WebService的简单介绍与入门使用
WebService是一个平台独立的,低耦合的,自包含的、基于可编程的web的应用程序,可使用开放的XML(标准通用标记语言下的一个子集)标准来描述、发布、发现、协调和配置这些应用程序,用于开发分布式的互操作的应用程序。
WebService只采用HTTP POST方式传输数据,不使用GET方式。

WebService的特点::
(1)互操作性
任何的WebService之间都可以进行交互。由于WebService与客户端之间一般使用SOAP协议传输XML数据,而因为SOAP这个所有主要供应商都支持的新标准协议,所以避免了在CORBA、DCOM和其他协议之间需要转换的麻烦,并且可以使用任何程序语言来编写WebService,节约了编程者的开发成本。
(2)普遍性
WebService通过HTTP POST方式接受客户的请求,利用HTTP和XML进行通信,因此,任何支持这些技术的设备都可以拥有和访问Web Service。
(3)易于使用
Web Service蕴涵的基本概念易于理解,开发不受程序语言和平台的限制,它本身就是为了跨平台或跨语言而设计的。
(4)行业支持
所有主要的供应商都支持SOAP和WebService技术。
说WebService之前先介绍一下两个很重要的概念SOAP和WSDL。
首先是SOAP(Simple Object Access Protocol)简单对象访问协议
简单对象访问协议是交换数据的一种协议规范,是一种轻量的、简单的、基于XML(标准通用标记语言下的一个子集)的协议,它被设计成在WEB上交换结构化的和固化的信息。
其实就是在HTTP协议是传输XML文件,就变成了SOAP协议。
(1)SOAP作为一个基于XML语言的协议用于在网上传输数据。
(2)SOAP是基于HTTP的,SOAP = 在HTTP的基础上+XML数据。
(3)SOAP的组成如下:
Envelope – 必须的部分。以XML的根元素出现。
Headers – 可选的。
Body – 必须的。在body部分,包含要执行的服务器的方法。和发送到服务器的数据。
soap示例
<!-- 请求 -->
POST /WebServices/MobileCodeWS.asmx HTTP/1.1 Host: ws.webxml.com.cn Content-Type: text/xml; charset=utf-8 Content-Length: length SOAPAction: "http://WebXml.com.cn/getMobileCodeInfo" <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <soap:Envelope xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soap:Body> <getMobileCodeInfo xmlns="http://WebXml.com.cn/"> <mobileCode>string</mobileCode> <userID>string</userID> </getMobileCodeInfo> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
<!-- 响应 -->
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: text/xml; charset=utf-8 Content-Length: length <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <soap:Envelope xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soap:Body> <getMobileCodeInfoResponse xmlns="http://WebXml.com.cn/"> <getMobileCodeInfoResult>string</getMobileCodeInfoResult> </getMobileCodeInfoResponse> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
然后是WSDL (WebService Description Language)Web服务描述语言
它包含一系列描述某个web service的定,其实就是一个xml文档,用于描述当前服务的一些信息(服务名称、服务的发布地址、服务提供的方法、方法的参数类型、方法的返回值类型等)
WSDL示例
<!-- Published by JAX-WS RI (http://jax-ws.java.net). RI's version is JAX-WS RI 2.2.9-b130926.1035 svn-revision#5f6196f2b90e9460065a4c2f4e30e065b245e51e. --> <!-- Generated by JAX-WS RI (http://jax-ws.java.net). RI's version is JAX-WS RI 2.2.9-b130926.1035 svn-revision#5f6196f2b90e9460065a4c2f4e30e065b245e51e. --> <definitions xmlns:wsu="http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-wssecurity-utility-1.0.xsd" xmlns:wsp="http://www.w3.org/ns/ws-policy" xmlns:wsp1_2="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/09/policy" xmlns:wsam="http://www.w3.org/2007/05/addressing/metadata" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/" xmlns:tns="http://webxml.com.cn/" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" targetNamespace="http://webxml.com.cn/" name="TestWebServiceService"> <types> <xsd:schema> <xsd:import namespace="http://webxml.com.cn/" schemaLocation="http://localhost:8080/first?xsd=1"/> </xsd:schema> </types> <message name="firstWebService"> <part name="parameters" element="tns:firstWebService"/> </message> <message name="firstWebServiceResponse"> <part name="parameters" element="tns:firstWebServiceResponse"/> </message> <portType name="TestWebService"> <operation name="firstWebService"> <input wsam:Action="http://webxml.com.cn/TestWebService/firstWebServiceRequest" message="tns:firstWebService"/> <output wsam:Action="http://webxml.com.cn/TestWebService/firstWebServiceResponse" message="tns:firstWebServiceResponse"/> </operation> </portType> <binding name="TestWebServicePortBinding" type="tns:TestWebService"> <soap:binding transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http" style="document"/> <operation name="firstWebService"> <soap:operation soapAction=""/> <input> <soap:body use="literal"/> </input> <output> <soap:body use="literal"/> </output> </operation> </binding> <service name="TestWebServiceService"> <port name="TestWebServicePort" binding="tns:TestWebServicePortBinding"> <soap:address location="http://localhost:8080/first"/> </port> </service> </definitions>
WebService的简单使用
服务端的发布:基于JDK1.8发布一个WebService服务
第一步:创建一个Java项目
第二步:创建一个类,加入Webservice注解
@WebService是jdk提供的一个注解,它位于javax.jws.*这个包中。
第三步:创建一个方法
第四步:在main方法中调用jdk提供的发布服务的方法
通过EndPoint(端点服务)发布一个webService。
Endpoint也是jdk提供的一个专门用于发布服务的类,它的publish方法接收两个参数,一个是本地的服务地址,二是提供服务的类。它位于javax.xml.ws.*包中。
static Endpoint.publish(String address, Object implementor) 在给定地址处针对指定的实现者对象创建并发布端点。
stop方法用于停止服务。
EndPoint发布完成服务以后,将会独立的线程运行。所以,publish之后的代码,可以正常执行。
注意事项:
(1)给类添加上@WebService注解后,类中所有的非静态方法都将会对外公布。
(2)不支持静态方法,final方法。-
(3)如果希望某个方法(非static,非final)不对外公开,可以在方法上添加@WebMethod(exclude=true),阻止对外公开。
(4)如果一个类上,被添加了@WebService注解,则必须此类至少有一个可以公开的方法,否则将会启动失败。
import javax.jws.WebService; import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint; @WebService public class TestWebService { public static void main(String[] args) { String address = "http://localhost:8080/first"; Object implementor = new TestWebService(); Endpoint.publish(address, implementor); } public String firstWebService(String name){ System.out.println("一个简单的WebService服务"); return "Hello "+name; } }
第五步:访问服务的wsdl文档(服务的发布地址+?wsdl)http://localhost:8080/first?wsdl
出来的页面就是刚刚上面的wsdl示例
目前不是访问webService,只是获取一个用于描述WebService的说明文件,即:wsdl文件.
wsdl是以XML文件形式来描述WebService的”说明书”,有了说明书,我们才可以知道如何使用或是调用
而基于JDK发布的WebService服务与普通的不太一样,方法的参数与返回值需要访问http://localhost:8080/first?xsd=1来查看
<!-- Published by JAX-WS RI (http://jax-ws.java.net). RI's version is JAX-WS RI 2.2.9-b130926.1035 svn-revision#5f6196f2b90e9460065a4c2f4e30e065b245e51e. --> <xs:schema xmlns:tns="http://webxml.com.cn/" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" version="1.0" targetNamespace="http://webxml.com.cn/"> <xs:element name="firstWebService" type="tns:firstWebService"/> <xs:element name="firstWebServiceResponse" type="tns:firstWebServiceResponse"/> <xs:complexType name="firstWebService"> <xs:sequence> <xs:element name="arg0" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> <xs:complexType name="firstWebServiceResponse"> <xs:sequence> <xs:element name="return" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:schema>
客户端调用
首先,使用JDK中的wsimport命令,他的作用是解析wsdl文件,生成客户端本地代码。
wsimport是jdk自带的,可以根据wsdl文档生成客户端调用代码的工具.当然,无论服务器端的WebService是用什么语言写的,都将在客户端生成Java代码.服务器端用什么写的并不重要.
wsimport.exe位于JAVA_HOME\bin目录下.
常用参数为:
-d<目录> - 将生成.class文件。默认参数。
-s<目录> - 将生成.java文件。
-p<生成的新包名> -将生成的类,放于指定的包下。
(wsdlurl) - http://server:port/service?wsdl,必须的参数。
示例:
在cmd中执行这条命令
wsimport -s . http://localhost:8080/first?wsdl
注意:(1)-s不能分开,-s后面有个小点,用于指定源代码生成的目录。点即当前目录。
(2)如果使用了-s参数则会在目录下生成两份代码,一份为.class代码。一份为.java代码。
(3).class代码,可以经过打包以后使用。.java代码可以直接Copy到我们的项目中运行。
执行完这句指令后,在相应的文件夹中会生成以下文件
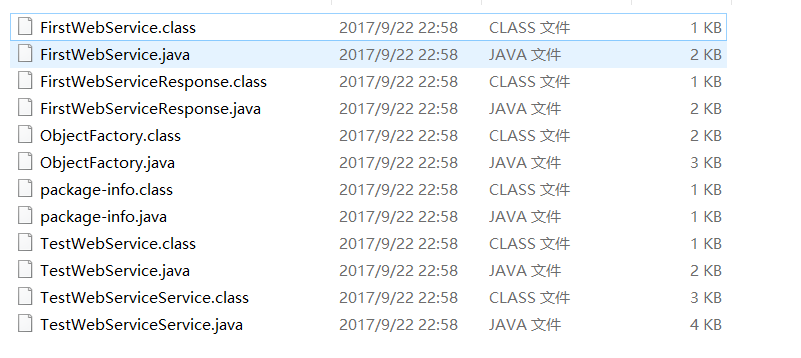
接下来,把这些文件中的Java文件拷贝到工程的src目录下
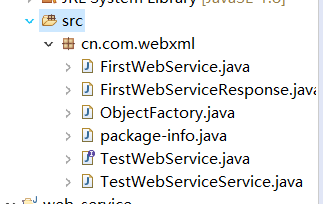
写一个测试类
package cn.com.webxml; /** * 1、使用wsimport命令解析wsdl文件生成本地代码 * 2、通过本地代码创建一个代理对象 * 3、通过代理对象实现远程调用 */ public class TestApp { public static void main(String[] args) { TestWebServiceService ts = new TestWebServiceService(); //创建客户端代理对象,用于远程调用 TestWebService proxy = ts.getTestWebServicePort(); String result = proxy.firstWebService("小明"); System.out.println(result); } }
执行后,发现产生如下结果,客户端控制台与服务端控制台打印
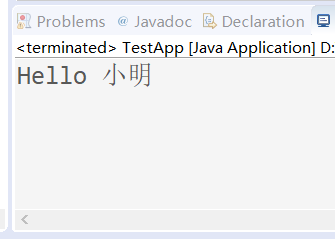

到现在,一个简单的WebService程序就完成了。
如果对WebService有了一定了解,可以了解一下CXF,因为我们很少直接用WebService进行开发。
链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaobai1226/p/7583758.html



