HttpClient-RestTemplate-Feign
如何通过Java发送HTTP请求,通俗点讲,如何通过Java(模拟浏览器)发送HTTP请求。
Java有原生的API可用于发送HTTP请求,即java.net.URL、java.net.URLConnection,这些API很好用、很常用,但不够简便;
所以,也流行有许多Java HTTP请求的framework,如,Apache的HttpClient。
httpclient之外RPC 以及队列的使用看可以说也是越来越广泛了。
在netty等NIO框架因为需要高效的传输所以往往选择RPC,队列则用于回调以及设备消息之间的传递。
Http这个经久不衰的大佬自然不用多说,简单,支持广泛,高度兼容性。
HttpClient
HttpClient相比传统JDK自带的URLConnection,增加了易用性和灵活性,使得客户端发送Http请求变得容易。
HttpClient使用:
使用HttpClient发送请求、接收响应很简单,一般需要如下几步即可。
1. 创建HttpClient对象。
2. 创建请求方法的实例,并指定请求URL。如果需要发送GET请求,创建HttpGet对象;如果需要发送POST请求,创建HttpPost对象。
3. 如果需要发送请求参数,可调用HttpGet、HttpPost共同的setParams(HetpParams params)方法来添加请求参数;对于HttpPost对象而言,也可调用setEntity(HttpEntity entity)方法来设置请求参数。
4. 调用HttpClient对象的execute(HttpUriRequest request)发送请求,该方法返回一个HttpResponse。
5. 调用HttpResponse的getAllHeaders()、getHeaders(String name)等方法可获取服务器的响应头;调用HttpResponse的getEntity()方法可获取HttpEntity对象,该对象包装了服务器的响应内容。程序可通过该对象获取服务器的响应内容。
6. 释放连接。无论执行方法是否成功,都必须释放连接
RestTemplate
RestTemplate本是spring-web项目中的一个REST客户端,它遵循REST的设计原则,提供简单的API让我们可以调用HTTP服务。底层是对httpclient进行了封装。
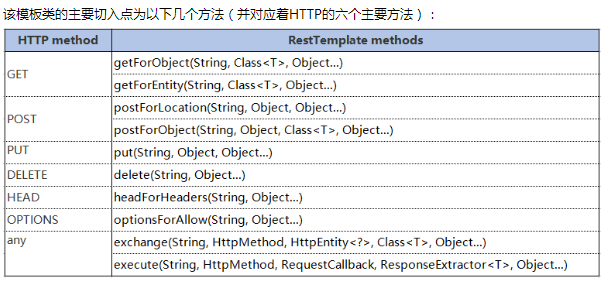
ps:建议使用exchange ,其他方法都是对execute进行了封装,都拥有各自的局限性。
RestTemplate可以用来做负载均衡,RestTemplate本身不具有负载均衡的功能,该类也与Spring Cloud没有关系,但为何加入@LoadBalanced注解后,一个RestTemplate实例就具有负载均衡的功能呢?
实际上这要得益于RestTemplate的拦截器功能。
下面举例:基于自己配置的HttpClient,创建一个可负载均衡的RestTemplate
HttpClientProperties
HttpClient的配置信息

@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="spring.httpclient") public class HttpClientProperties { private Integer connectTimeOut = 1000; private Integer socketTimeOut = 1000000; private String agent = "agent"; private Integer maxConnPerRoute = 10; private Integer maxConnTotaol = 50; public Integer getConnectTimeOut() { return connectTimeOut; } public void setConnectTimeOut(Integer connectTimeOut) { this.connectTimeOut = connectTimeOut; } public Integer getSocketTimeOut() { return socketTimeOut; } public void setSocketTimeOut(Integer socketTimeOut) { this.socketTimeOut = socketTimeOut; } public String getAgent() { return agent; } public void setAgent(String agent) { this.agent = agent; } public Integer getMaxConnPerRoute() { return maxConnPerRoute; } public void setMaxConnPerRoute(Integer maxConnPerRoute) { this.maxConnPerRoute = maxConnPerRoute; } public Integer getMaxConnTotaol() { return maxConnTotaol; } public void setMaxConnTotaol(Integer maxConnTotaol) { this.maxConnTotaol = maxConnTotaol; } }
HttpClientAutoConfiguration
根据HttpClient.class是否存在,bean是否存在,自动进行配置

@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass({HttpClient.class}) @EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpClientProperties.class) public class HttpClientAutoConfiguration { private final HttpClientProperties properties; public HttpClientAutoConfiguration(HttpClientProperties properties){ this.properties = properties; } /** * httpclient bean 的定义 * @return */ @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(HttpClient.class) public HttpClient httpClient() { RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom() .setConnectTimeout(properties.getConnectTimeOut()) .setSocketTimeout(properties.getSocketTimeOut()).build();// 构建requestConfig HttpClient client = HttpClientBuilder.create().setDefaultRequestConfig(requestConfig) .setUserAgent(properties.getAgent()) .setMaxConnPerRoute(properties.getMaxConnPerRoute()) .setMaxConnTotal(properties.getMaxConnTotaol()) .build(); return client; } }
@ConditionalOnClass:该注解的参数对应的类必须存在,否则不解析该注解修饰的配置类;
@ConditionalOnMissingBean:该注解表示,如果存在它修饰的类的bean,则不需要再创建这个bean;可以给该注解传入参数例如@ConditionOnMissingBean(name = "example"),这个表示如果name为“example”的bean存在,这该注解修饰的代码块不执行。
RestAutoConfig
创建负载均衡和直连的RestTemplate

@Configuration public class RestAutoConfig { public static class RestTemplateConfig { @Bean//负载均衡的restTemplate @LoadBalanced //spring 对restTemplate bean进行定制,加入loadbalance拦截器进行ip:port的替换 //"http://user/getusername,就能解析成http://127.0.0.1:8083//getusername RestTemplate lbRestTemplate(HttpClient httpclient) { RestTemplate template = new RestTemplate(new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(httpclient)); template.getMessageConverters().add(0,new StringHttpMessageConverter(Charset.forName("utf-8"))); template.getMessageConverters().add(1,new FastJsonHttpMessageConvert5()); return template; } @Bean //直连的restTemplat,这时只能使用http://127.0.0.1:8083//getusername地址,不能解析http://user/getusername RestTemplate directRestTemplate(HttpClient httpclient) { RestTemplate template = new RestTemplate(new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(httpclient)); template.getMessageConverters().add(0,new StringHttpMessageConverter(Charset.forName("utf-8"))); template.getMessageConverters().add(1,new FastJsonHttpMessageConvert5()); return template; } // FastJsonHttpMessageConvert4有一个bug,它是默认支持MediaType.ALL,spring在处理MediaType.ALL的时候会识别成字节流,而不是json,这里就对他进行改造和处理 public static class FastJsonHttpMessageConvert5 extends FastJsonHttpMessageConverter4{ static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); public FastJsonHttpMessageConvert5(){ setDefaultCharset(DEFAULT_CHARSET); setSupportedMediaTypes(Arrays.asList(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON,new MediaType("application","*+json"))); } } } }
调用RestTemplate的默认构造函数,RestTemplate对象在底层通过使用java.net包下的实现创建HTTP 请求,可以通过使用ClientHttpRequestFactory指定不同的HTTP请求方式。
ClientHttpRequestFactory接口主要提供了两种实现方式
- 一种是SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory,使用J2SE提供的方式(既java.net包提供的方式)创建底层的Http请求连接。
- 一种方式是使用HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory方式,底层使用HttpClient访问远程的Http服务,使用HttpClient可以配置连接池和证书等信息。
GenericRest
既支持直连又支持服务发现的调用

/** * 既支持直连又支持服务发现的调用 * */ @Service public class GenericRest { @Autowired @Qualifier("lbRestTemplate") private RestTemplate lbRestTemplate; @Autowired @Qualifier("directRestTemplate") private RestTemplate directRestTemplate; private static final String directFlag = "direct://"; //返回的泛型用ParameterizedTypeReference<T>来指定 public <T> ResponseEntity<T> post(String url,Object reqBody,ParameterizedTypeReference<T> responseType){ RestTemplate template = getRestTemplate(url); url = url.replace(directFlag, ""); return template.exchange(url, HttpMethod.POST,new HttpEntity(reqBody),responseType); } public <T> ResponseEntity<T> get(String url,ParameterizedTypeReference<T> responseType){ RestTemplate template = getRestTemplate(url); url = url.replace(directFlag, ""); return template.exchange(url, HttpMethod.GET,HttpEntity.EMPTY,responseType); } private RestTemplate getRestTemplate(String url) { if (url.contains(directFlag)) { return directRestTemplate; }else { return lbRestTemplate; } } }
exchange支持‘含参数的类型’(即泛型类)作为返回类型,该特性通过‘ParameterizedTypeReference<T>responseType’描述。
进行服务调用:
public List<User> getUserList(User query) { ResponseEntity<RestResponse<List<User>>> resultEntity = rest.post("http://"+ userServiceName + "/user/getList",query, new ParameterizedTypeReference<RestResponse<List<User>>>() {}); RestResponse<List<User>> restResponse = resultEntity.getBody(); if (restResponse.getCode() == 0) { return restResponse.getResult(); }else { return null; } }
SpringCloud Feign—申明式服务调用
虽然RestTemplate已经可以将请求拦截来实现对依赖服务的接口调用,并对Http请求进行封装处理,形成一套模板化的调用方法,但是对服务依赖的调用可能不只一处,一个接口都会被多次调用,所以我们会像前面那样针对各个微服务字形封装一些客户端接口调用类来包装这些依赖服务的调用。
由于RestTemplate的封装,几乎每一个调用都是简单的模板化内容,Feign在此基础上做了进一步的封装,由它来帮助我们定义和实现依赖服务接口的定义。
在服务消费者创建服务调用接口,通过@FeignClient注解指定服务名来绑定服务,然后再使用SpringMVC的注解来绑定具体该服务提供的REST接口。
@FeignClient("biz-service-0") public interface UserClient { @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/getuser") public User getuserinfo(); @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/getuser") public String getuserinfostr(); }
在服务消费者的web层进行调用:
@RestController public class UserController { @Autowired UserClient userClient; @RequestMapping(value = "/getuserinfo", method = RequestMethod.GET) public User getuserinfo() { return userClient.getuserinfo(); } @RequestMapping(value = "/getuserinfostr", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getuserinfostr() { return userClient.getuserinfostr(); }
通过Feign我们只需要定义服务绑定接口,以申明式的方法,优雅而简单的实现了服务调用。





