数组、单链表和双链表
线性表是一种线性结构,它是具有相同类型的n(n≥0)个数据元素组成的有限序列。接下来介绍线性表的几个基本组成部分:数组、单向链表、双向链表。
一 数组
数组中稍微复杂一点的是多维数组和动态数组。对于C语言而言,多维数组本质上也是通过一维数组实现的。至于动态数组,是指数组的容量能动态增长的数组;对于C语言而言,若要提供动态数组,需要手动实现;而对于C++而言,STL提供了vector。
1.1 vector使用
(1)构造函数
- vector():创建一个空vector
- vector(int nSize):创建一个vector,元素个数为nSize
- vector(int nSize,const t& t):创建一个vector,元素个数为nSize,且值均为t
- vector(const vector&):复制构造函数
- vector(begin,end):复制[begin,end)区间内另一个数组的元素到vector中
(2)增加函数
- void push_back(const T& x):向量尾部增加一个元素X
- iterator insert(iterator it,const T& x):向量中迭代器指向元素前增加一个元素x
- iterator insert(iterator it,int n,const T& x):向量中迭代器指向元素前增加n个相同的元素x
- iterator insert(iterator it,const_iterator first,const_iterator last):向量中迭代器指向元素前插入另一个相同类型向量的[first,last)间的数据
(3)删除函数
- void pop_back():删除向量中最后一个元素
- void clear():清空向量中所有元素
- iterator erase(iterator it):删除向量中迭代器指向元素
- iterator erase(iterator first,iterator last):删除向量中[first,last)中元素
(4)遍历函数
- reference at(int pos):返回pos位置元素的引用
- iterator begin():返回向量头指针,指向第一个元素
- iterator end():返回向量尾指针,指向向量最后一个元素的下一个位置
- reverse_iterator rbegin():反向迭代器,指向最后一个元素
- reverse_iterator rend():反向迭代器,指向第一个元素之前的位置
- reference front():返回首元素的引用
- reference back():返回尾元素的引用
(5)判断函数
- bool empty() const:判断向量是否为空,若为空,则向量中无元素
(6)大小函数
- int size() const:返回向量中元素的个数
- int capacity() const:返回当前向量张红所能容纳的最大元素值
- int max_size() const:返回最大可允许的vector元素数量值
(7)其他函数
- void swap(vector&):交换两个同类型向量的数据
- void assign(int n,const T& x):设置向量中第n个元素的值为x
- void assign(const_iterator first,const_iterator last):向量中[first,last)中元素设置成当前向量元素
二 单向链表
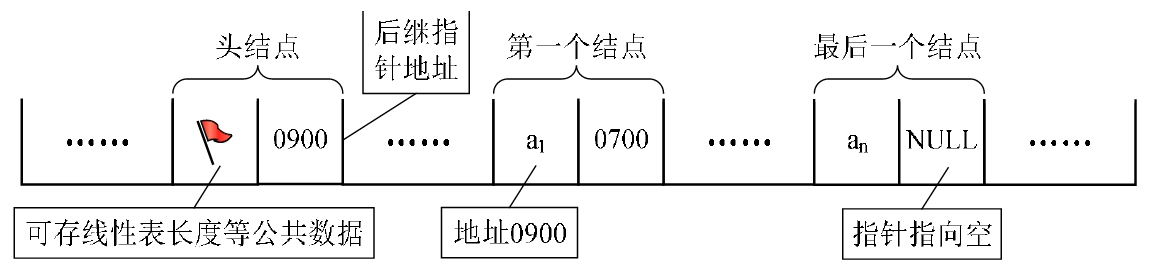
链表就是由N个节点链接而成的线性表,如果其中每个节点只包含一个指针域那么就称为单链表,如果含有两个指针域那么就称为双链表。在线性表的链式存储结构中,为了便于插入和删除操作的实现,每个链表都带有一个头指针(或尾指针),通过头指针可以唯一标识该链表。从头指针所指向的节点出发,沿着节点的链可以访问到每个节点。
单链表的特点是:节点的链接方向是单向的;相对于数组来说,单链表的的随机访问速度较慢,但是单链表删除/添加数据的效率很高。
三 双向链表
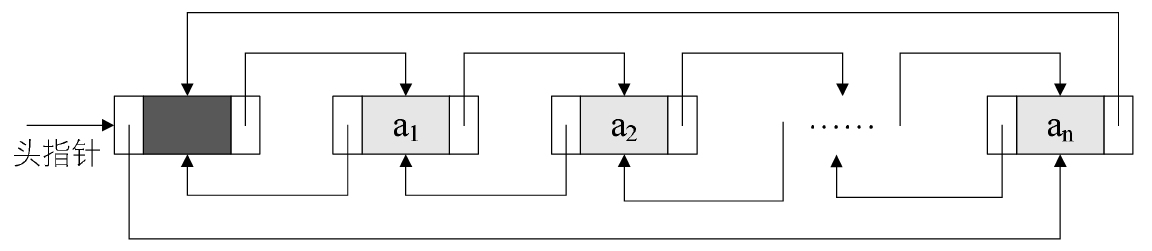
双链表中,每个节点都有两个指针,指向前驱和后继,这样可以方便地找到某个节点的前驱节点和后继节点,这在某些场合中是非常实用的。
3.1 双向链表代码实现
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> struct DNode { public: T value; DNode *prev; DNode *next; public: DNode() { } DNode(T t, DNode *prev, DNode *next) { this->value = t; this->prev = prev; this->next = next; } }; template<class T> class DoubleLink { public: DoubleLink(); ~DoubleLink(); int size(); int is_empty(); T get(int index); T get_first(); T get_last(); int insert(int index, T t); int insert_first(T t); int append_last(T t); int del(int index); int delete_first(); int delete_last(); private: int count; DNode<T> *phead; private: DNode<T> *get_node(int index); }; template<class T> DoubleLink<T>::DoubleLink() : count(0) { // 创建“表头”。注意:表头没有存储数据! phead = new DNode<T>(); phead->prev = phead->next = phead; // 设置链表计数为0 //count = 0; } // 析构函数 template<class T> DoubleLink<T>::~DoubleLink() { // 删除所有的节点 DNode<T>* ptmp; DNode<T>* pnode = phead->next; while (pnode != phead) { ptmp = pnode; pnode=pnode->next; delete ptmp; } // 删除"表头" delete phead; phead = NULL; } // 返回节点数目 template<class T> int DoubleLink<T>::size() { return count; } // 返回链表是否为空 template<class T> int DoubleLink<T>::is_empty() { return count==0; } // 获取第index位置的节点 template<class T> DNode<T>* DoubleLink<T>::get_node(int index) { // 判断参数有效性 if (index<0 || index>=count) { cout << "get node failed! the index in out of bound!" << endl; return NULL; } // 正向查找 if (index <= count/2) { int i=0; DNode<T>* pindex = phead->next; while (i++ < index) { pindex = pindex->next; } return pindex; } // 反向查找 int j=0; int rindex = count - index -1; DNode<T>* prindex = phead->prev; while (j++ < rindex) { prindex = prindex->prev; } return prindex; } // 获取第index位置的节点的值 template<class T> T DoubleLink<T>::get(int index) { return get_node(index)->value; } // 获取第1个节点的值 template<class T> T DoubleLink<T>::get_first() { return get_node(0)->value; } // 获取最后一个节点的值 template<class T> T DoubleLink<T>::get_last() { return get_node(count-1)->value; } // 将节点插入到第index位置之前 template<class T> int DoubleLink<T>::insert(int index, T t) { if (index == 0) return insert_first(t); DNode<T>* pindex = get_node(index); DNode<T>* pnode = new DNode<T>(t, pindex->prev, pindex); pindex->prev->next = pnode; pindex->prev = pnode; count++; return 0; } // 将节点插入第一个节点处。 template<class T> int DoubleLink<T>::insert_first(T t) { DNode<T>* pnode = new DNode<T>(t, phead, phead->next); phead->next->prev = pnode; phead->next = pnode; count++; return 0; } // 将节点追加到链表的末尾 template<class T> int DoubleLink<T>::append_last(T t) { DNode<T>* pnode = new DNode<T>(t, phead->prev, phead); phead->prev->next = pnode; phead->prev = pnode; count++; return 0; } // 删除index位置的节点 template<class T> int DoubleLink<T>::del(int index) { DNode<T>* pindex = get_node(index); pindex->next->prev = pindex->prev; pindex->prev->next = pindex->next; delete pindex; count--; return 0; } // 删除第一个节点 template<class T> int DoubleLink<T>::delete_first() { return del(0); } // 删除最后一个节点 template<class T> int DoubleLink<T>::delete_last() { return del(count-1); }


