Java——集合(Collection接口),迭代器,增强for循环,泛型
一、集合
Collection接口中的方法是集合中所有实现类必须拥有的方法。
- ArrayList implements List
- List extends Collection
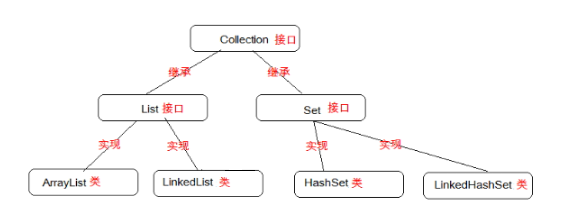
1、基本使用
import java.util.ArrayList; /* * 集合体系, * 目标 集合本身是一个存储的容器: * 必须使用集合存储对象 * 遍历集合,取出对象 * 集合自己的特性 */ public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { /* * 集合ArrayList,存储int类型数 * 集合本身不接受基本类,自动装箱存储 */ ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>(); array.add(11); array.add(12); for(int i = 0 ; i < array.size() ;i++){ System.out.println(array.get(i)); } /* * 集合存储自定义的Person类的对象 */ ArrayList<Person> arrayPer = new ArrayList<Person>(); arrayPer.add(new Person("a",20)); arrayPer.add(new Person("b",18)); arrayPer.add(new Person("c",22)); for(int i = 0 ; i < arrayPer.size();i++){ //get(0),取出的对象Person对象 //打印的是一个对象,必须调用的toString() System.out.println(arrayPer.get(i)); } } }
2、清空集合中的元素
/*
* Collection接口的方法
* void clear() 清空集合中的所有元素
* 集合容器本身依然存在
*/
public static void function(){
//接口多态的方式调用
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>();
coll.add("abc");
coll.add("bcd");
System.out.println(coll); // ["abc","bcd"]
coll.clear();
System.out.println(coll);
}
3、判断对象是否存在于集合中
/*
* Collection接口方法
* boolean contains(Object o) 判断对象是否存在于集合中,对象存在返回true
* 方法参数是Object类型
*/
private static void function_1() {
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>();
coll.add("abc");
coll.add("money");
coll.add("123");
boolean b = coll.contains("abc");
System.out.println(b);
}
4、将集合转成数组
/* Collection接口方法
* Object[] toArray() 集合中的元素,转成一个数组中的元素, 集合转成数组
* 返回是一个存储对象的数组, 数组存储的数据类型是Object
*/
private static void function_2() {
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>();
coll.add("abc");
coll.add("itcast");
coll.add("itheima");
coll.add("money");
coll.add("123");
Object[] objs = coll.toArray();
for(int i = 0 ; i < objs.length ; i++){
System.out.println(objs[i]);
}
}
5、移除元素
/*
* Collection接口方法
* boolean remove(Object o)移除集合中指定的元素
*/
private static void function_3(){
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>();
coll.add("abc");
coll.add("money");
coll.add("money");
coll.add("123");
System.out.println(coll);
boolean b = coll.remove("money"); //只会移除第一个
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(coll);
}
二、迭代器
迭代器是一种设计模式,它是一个对象,它可以遍历并选择序列中的对象,而开发人员不需要了解该序列的底层结构。迭代器通常被称为“轻量级”对象,因为创建它的代价小。
集合中的迭代器
由于Java中有多种不同的集合,我们又想有一个统一的方式来获取它的值,所以有了迭代器。
接口Iterator : 其中有两个抽象方法
- boolean hasNext() 判断集合中还有没有可以被取出的元素,如果有返回true
- next() 取出集合中的下一个元素
ArrayList重写方法 iterator(),返回了Iterator接口的实现类的对象
Iterator it = array.iterator(),运行结果就是Iterator接口的实现类的对象
it是接口的实现类对象,调用方法 hasNext 和 next 集合元素迭代
1、基本使用
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class CollectionDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//集合可以存储任意类型的对象
//集合中,不指定存储的数据类型, 集合就可以什么都存
Collection coll = new ArrayList(); // 多态
coll.add("abc");
coll.add("uyjgtfd");
//迭代器获取
Iterator it = coll.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
//it.next()获取出来的是什么数据类型,Object类
//Object obj = it.next();
//System.out.println(obj);
String s = (String)it.next();
System.out.println(s.length());
}
}
}
2、指定迭代数据类型
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>();
coll.add("abc1");
coll.add("abc2");
coll.add("abc3");
coll.add("abc4");
//迭代器,对集合ArrayList中的元素进行取出
//调用集合的方法iterator()获取出,Iterator接口的实现类的对象
Iterator<String> it = coll.iterator();
//接口实现类对象,调用方法hasNext()判断集合中是否有元素
//boolean b = it.hasNext();
//System.out.println(b);
//接口的实现类对象,调用方法next()取出集合中的元素
//String s = it.next();
//System.out.println(s);
//迭代是反复内容,使用循环实现,循环的条件,集合中没元素, hasNext()返回了false
while(it.hasNext()){
String s = it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
/*for (Iterator<String> it2 = coll.iterator(); it2.hasNext(); ) { // for循环实现迭代器
System.out.println(it2.next());
}*/
}
三、增强for循环
JDK1.5新特性,增强for循环
JDK1.5版本后,出现新的接口 java.lang.Iterable,Collection接口是继承Iterable
增强for循环格式:
for( 数据类型 变量名 : 数组或者集合 ){
sout(变量);
}
/*
* 增强for循环遍历集合
* 存储自定义Person类型
*/
public static void function_2(){
ArrayList<Person> array = new ArrayList<Person>();
array.add(new Person("a",20));
array.add(new Person("b",10));
for(Person p : array){
System.out.println(p);
}
}
public static void function_1(){
//for对于对象数组遍历的时候,能否调用对象的方法呢?当然能,s就是遍历出的对象
String[] str = {"abc","itcast","cn"};
for(String s : str){
System.out.println(s.length());
}
}
/*
* 实现for循环,遍历数组
* 好处: 代码少了,方便对容器遍历
* 弊端: 没有索引,不能操作容器里面的元素
*/
public static void function(){
int[] arr = {3,1,9,0};
for(int i : arr){
System.out.println(i+1);
}
System.out.println(arr[0]);
}
四、泛型
泛型是JDK1.5出现新的安全机制,保证程序的安全性
- 泛型: 指明了集合中存储数据的类型 <数据类型>
public static void function(){
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>();
coll.add("abc");
coll.add("rtyg");
coll.add("43rt5yhju");
//coll.add(1);
Iterator<String> it = coll.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String s = it.next();
System.out.println(s.length());
}
}
1、带有泛型的类
/*
* 带有泛型的类
* ArrayList
* E: Element 元素, 实际思想就是一个变量而已
* ArrayList<Integer> , E 接受到类型,就是Integer类型
* public class ArrayList<E>{
*
* public boolean add(Integer e){
* elementData[size++] = e;
* }
*
* public boolean add(E e){}
* }
*
* Iterator<E>
* E next()
*
* Iterator<Integer>
* Integer next()
*
*/
public class GenericDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer> ();
array.add(123);
array.add(456);
// ArrayList集合,自己有个方法
// <T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
Integer[] i = new Integer[array.size()];
Integer [] j = array.toArray(i);
for(Integer k : j){
System.out.println(k);
}
}
}
2、带有泛型的接口
public static void function(){
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>();
coll.add("abc");
coll.add("rtyg");
coll.add("43rt5yhju");
//coll.add(1);
Iterator<String> it = coll.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String s = it.next();
System.out.println(s.length());
}
}
3、泛型的通配符
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
/*
* 泛型的通配符
*/
public class GenericDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>();
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
array.add("123");
array.add("456");
set.add(789);
set.add(890);
iterator(array);
iterator(set);
}
/*
* 定义方法,可以同时迭代2个集合
* 参数: 怎么实现 , 不能写ArrayList,也不能写HashSet
* 参数: 或者共同实现的接口
* 泛型的通配,匹配所有的数据类型 ?
*/
public static void iterator(Collection<?> coll){
Iterator<?> it = coll.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
//it.next()获取的对象,什么类型
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
4、示例
/*
* 将的酒店员工,厨师,服务员,经理,分别存储到3个集合中
* 定义方法,可以同时遍历3集合,遍历三个集合的同时,可以调用工作方法
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class GenericTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建3个集合对象
ArrayList<ChuShi> cs = new ArrayList<ChuShi>();
ArrayList<FuWuYuan> fwy = new ArrayList<FuWuYuan>();
ArrayList<JingLi> jl = new ArrayList<JingLi>();
//每个集合存储自己的元素
cs.add(new ChuShi("张三", "后厨001"));
cs.add(new ChuShi("李四", "后厨002"));
fwy.add(new FuWuYuan("翠花", "服务部001"));
fwy.add(new FuWuYuan("酸菜", "服务部002"));
jl.add(new JingLi("小名", "董事会001", 123456789.32));
jl.add(new JingLi("小强", "董事会002", 123456789.33));
// ArrayList<String> arrayString = new ArrayList<String>();
iterator(jl);
iterator(fwy);
iterator(cs);
}
/*
* 定义方法,可以同时遍历3集合,遍历三个集合的同时,可以调用工作方法 work
* ? 通配符,迭代器it.next()方法取出来的是Object类型,怎么调用work方法
* 强制转换: it.next()=Object o ==> Employee
* 方法参数: 控制,可以传递Employee对象,也可以传递Employee的子类的对象
* 泛型的限定 本案例,父类固定Employee,但是子类可以无限?
* ? extends Employee 限制的是父类, 上限限定, 可以传递Employee,传递他的子类对象
* ? super Employee 限制的是子类, 下限限定, 可以传递Employee,传递他的父类对象
*/
public static void iterator(ArrayList<? extends Employee> array){
Iterator<? extends Employee> it = array.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
//获取出的next() 数据类型,是什么Employee
Employee e = it.next();
e.work();
}
}
}


