javascript运动系列第三篇——曲线运动

前面的话
上一篇介绍了变速运动,但只实现了直线运动。如果元素的left和top同时运动,并遵循不同的曲线公式,则会进行不同形式的曲线运动。本文将详细介绍圆周运动、钟摆运动、抛物线运动和流体运动这四种曲线运动形式
圆周运动
圆周运动可能是最好理解的曲线运动了
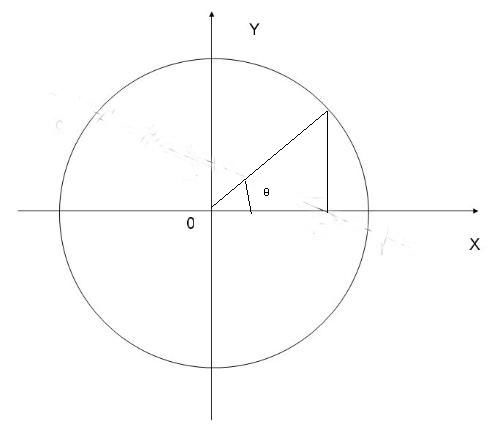
若(x0,y0)为圆心,则圆的公式为(x-x0)*(x-x0) + (y-y0)*(y-y0) = r*r
写成三角函数的形式为
x = x0 + cosa*r
y = y0 + sina*r
所以,实际上只要知道夹角a和圆心(x0,y0)就可以计算出x和y
圆周运动可以封装为函数circleMove.js
function getCSS(obj,style){ if(window.getComputedStyle){ return getComputedStyle(obj)[style]; } return obj.currentStyle[style]; } function circleMove(json){ //要操作的元素 var obj = json.obj; //方向(顺时针'+'或逆时针'-') var dir = json.dir; dir = dir || '+'; //最大圈数 var max = json.max; max = Number(max) || 'all'; //半径 var r = json.r; r = Number(r) || 100; //圆心x轴坐标 var x0 = json.x0 || parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'left')); //圆心y轴坐标 var y0 = json.y0 || parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'top')) - r; //初始夹角,以角度为单位 var a0 = json.a0; a0 = Number(a) || 90; //当前夹角 var a = json.a ||a0; //当前圈数 var num = json.num || 0; //清除定时器 if(obj.timer){return;} //声明当前值cur var cur = {}; obj.timer = setInterval(function(){ //将这些瞬时值储存在obj对象中的属性中 obj.a = a; obj.x0 = x0; obj.y0 = y0; obj.x = x; obj.y = y; obj.num = num; //如果元素运动到指定圈数则停止定时器 if(num == max){ clearInterval(obj.timer); } //顺时针 if(dir == '+'){ a++; if(a == a0 + 360){ a = a0; num++; } //逆时针 }else{ a--; if(a == a0 - 360){ a = a0; num++; } } //更新当前值 cur.left = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'left')); cur.top = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'top')); //更新left和top值 var x = x0 + r*Math.cos(a*Math.PI/180); var y = y0 + r*Math.sin(a*Math.PI/180) test.style.left = x + 'px'; test.style.top = y + 'px'; },20); }
下面利用封装的circleMove.js来实现简单的圆周运动
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn1">顺时针旋转</button>
<button id="btn2">逆时针旋转</button>
<button id="btn3">暂停</button>
<button id="reset">还原</button>
<div id="result"></div>
<div id="backup" style="height: 298px;width:298px;border:1px solid black;border-radius:50%;position:absolute;top:50px;left:50px;">
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color:pink;position:relative;left:130px;top:280px;border-radius:50%"></div>
</div>
<script src="https://files.cnblogs.com/files/xiaohuochai/circleMove.js"></script>
<script>
reset.onclick = function(){
history.go();
}
btn1.onclick = function(){
circleMove({obj:test,r:150,x0:test.x0,y0:test.y0,a:test.a,num:test.num});
}
btn2.onclick = function(){
circleMove({obj:test,r:150,dir:'-',x0:test.x0,y0:test.y0,a:test.a,num:test.num});
}
btn3.onclick = function(){
clearInterval(test.timer);
test.timer = 0;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
【css3】
css3新增了transform和animation等新的样式,也可以用来做圆周运动。transform里面有一个变形函数是rotate,这时就需要使用逆向思维。元素本身并不发生运动,而是轨道自身在旋转,会实现视觉上的圆周运动效果
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> @keyframes rotate1{ 100%{transform:rotate(360deg);} } @keyframes rotate2{ 100%{transform:rotate(-360deg);} } #backup{ height: 298px;width:298px;border:1px solid black;border-radius:50%;position:absolute;top:50px;left:50px; } #test{ height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color:pink;position:relative;left:130px;top:280px;border-radius:50% } </style> </head> <body> <button id="btn1">顺时针旋转</button> <button id="btn2">逆时针旋转</button> <button id="btn3">暂停</button> <button id="reset">还原</button> <div id="result"></div> <div id="backup"> <div id="test"></div> </div> <script> reset.onclick = function(){ history.go(); } btn1.onclick = function(){ backup.style.animation= 'rotate1 4s infinite linear'; } btn2.onclick = function(){ backup.style.animation= 'rotate2 4s infinite linear'; } btn3.onclick = function(){ backup.style.animationPlayState = 'paused'; } </script> </body> </html>
三维圆周
前面我们介绍了二维圆周运动,如果是三维圆周运动,则需要考虑x、y、z立体坐标轴
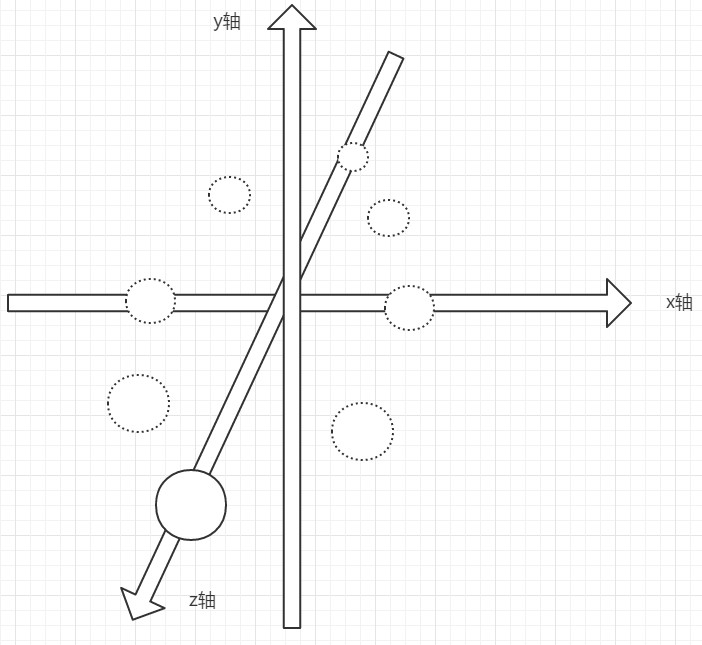
从示意图中可知,三维圆周运动的模拟实现实际上是元素的宽高发生了变化,元素的x轴变化依然按照三角函数公式进行,元素的y轴一直保存为0
假设圆的宽(或高)在z轴正方向最远处时为100px,当z轴值为0时,宽(或高)为50px,在z轴负方向最远处时为0px
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <button id="btn1">开始旋转</button> <button id="btn2">暂停</button> <button id="reset">还原</button> <div id="result"></div> <div id="test" style="height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color:pink;position:relative;left:200px;top:60px;border-radius:50%"></div> <script> reset.onclick = function(){ history.go(); } btn1.onclick = function(){ threeCircleMove({ obj:test,r:200,x0:test.x0,width:test.width,height:test.height,a:test.a,num:test.num }) } btn2.onclick = function(){ clearInterval(test.timer); test.timer = 0; } function getCSS(obj,style){ if(window.getComputedStyle){ return getComputedStyle(obj)[style]; } return obj.currentStyle[style]; } function threeCircleMove(json){ //要操作的元素 var obj = json.obj; //方向(顺时针'+'或逆时针'-') var dir = json.dir; dir = dir || '+'; //最大圈数 var max = json.max; max = Number(max) || 'all'; //半径 var r = json.r; r = Number(r) || 100; //圆心x轴坐标 var x0 = json.x0 || parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'left')); //元素的初始宽高 var offsetHeight = obj.offsetHeight; var offsetWidth = obj.offsetWidth; //元素的宽高 var height,width; //初始夹角,以角度为单位 var a0 = json.a0; a0 = Number(a) || 90; //当前夹角 var a = json.a ||a0; //当前圈数 var num = json.num || 0; //清除定时器 if(obj.timer){return;} //声明当前值cur var cur = {}; obj.timer = setInterval(function(){ //将这些瞬时值储存在obj对象中的属性中 obj.a = a; obj.x0 = x0; obj.width = width; obj.height = height; obj.x = x; obj.num = num; //如果元素运动到指定圈数则停止定时器 if(num == max){ clearInterval(obj.timer); } //顺时针 if(dir == '+'){ a++; if(a == a0 + 360){ a = a0; num++; } //逆时针 }else{ a--; if(a == a0 - 360){ a = a0; num++; } } //更新当前值 cur.left = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'left')); //更新left值和宽高值 var x = x0 + r*Math.cos((90 + a*Math.PI)/180); width = (offsetWidth/2) + offsetWidth/2*Math.sin((90 + a*Math.PI)/180); height = (offsetHeight/2) + offsetWidth/2*Math.sin((90 + a*Math.PI)/180); test.style.left = x + 'px'; test.style.width = width + 'px'; test.style.height = height + 'px'; },20); } </script> </body> </html>
【css3】
同样地,使用强大的css3属性可以实现三维圆周效果
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> @keyframes rotate1{ 100%{transform:rotateX(60deg) rotate(360deg);} } @keyframes rotate2{ 100%{transform:rotateX(60deg) rotate(-360deg);} } body{ perspective: 700px; } #backup{ height: 298px;width:298px;border:1px solid black;border-radius:50%;position:absolute;top:100px;left:100px;transform:rotateX(60deg) rotate(0); } #test{ height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color:pink;position:relative;left:130px;top:280px;border-radius:50% } </style> </head> <body> <button id="btn1">顺时针旋转</button> <button id="btn2">逆时针旋转</button> <button id="btn3">暂停</button> <button id="reset">还原</button> <div id="result"></div> <div id="backup"> <div id="test"></div> </div> <script> reset.onclick = function(){ history.go(); } btn1.onclick = function(){ backup.style.animation= 'rotate1 4s infinite linear'; } btn2.onclick = function(){ backup.style.animation= 'rotate2 4s infinite linear'; } btn3.onclick = function(){ backup.style.animationPlayState = 'paused'; } </script> </body> </html>
钟摆运动
一个钟摆,一会儿朝左,一会儿朝右,周而复始,来回摆动。钟摆总是围绕着一个中心值在一定范围内作有规律的摆动,这种运动称为钟摆运动,可以把钟摆运动看做圆周运动的一部分,进而比较简单的实现钟摆运动
假设,元素初始时处于钟摆的最底点。当钟摆与竖直线夹角为60度时,为最高点
若钟摆运动的圆心为(x0,y0),则圆的公式为(x-x0)*(x-x0) + (y-y0)*(y-y0) = r*r
若夹角a为钟摆与竖直线夹角,写成三角函数的形式为
x = x0 + sina*r
y = y0 + cosa*r
当夹角a从0增加到60或减小到-60时,元素开始做反向运动
将钟摆运动写成pendulMove.js的形式
function getCSS(obj,style){ if(window.getComputedStyle){ return getComputedStyle(obj)[style]; } return obj.currentStyle[style]; } function pendulMove(json){ //要操作的元素 var obj = json.obj; //起始方向(顺时针'+'或逆时针'-') var dir = json.dir; dir = dir || '+'; //最大次数(再次经过最低点为一次) var max = json.max; max = Number(max) || 'all'; //半径 var r = json.r; r = Number(r) || 100; //圆心x轴坐标 var x0 = json.x0 || parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'left')); //圆心y轴坐标 var y0 = json.y0 || parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'top')) - r; //初始夹角,以角度为单位 var a0 = json.a0; a0 = Number(a) || 0; //当前夹角 var a = json.a ||0; //当前次数 var num = 0; //清除定时器 if(obj.timer){return;} //声明当前值cur var cur = {}; obj.timer = setInterval(function(){ //将这些瞬时值储存在obj对象中的属性中 obj.a = a; obj.x0 = x0; obj.y0 = y0; obj.x = x; obj.y = y; obj.num = num; //如果元素运动到指定圈数则停止定时器 if(num == max){ clearInterval(obj.timer); } //起始向右运动 if(dir == '+'){ a++; if(a == 60){ //方向变成向左 dir = '-'; } }else{ a--; if(a == -60){ //方向变成向右 dir = '+'; } } //更新当前值 cur.left = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'left')); cur.top = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'top')); //更新left和top值 var x = x0 + r*Math.sin(a*Math.PI/180); var y = y0 + r*Math.cos(a*Math.PI/180) test.style.left = x + 'px'; test.style.top = y + 'px'; },20); }
下面利用封装的pendulMove.js来实现简单的钟摆运动
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn1">起始正向运动</button>
<button id="btn2">起始逆向运动</button>
<button id="btn3">暂停</button>
<button id="reset">还原</button>
<div id="result"></div>
<div id="backup" style="height: 298px;width:298px;border-bottom:1px solid black;border-radius:50%;position:absolute;top:50px;left:50px;">
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color:pink;position:relative;left:130px;top:280px;border-radius:50%"></div>
</div>
<script src="https://files.cnblogs.com/files/xiaohuochai/pendulMove.js"></script>
<script>
reset.onclick = function(){
history.go();
}
btn1.onclick = function(){
pendulMove({obj:test,r:150,x0:test.x0,y0:test.y0,a:test.a,num:test.num});
}
btn2.onclick = function(){
pendulMove({obj:test,r:150,dir:'-',x0:test.x0,y0:test.y0,a:test.a,num:test.num});
}
btn3.onclick = function(){
clearInterval(test.timer);
test.timer = 0;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
【弹性运动】
实际情况下,钟摆运动并不是匀速运动,而是一个重复的加减速运动,正好弹性运动可以轻松的实现类似效果
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <button id="btn1">开始运动</button> <button id="btn2">暂停</button> <button id="reset">还原</button> <div id="test" style="height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color: pink;position:absolute;left:0;top: 30px;border-radius:50%"></div> <script> function getCSS(obj,style){ if(window.getComputedStyle){ return getComputedStyle(obj)[style]; } return obj.currentStyle[style]; } reset.onclick = function(){history.go();} btn2.onclick = function(){ clearInterval(test.timer); } //声明步长值stepY、stepX var stepY = 30; var stepX = 10; btn1.onclick = function(){ //声明当前值curY、curX var curY,curX; //声明目标值 var targetY = parseFloat('400px'); clearInterval(test.timer); test.timer = setInterval(function(){ //更新当前值 curY = parseFloat(getCSS(test,'top')); curX = parseFloat(getCSS(test,'left')); //更新步长值 stepY -= 1; //当元素返回到初始高度时 if(stepY == -30){ stepY = 29; stepX = -stepX; } //更新top、left值 test.style.top = curY + stepY + 'px'; test.style.left = curX + stepX + 'px'; },20); } </script> </body> </html>
抛物线运动
平面内到定点与定直线的距离相等的点的轨迹叫做抛物线。其中定点叫抛物线的焦点,定直线叫抛物线的准线。抛物线实际上就是一段特殊形式的曲线
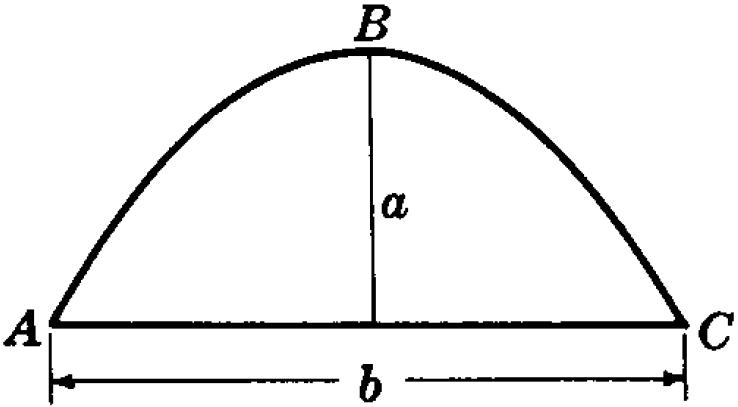
抛物线方程为y=a*x*x+b*x+c
其中a、b、c为参数,以x为参照的话,当x以固定值递增的方式进行变化时,y也会有相应变化
若a>0时,抛物线的开口向下;否则,开口向上
抛物线的准线的x轴坐标为(-2*a/b)。如果target目标设置为100,则(-2*a/b)尽量设置为50
若a = 0.01,则b=-1
将抛物线运动写成parabolMove.js的形式
function getCSS(obj,style){ if(window.getComputedStyle){ return getComputedStyle(obj)[style]; } return obj.currentStyle[style]; } function parabolMove(json){ //设置要操作的元素 var obj = json.obj; //设置x轴上的目标值 var target = json.target; target = Number(target) || 300; //设置x轴的步长值 var stepValue = json.step || 2; //设置x轴的步长 var step = 0; //设置回调函数 var fn = json.fn; //参数a、b、c var a = json.a; a = Number(a) || 0.01; var b = json.b; b = Number(b) || -1*target/100; var c = json.c; c = Number(c) || 0; //初始值 var left = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'left')); if(left >= target){return;} var top = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,'top')); //清除定时器 if(obj.timer){return;} //声明当前值cur var cur = {}; obj.timer = setInterval(function(){ //更新步长值 step += stepValue; //更新left和top值 var x = left + step; var y = top + a*step*step + b*step + c; if(x > target){ x = target; } test.style.left = x + 'px'; test.style.top = y + 'px'; //如果到达目标点,清除定时器 if(x == target){ clearInterval(obj.timer); obj.timer = 0; fn && fn.call(obj); } },20); }
下面利用封装的parabolMove.js来实现简单的抛物线运动
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <button id="btn1">开始运动</button> <button id="reset">还原</button> <div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color:pink;position:absolute;left:0px;top:100px;"></div> <script src="https://files.cnblogs.com/files/xiaohuochai/parabolMove.js"></script> <script> reset.onclick = function(){ history.go(); } btn1.onclick = function(){ parabolMove({obj:test,target:200}); } </script> </body> </html>
流体运动
流体运动实际上就是三角函数曲线运动,以sin为例,y = asin(b*x),当a和b取不同的值时,就可以得到不同的曲线形式
在这里要注意的是,sin里面的参数一定要写成弧度的形式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> .track{width: 2px;height: 2px;background-color:#000;position:absolute;} </style> </head> <body> <label for="a" id="labelA">参数a:100</label> <input id="a" type="range" min="50" max="100" step="10" value="100" /> <label for="b" id="labelB">参数b:1</label> <input id="b" type="range" min="1" max="5" step="1" value="1" /> <button id="reset">还原</button> <span>三角函数的公式为: y = a*sin(b*x)</span> <span id="result">所以,实际公式为:y = 100*sin(1*x)</span> <div id="test" style="height: 50px;width: 50px;background-color: pink;border-radius:50%;position: absolute;left: 30px;top:50px;"></div> <script> reset.onclick = function(){ history.go(); } function createTracks(x,y){ var ele = document.createElement('div'); ele.className = 'track'; ele.style.left = x + 'px'; ele.style.top = y + 'px'; document.body.appendChild(ele); } function deleteTracks(){ var eles = document.getElementsByTagName('div'); for(var i = 0 ;i < eles.length; i++){ if(eles[i].className == 'track'){ document.body.removeChild(eles[i]); i--; } } } function getResult(){ result.innerHTML = '所以,实际公式为: y=' + a.value + '*sin(' + b.value + '*x)'; } show(); function show(){ clearInterval(test.timer); //重置left、top值 test.style.left = 30 + 'px'; test.style.top = 50 + 'px'; //声明定时器运行次数 var n = 0; //声明拓展倍数 var value = 100; //清除轨迹 deleteTracks(); test.timer = setInterval(function(){ var A = Number(a.value); var B = Number(b.value); n++; var x = (B*n)*Math.PI/180; var y = A*Math.sin(x); test.style.left = x*value + 'px'; test.style.top = 2*A+y + 'px'; createTracks(x*value,2*A+y); if(x*value >= document.documentElement.clientWidth - 2*test.offsetWidth){ clearInterval(test.timer) } },20) } a.oninput = function(){ labelA.innerHTML = '参数a:' + this.value; getResult(); show(); } b.oninput = function(){ labelB.innerHTML = '参数b:' + this.value; getResult(); show(); } </script> </body> </html>
好的代码像粥一样,都是用时间熬出来的






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?