcfile, $tofile);//复制文件 } } } } copydir("test", "d:/t"); ?>
文件操作
touch()
touch()函数用来设定文件的访问和修改时间。如果文件不存在,则会被创建。成功时返回 TRUE, 或者在失败时返回 FALSE
bool touch ( string $filename [, int $time = time() [, int $atime ]] )
参数filename表示要设定的文件名,time表示要设定的时间。如果没有提供参数 time 则会使用当前系统的时间;atime表示如果给出了这个参数,则给定文件的访问时间会被设为atime,否则会设置为time。如果没有给出这两个参数,则使用当前系统时间
<?php touch('abc.txt') ?>
copy()
copy()函数用于拷贝文件
bool copy ( string $source , string $dest [, resource $context ] )
[注意]copy()函数不能用于复制目录
<?php $file = 'a.txt'; $newfile = 'a.bak'; copy($file, $newfile); ?>
rename()
rename()函数用于重命名一个文件或目录
bool rename ( string $oldname , string $newname [, resource $context ] )
[注意]rename()函数具有移动文件或目录的功能
<?php rename("abc.txt", "d:/cba.txt"); ?>
unlink()
unlink()函数用于删除文件
bool unlink ( string $filename [, resource $context ] )
<?php unlink("d:/cba.txt"); ?>
文件内容
fopen()
fopen()函数用于打开文件或者URL,fopen()将 filename 指定的名字资源绑定到一个流上
[注意]如果文件不存在,将新建并打开文件
fopen('test.png',w);
fopen() 中 mode 的可能值列表
mode 说明 'r' 只读方式打开,将文件指针指向文件头。 'r+' 读写方式打开,将文件指针指向文件头。 'w' 写入方式打开,将文件指针指向文件头并将文件大小截为零。如果文件不存在则尝试创建之。 'w+' 读写方式打开,将文件指针指向文件头并将文件大小截为零。如果文件不存在则尝试创建之。 'a' 写入方式打开,将文件指针指向文件末尾。如果文件不存在则尝试创建之。 'a+' 读写方式打开,将文件指针指向文件末尾。如果文件不存在则尝试创建之。
<?php //使用绝对路径打开file.txt文件,选择只读模式,并返回资源$handle $handle = fopen("/home/rasmus/file.txt", "r"); //访问文档根目录下的文件,也以只读模式打开 $handle = fopen(“{$_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT']}/data/info.txt", "r"); //在 Windows 平台上,转义文件路径中的每个反斜线,或者用斜线, 以二进制和只写模式组合 $handle = fopen("c:\\data\\file.gif", "wb"); //使用相对路径打开file.txt文件,选择只读模式,并返回资源$handle $handle = fopen("../data/info.txt", "r"); //打开远程文件, 使用HTTP协议只能以只读的模式打开 $handle = fopen("http://www.example.com/", "r"); //使用FTP协议打开远程文件,如果FTP服务器可写,则可以以写的模式打开 $handle = fopen("ftp://user:password@example.com/somefile.txt", "w"); ?>
fclose()
fclose()函数用于关闭一个已打开的文件指针
bool fclose ( resource $handle )
<?php $handle = fopen('test/a.txt', 'r'); fclose($handle); ?>
fwrite()
fwrite()函数用于写入文件(可安全用于二进制文件),返回写入的字符数,出现错误时则返回 FALSE
int fwrite ( resource $handle , string $string [, int $length ] )
当打开方式为只读模式时,无法向文件写入字符
<?php $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'r'); echo fwrite($fp, '1');//0 echo "<br>"; echo fwrite($fp, '23');//0 echo "<br>"; fclose($fp); ?>
当打开方式为写模式时,可以向文件写入字符
<?php $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'w'); echo fwrite($fp, '1');//1 echo "<br>"; echo fwrite($fp, '23');//2 echo "<br>"; fclose($fp); /* 文件内容为123 */ ?>
当打开方式为追加模式时,将向文件的尾部追加新的字符
<?php $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'a'); echo fwrite($fp, '1');//1 echo "<br>"; echo fwrite($fp, '23');//2 echo "<br>"; fclose($fp); /* 刷新两次时,文件内容为123123 */ ?>
fgetc()
fgetc()函数用于从文件指针中读取字符
[注意]使用fgetc()函数时,需要在fopen()函数中使用读模式
string fgetc ( resource $handle )
<?php $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'r'); echo fgetc($fp);//1 echo fgetc($fp);//2 echo fgetc($fp);//3 fclose($fp); ?>
feof()
feof()函数用于测试文件指针是否到了文件结束的位置
bool feof ( resource $handle )
<?php $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'r'); while(!feof($fp)){ echo fgetc($fp);//123123 } fclose($fp); ?>
fgets()
fgets()函数用于从文件指针中读取一行
string fgets ( resource $handle [, int $length ] )
将test目录下的a.txt文件内容修改为
aa
bbb
<?php $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'r'); echo fgets($fp);//'aa' echo fgets($fp);//'bbb' echo fgets($fp);//'' fclose($fp); ?>
fread()
fread()函数用于读取文件(可安全用于二进制文件)。fread()从文件指针handle读取最多length个字节。该函数在读取了length个字节或到达了文件末尾(EOF)时将停止读取文件
string fread ( resource $handle , int $length )
<?php $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'r'); echo fread($fp,3);//'aa ' fclose($fp); $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'r'); echo fread($fp,filesize('test/a.txt'));//'aa bbb' fclose($fp); ?>
fseek()
fseek()函数用于在文件指针中定位,成功则返回 0;否则返回 -1
int fseek ( resource $handle , int $offset [, int $whence = SEEK_SET ] )
将test目录下的a.txt文件内容修改为'12345'
<?php $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'r'); echo fgetc($fp);//'1' fseek($fp,4); echo fgetc($fp);//'5' fclose($fp); ?>
<?php $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'r'); echo fread($fp,2)."<br>";//12 fseek($fp,4); echo fread($fp,2)."<br>";//5 fseek($fp,-3,SEEK_END); echo fread($fp,2)."<br>";//34 fclose($fp); ?>
ftell()
ftell()函数用于返回文件指针读/写的位置
int ftell ( resource $handle )
<?php $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'r'); echo ftell($fp);//0 fgetc($fp); echo ftell($fp);//1 fseek($fp,4); echo ftell($fp);//4 fclose($fp); ?>
rewind()
rewind()函数用于倒回文件指针的位置,将handle的文件位置指针设为文件流的开头
bool rewind ( resource $handle )
<?php $fp = fopen('test/a.txt', 'r'); fseek($fp,2); echo ftell($fp);//2 rewind($fp); echo ftell($fp);//0 ?>
file_get_contents()
file_get_contents()函数用于将整个文件读入一个字符串
string file_get_contents ( string $filename [, bool $use_include_path = false [, resource $context [, int $offset = -1 [, int $maxlen ]]]] )
<?php $homepage = file_get_contents('test/a.txt'); echo $homepage;//'12345' ?>
页面变为百度首页
<?php $homepage = file_get_contents('http://www.baidu.com/'); echo $homepage; ?>
file_put_contents()
file_put_contents()函数用于将一个字符串写入文件
int file_put_contents ( string $filename , mixed $data [, int $flags = 0 [, resource $context ]] )
使用该函数和依次调用 fopen(),fwrite() 以及 fclose() 功能一样
[注意]默认为写模式,若设置第三个参数为FILE_APPEND,则变为追加模式
<?php file_put_contents('test/a.txt','abc'); ?>
readfile()
readfile()函数用于读取文件并写入到输出缓冲
int readfile ( string $filename [, bool $use_include_path = false [, resource $context ]] )
<?php readfile('http://www.baidu.com/');//页面中显示百度首页 ?> <?php readfile('test/a.txt');//页面中显示abc ?>
file()
file()函数用于把整个文件读入一个数组中,每一行作为一个数组的元素
array file ( string $filename [, int $flags = 0 [, resource $context ]] )
将a.txt的文件内容改为每一行一个数字,分别是1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9
<?php $arr = file('test/a.txt',0); echo $arr[0]."<br>";//1 echo count($arr);//9 ?>
ftruncate()
ftruncate()函数用于将文件截断到给定的长度
bool ftruncate ( resource $handle , int $size )
[注意]使用ftruncate()函数时,需要使用追加模式。经测试,使用读模式时无效,使用写模式时,文件内容被清空
<?php $fp = fopen("test/a.txt","a"); ftruncate($fp,100); ?>
【新建文件】
php中并没有专门的新建一个空文件的函数,但是可以利用fopen()和touch()方法实现
$file = fopen('a.png',w);
fclose($file);
touchu('a.png');
文件锁定
文件操作是在网络环境下完成的,可能有多个客户端用户在同一时刻对服务器上的同一个文件访问。当这种并发访问发生时,很可能会破坏文件中的数据。例如,一个用户正向文件中写入数据,还没有写完时,其他用户在这一时刻也向这个文件写入数据,就会造成数据写入混乱。还有,当用户没有将数据写完时,其他用户就去获取这个文件中的内容,也会得到残缺的数据
在PHP中提供了flock()函数,可以对文件使用锁定机制(锁定或释放文件)。当一个进程在访问文件时加上锁,其他进程想对该文件进行访问,则必须等到锁定被释放以后。这样就可以避免在并发访问同一个文件时破坏数据
语法: bool flock ( int handle, int operation [, int &wouldblock] )
PHP支持以咨询方式(也就是说所有访问程序必须使用同一方式锁定,否则它不会工作)锁定全部文件的一种轻便方法
handle 必须是一个已经打开的文件指针
operation 可以是以下值之一:
要取得共享锁定(读取程序),将 operation 设为 LOCK_SH
要取得独占锁定(写入程序),将 operation 设为 LOCK_EX
要释放锁定(无论共享或独占),将 operation 设为 LOCK_UN
如果不希望flock()在锁定时堵塞,则给 operation 加上 LOCK_NB
如果成功则返回 TRUE,失败则返回 FALSE
下面是一个网络留言本的示例,一方面应用锁机制,另一方面综合地使用PHP中文件操作的内容
<?php header("Content-Type:text/html;charset=utf8"); //功能类似于数据库的文件 $filename = "message.txt"; //检查函数 function test_input($data) { $data = trim($data); $data = stripslashes($data); $data = htmlspecialchars($data); return $data; } //如果用户提交了,就按一定格式写入文件 if(isset($_POST['dosubmit'])) { $name = test_input($_POST['username']); $content = test_input($_POST['content']); //字段的分隔使用||,行的分隔使用[n] $mess = "$name||$content||".time()."[n]"; //调用写信息函数 writemessage($filename, $mess); } //如果文件存在,则读文件内容 if(file_exists($filename)) { readmessage($filename); } //写函数 function writemessage($filename, $mess) { global $name,$content; //以追加模式打开文件 $fp = fopen($filename, "a"); //如果锁定成功 if(flock($fp, LOCK_EX+LOCK_NB)) { //将数据写入文件 if($name && $content){ fwrite($fp, $mess); } //释放锁定 flock($fp, LOCK_UN+LOCK_NB); }else{ echo "写入锁定失败!"; } //关闭文件 fclose($fp); } //读函数 function readmessage($filename) { //以只读模式打开文件 $fp = fopen($filename, "r"); //读锁定 flock($fp, LOCK_SH+LOCK_NB); $mess = ""; //将数据遍历到$mess中 while(!feof($fp)) { $mess.=fread($fp, 1024); } //释放锁定 flock($fp, LOCK_UN+LOCK_NB); if(!empty($mess)){ $mess = rtrim($mess, "[n]"); //通过[n]将每行留言分割并存入数组中 $arrmess = explode("[n]", $mess); foreach($arrmess as $m) { //将每行数据使用'||'分割 list($username,$content,$t) = explode("||", $m); date_default_timezone_set('PRC'); echo "<b>{$username}</b>说:<u>{$content}</u>(".date('Y-m-d H:i:s',$t).")<hr><br>"; } } //关闭文件 fclose($fp); } ?> <form action="message.php" method="post"> 用户:<input type="text" name="username" value="" /><br> 内容:<textarea name="content" cols="22" rows="3"></textarea><br> <input type="submit" name="dosubmit" value="留言" /><br> </form>
文件上传
要想通过PHP成功地管理上传文件,需要通过以下三方面信息:
1、设置PHP配置文件中的指令:用于精细地调节PHP的文件上传功能

2、$_FILES多维数组:用于存储各种与上传文件有关的信息,其他数据还使用$_POST去接收
$_FILES["myfile"]["name"]中的值是:客户端文件系统的文件的名称
$_FILES["myfile"]["type"]中的值是:客户端传递的文件的类型
$_FILES["myfile"]["size"]中的值是:文件的字节的大小
$_FILES["myfile"]["tmp_name"]中的值是:文件被上传后在服务器存储的临时全路径
$_FILES["myfile"]["error"]中的值是:文件上传的错误代码(php 4.2以后增加的功能)
伴随文件上传时产生的错误信息代码具体如下:
值为0(UPLOAD_ERR_OK):表示没有发生任何错误
值为1(UPLOAD_ERR_INI_SIZE):表示上传文件的大小超出了约定值。文件大小的最大值是在PHP配置文件中指定的,该指令是:upload_max_filesize
值为2(UPLOAD_ERR_FORM_SIZE):表示上传文件大小超出了HTML表单隐藏域属性的MAX_FILE_SIZE元素所指定的最大值
值为3(UPLOAD_ERR_PARTIAL):表示文件只被部分上传
值为4(UPLOAD_ERR_NO_FILE):表示没有上传任何文件
值为6(UPLOAD_ERR_NO_TMP_DIR):表示找不到临时文件夹(PHP4.3.10和PHP5.0.3)
值为7(UPLOAD_ERR_CANT_WRITE):表示文件写入失败(PHP 5.1.0)
3、PHP的文件上传处理函数:用于上传文件的后续处理
只要把临时目录下的上传的文件,复制到指定目录下指定的名字就可以完成上传
PHP提供了专门用于文件上传所使用的is_uploaded_file()和move_uploaded_file()函数
【is_uploaded_file()】
is_uploaded_file()判断文件是否是通过 HTTP POST 上传的
bool is_uploaded_file ( string $filename )
如果filename所给出的文件是通过 HTTP POST 上传的则返回 TRUE。这可以用来确保恶意的用户无法欺骗脚本去访问本不能访问的文件
[注意]为了能使is_uploaded_file() 函数正常工作,必须使用$_FILES['userfile']['tmp_name'],而在从客户端上传的文件名$_FILES['userfile']['name']不能正常运作
【move_uploaded_file()】
move_uploaded_file()方法用于将上传的文件移动到新位置
bool move_uploaded_file ( string $filename , string $destination )
本函数检查并确保由 filename 指定的文件是合法的上传文件(即通过 PHP 的 HTTP POST 上传机制所上传的)。如果文件合法,则将其移动为由 destination 指定的文件
该函数成功时返回TRUE;如果filename不是合法的上传文件,不会出现任何操作,move_uploaded_file()将返回 FALSE;如果 filename 是合法的上传文件,但出于某些原因无法移动,不会出现任何操作,move_uploaded_file()将返回 FALSE。此外还会发出一条警告
<?php header("Content-Type:text/plain;charset=utf-8"); //判断错误 if($_FILES['file1']['error'] > 0) { switch($_FILES['file1']['error']) { case 1: case 2: echo "上传文件太大"; break; case 3: echo "文件只被部分上传"; break; case 4: echo "没有上传任何文件"; break; default: echo "末知错误"; } exit; } //判断类型 $arr = explode(".", basename($_FILES['file1']['name'])); $hz = array_pop($arr); $allowtype =array("gif", "png", "jpg", "jpeg"); if(!in_array($hz, $allowtype)) { echo "上传的类型不合法"; exit; } //判断大小 $maxsize= 1000000; if($_FILES['file1']['size'] > $maxsize) { echo "上传的文件超过了{$maxsize}字节!"; exit; } //随机文件名 $tmp_name = $_FILES['file1']['tmp_name']; $src_name = "./uploads/".date("YmdHis").rand(100, 999).".".$hz; if(move_uploaded_file($tmp_name, "$src_name")){ echo '上传成功'; }else{ echo '上传失败'; } ?>
文件下载
简单的文件下载只需要使用HTML的链接标记<a>,并将属性href的URL值指定为下载的文件即可
<a href="http://baidu.com/test/book.rar">下载</a>
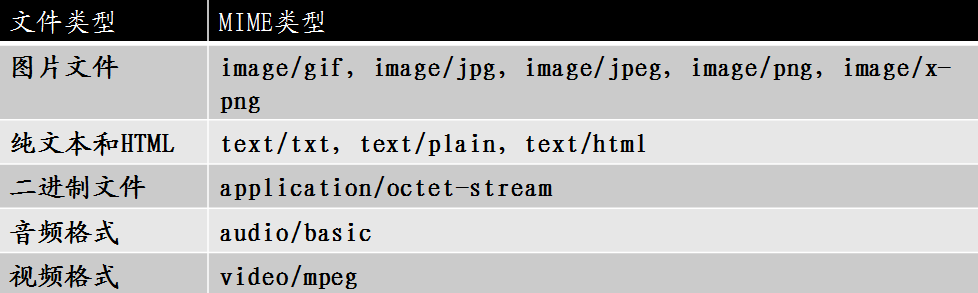
如果通过上面的代码实现文件下载,只能处理一些浏览器不能默认识别的MIME类型文件,如访问book.rar时,浏览器没有直接打开,而是弹出一个下载提示框,提示用户下载还是打开。如果需要下载'.html'、图片文件等浏览器识别的MIME类型文件时,浏览器将直接打开该文件
常见数据格式(MIME)如下
为了提高文件的安全性,不希望在<a>标签中给出文件的链接,则必须向浏览器发送必要的头信息,以通知浏览器将要进行下载文件的处理
【header()】
PHP使用header()函数发送网页的HTTP头部信息
void header ( string $string [, bool $replace = true [, int $http_response_code ]] )
[注意]header() 必须在任何实际输出之前调用
<?php
//该行不是必须的
header('Content-type: image/png');
//将文件设置为附件格式(浏览器只会下载而不会打开附件格式),设置下载时显示的文件名
header('Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="downloaded.png"');
//读取文件并写入到输出缓冲
readfile('./uploads/20170315085246943.png'); ?>
好的代码像粥一样,都是用时间熬出来的






【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· 一个奇形怪状的面试题:Bean中的CHM要不要加volatile?
· [.NET]调用本地 Deepseek 模型
· 一个费力不讨好的项目,让我损失了近一半的绩效!
· .NET Core 托管堆内存泄露/CPU异常的常见思路
· 微软正式发布.NET 10 Preview 1:开启下一代开发框架新篇章
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· NetPad:一个.NET开源、跨平台的C#编辑器
· PowerShell开发游戏 · 打蜜蜂
· 在鹅厂做java开发是什么体验