多线程中join()的用法
Thread中,join()方法的作用是调用线程等待该线程完成后,才能继续用下运行。
public class TestThread5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runner0 run5 = new Runner0();
Thread th5 = new Thread(run5);
th5.start();
th5.join();//join()方法用在此处是为了等待主线程结束后运行子线程
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
System.out.println("子线程:"+i);
}
}
}
class Runner0 implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
System.out.println("主线程:"+i);
}
}
上述代码的运行结构如下所示:
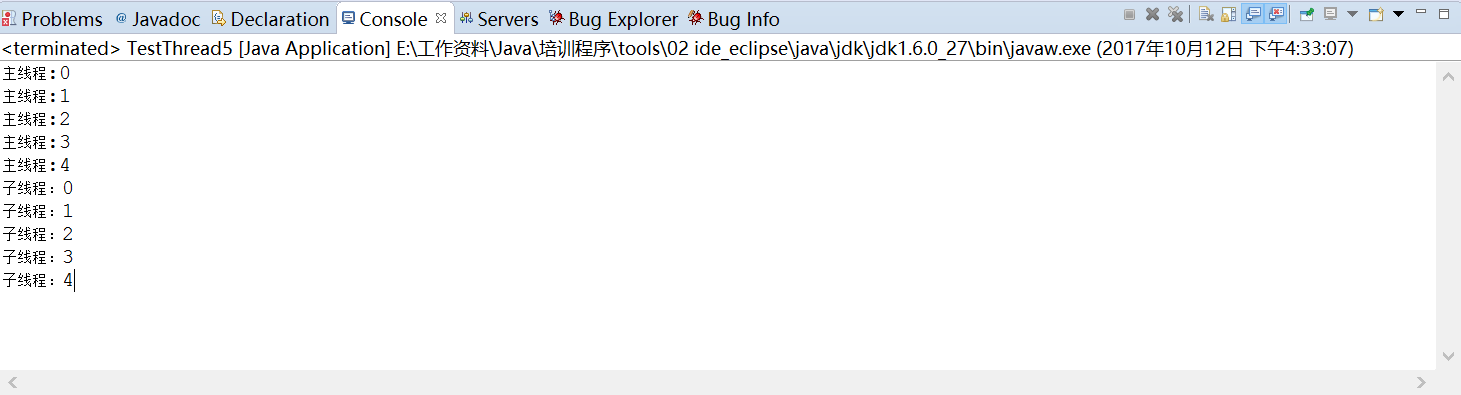
当然,如果不使用join()方法
public class TestThread6{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runner0 run5 = new Runner0();
Thread th5 = new Thread(run5);
th5.start();
// th5.join();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
System.out.println("子线程:"+i);
}
}
}
class Runner0 implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
System.out.println("主线程:"+i);
}
}
如上代码注释掉jion()方法,
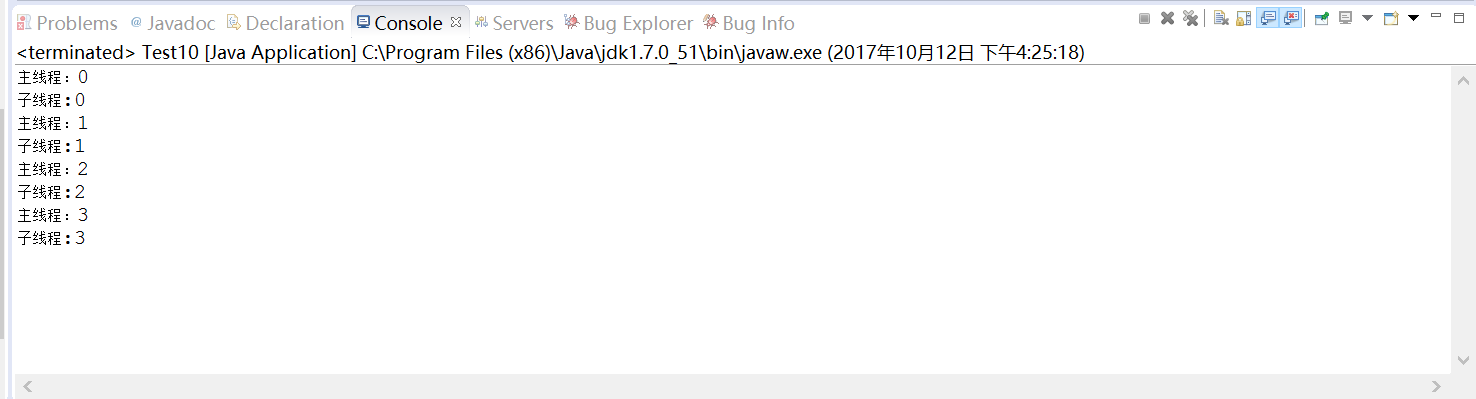
根据上面两个不同的代码,输出的不同,很容易就能理解join()方法。
yian




