python中的运算符及表达式及常用内置函数
知识内容:
1.运算符与表达式
2.for\while初步了解
3.常用内置函数
一、运算符与表达式
python与其他语言一样支持大多数算数运算符、关系运算符、逻辑运算符以及位运算符,并且有和大多数语言一样的运算符优先级。除此之外,还有一些是python独有的运算符。
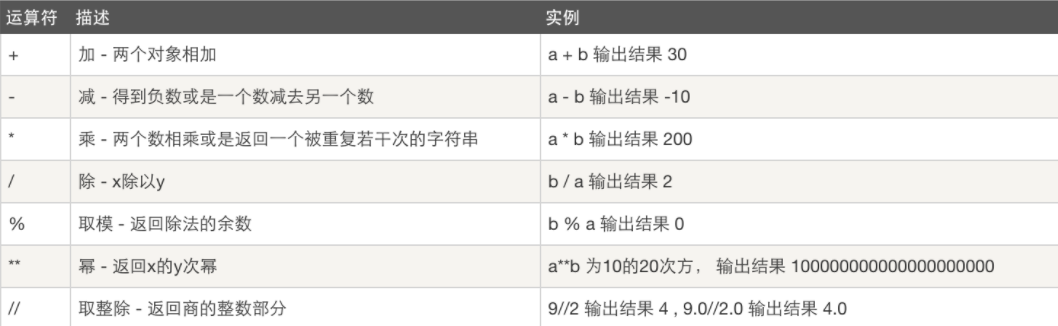
1.算术运算符
a=10, b=20
2.比较运算符
a=10, b=20
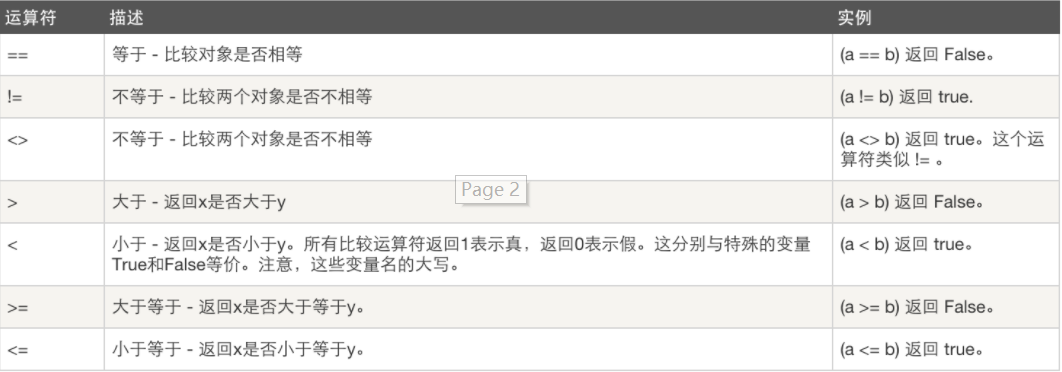
注: 在python3中不存在<>,只在python2中存在<>
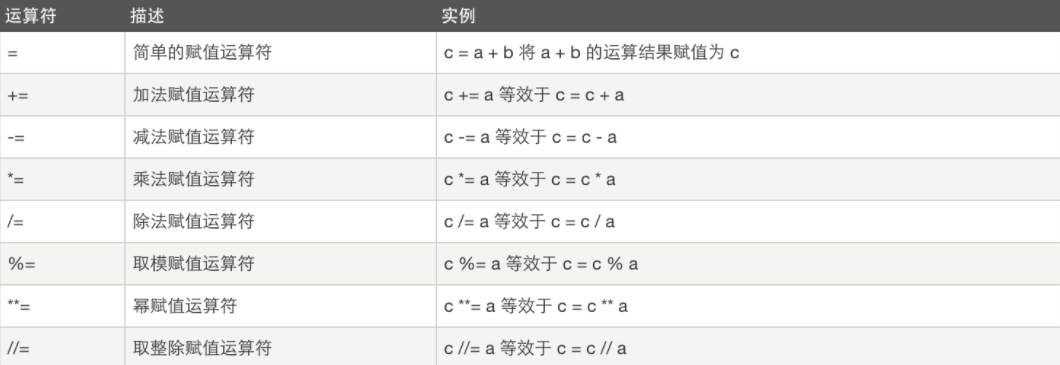
3.赋值运算符
4.逻辑运算符
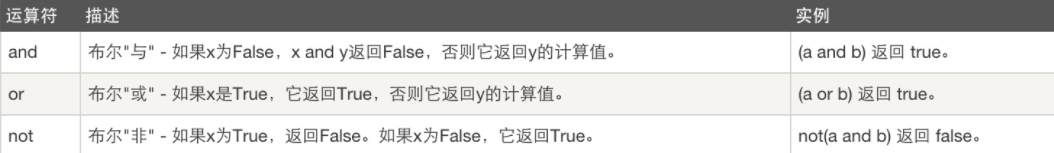
and两边条件都成立(或都为True)时返回True,而or两边条件只要有一个成立(或只要一个为True)时就返回True
not就是取反,原值为True,not返回False,原值为False,not返回True
1 >>> a = 10 2 >>> b = 20 3 >>> a 4 10 5 >>> b 6 20 7 >>> a == 10 and b == 20 8 True 9 >>> a == 10 and b == 21 10 False 11 >>> a == 10 or b == 21 12 True 13 >>> a == 11 or b == 20 14 True 15 >>> a == 11 or b == 23 16 False 17 >>> a == 0 18 False 19 >>> not a == 0 20 True
5.成员运算符
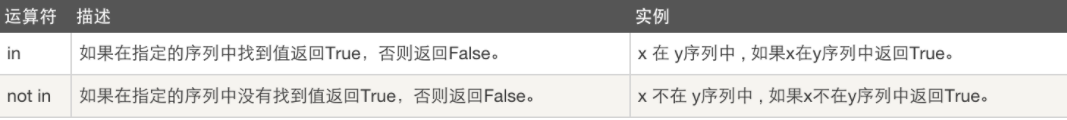
6.身份运算符
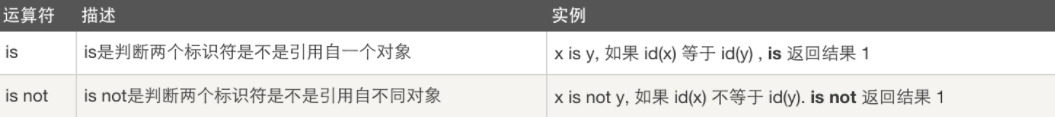
7.位运算
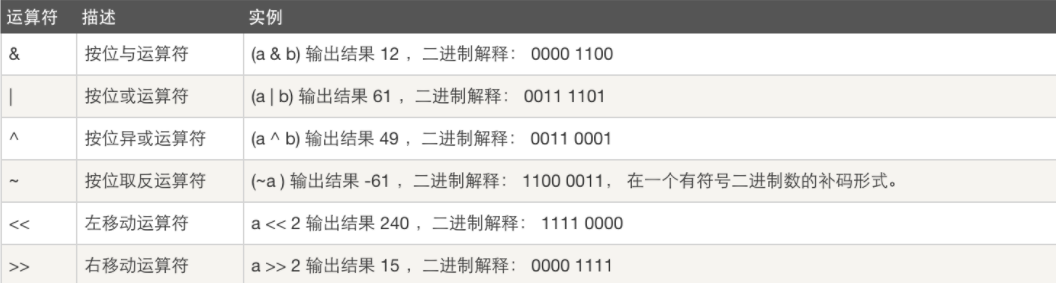
8.运算符优先级
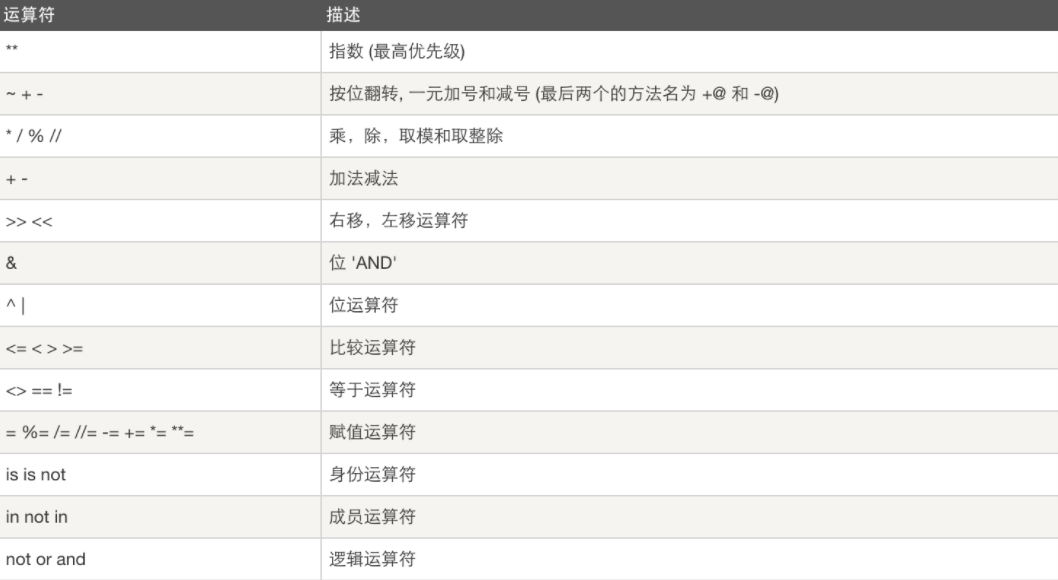
注:
(1)除法在python中有两种运算符: /和//,/在python2中为普通除法(地板除法),/在python3中为真除法,/和//在python2和python3中均为普通除法(地板除法)
示例:

(2) python中很多运算符有多重含义,在程序中运算符的具体含义取决于操作数的类型,将在后面继续介绍。eg: +是一个比较特殊的运算符,除了用于算术加法以外,还可以用于列表、元组、字符串的连接,但不支持不同类型的对象之间相加或连接; *也是其中比较特殊的一个运算符,不仅可以用于数值乘法,还可以用于列表、字符串、元组等类型,当列表、字符串或元组等类型变量与整数就行*运算时,表示对内容进行重复并返回重复后的新对象
示例:

(3)python中的比较运算符可以连用,并且比较字符串和列表也可以用比较运算符
示例:
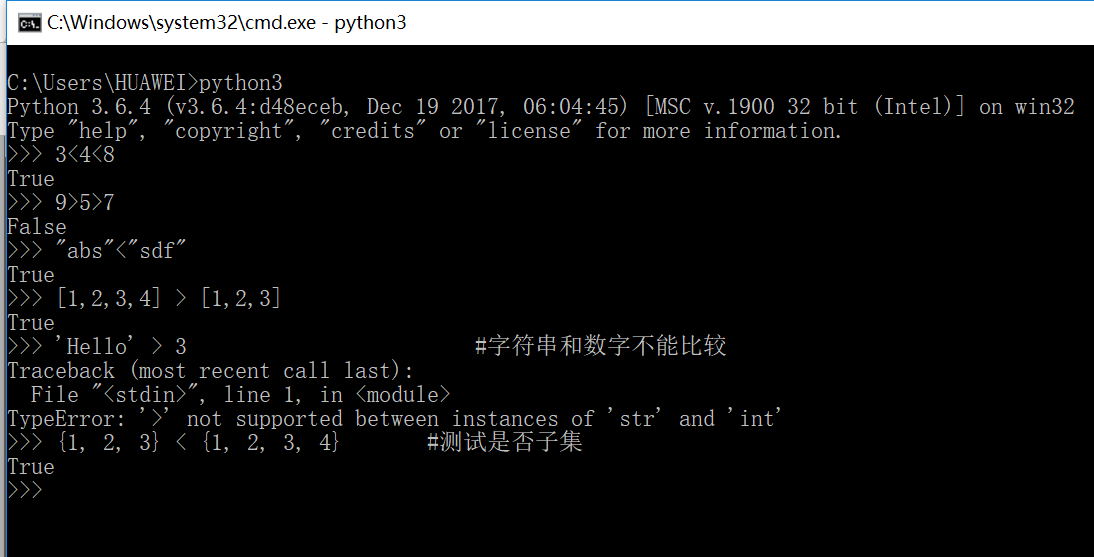
(4)python中没有C/C++中的++、--运算符,可以使用+=、-=来代替
1 >>> a = 5 2 >>> a++ 3 File "<stdin>", line 1 4 a++ 5 ^ 6 SyntaxError: invalid syntax 7 >>> a += 1 8 >>> a 9 6 10 >>> a-- 11 File "<stdin>", line 1 12 a-- 13 ^ 14 SyntaxError: invalid syntax 15 >>> a-=1 16 >>> a 17 5
(5)python3中新增了一个新的矩阵相乘运算符@
示例:

1 import numpy # numpy是用于科学计算的python拓展库需要自行使用pip安装或手动安装 2 3 x = numpy.ones(3) # ones函数用于生成全1矩阵,参数表示矩阵大小 4 m = numpy.eye(3)*3 # eye函数用于生成单元矩阵 5 m[0, 2] = 5 # 设置矩阵上指定位置的值 6 m[2, 0] = 3 7 print(x @ m) 8 9 # 输出结果: [6. 3. 8.]
9.表达式的概念
在python中单个任何类型的对象或常数属于合法表达式,使用上表中的运算符将变量、常量以及对象连接起来的任意组合也属于合法的表达式,请注意逗号(,)在python中不是运算符,而只是一个普通的分隔符
二、for\while初步了解
python中提供了for循环和while循环(注: 在Python中没有do..while循环)
1. for循环
for循环的格式:
for iterating_var in sequence:
statements(s)
2.while循环
while循环的格式:
while 判断条件:
执行语句……
示例:
1 # for 2 # 输出从1到10的整数: 3 for i in range(1, 11): # range(1, 11)是产生从1到10的整数 4 print(i, end=' ') 5 print() # 换行 6 7 # while 8 # 计算1到100的和: 9 i = 0 10 number_sum = 0 11 while i < 100: 12 i = i + 1 13 number_sum = number_sum + i 14 print(number_sum) 15 16 # 输出结果: 17 # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 18 # 5050
三、常用内置函数
1. 内置函数的概念
python中的内置函数不用导入任何模块即可直接使用,可以在命令行中使用dir(__builtins__)查看所有内置函数
查看所有内置函数:

1 # __author__ = "wyb" 2 # date: 2018/3/7 3 4 for item in dir(__builtins__): 5 print(item) 6 # python3.6上运行的结果: 7 # ArithmeticError 8 # AssertionError 9 # AttributeError 10 # BaseException 11 # BlockingIOError 12 # BrokenPipeError 13 # BufferError 14 # BytesWarning 15 # ChildProcessError 16 # ConnectionAbortedError 17 # ConnectionError 18 # ConnectionRefusedError 19 # ConnectionResetError 20 # DeprecationWarning 21 # EOFError 22 # Ellipsis 23 # EnvironmentError 24 # Exception 25 # False 26 # FileExistsError 27 # FileNotFoundError 28 # FloatingPointError 29 # FutureWarning 30 # GeneratorExit 31 # IOError 32 # ImportError 33 # ImportWarning 34 # IndentationError 35 # IndexError 36 # InterruptedError 37 # IsADirectoryError 38 # KeyError 39 # KeyboardInterrupt 40 # LookupError 41 # MemoryError 42 # ModuleNotFoundError 43 # NameError 44 # None 45 # NotADirectoryError 46 # NotImplemented 47 # NotImplementedError 48 # OSError 49 # OverflowError 50 # PendingDeprecationWarning 51 # PermissionError 52 # ProcessLookupError 53 # RecursionError 54 # ReferenceError 55 # ResourceWarning 56 # RuntimeError 57 # RuntimeWarning 58 # StopAsyncIteration 59 # StopIteration 60 # SyntaxError 61 # SyntaxWarning 62 # SystemError 63 # SystemExit 64 # TabError 65 # TimeoutError 66 # True 67 # TypeError 68 # UnboundLocalError 69 # UnicodeDecodeError 70 # UnicodeEncodeError 71 # UnicodeError 72 # UnicodeTranslateError 73 # UnicodeWarning 74 # UserWarning 75 # ValueError 76 # Warning 77 # WindowsError 78 # ZeroDivisionError 79 # __build_class__ 80 # __debug__ 81 # __doc__ 82 # __import__ 83 # __loader__ 84 # __name__ 85 # __package__ 86 # __spec__ 87 # abs 88 # all 89 # any 90 # ascii 91 # bin 92 # bool 93 # bytearray 94 # bytes 95 # callable 96 # chr 97 # classmethod 98 # compile 99 # complex 100 # copyright 101 # credits 102 # delattr 103 # dict 104 # dir 105 # divmod 106 # enumerate 107 # eval 108 # exec 109 # exit 110 # filter 111 # float 112 # format 113 # frozenset 114 # getattr 115 # globals 116 # hasattr 117 # hash 118 # help 119 # hex 120 # id 121 # input 122 # int 123 # isinstance 124 # issubclass 125 # iter 126 # len 127 # license 128 # list 129 # locals 130 # map 131 # max 132 # memoryview 133 # min 134 # next 135 # object 136 # oct 137 # open 138 # ord 139 # pow 140 # print 141 # property 142 # quit 143 # range 144 # repr 145 # reversed 146 # round 147 # set 148 # setattr 149 # slice 150 # sorted 151 # staticmethod 152 # str 153 # sum 154 # super 155 # tuple 156 # type 157 # vars 158 zip
2.python中常见及常用的内置函数
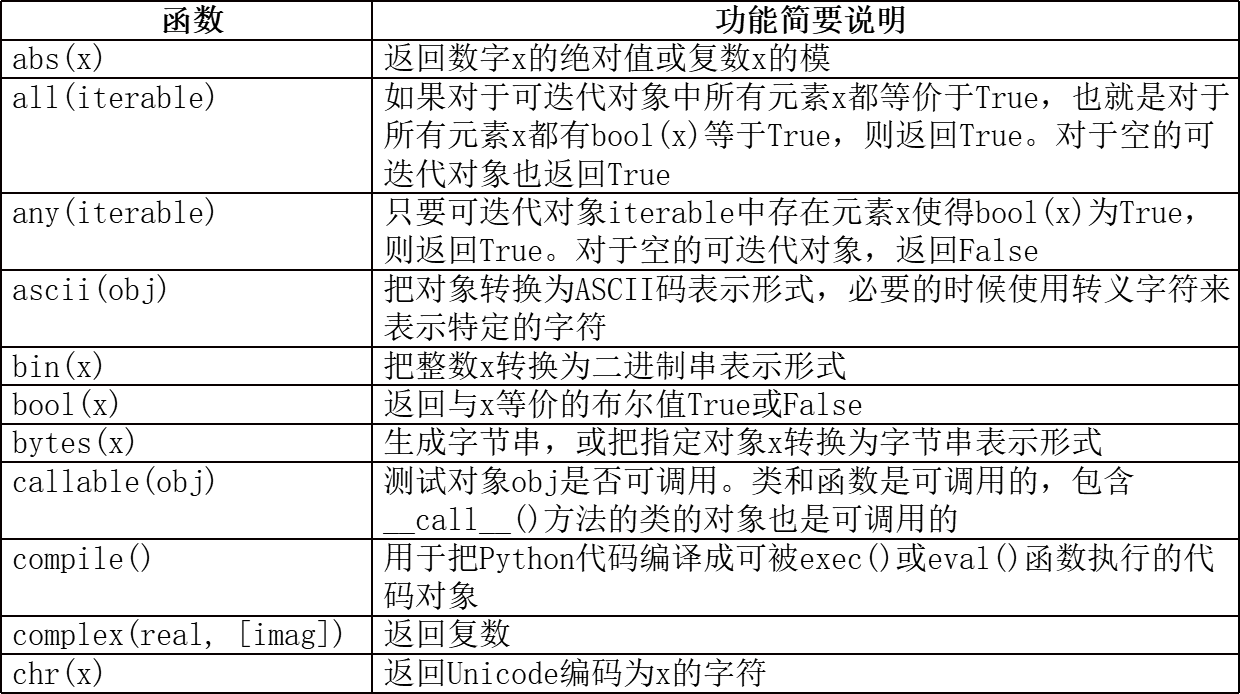
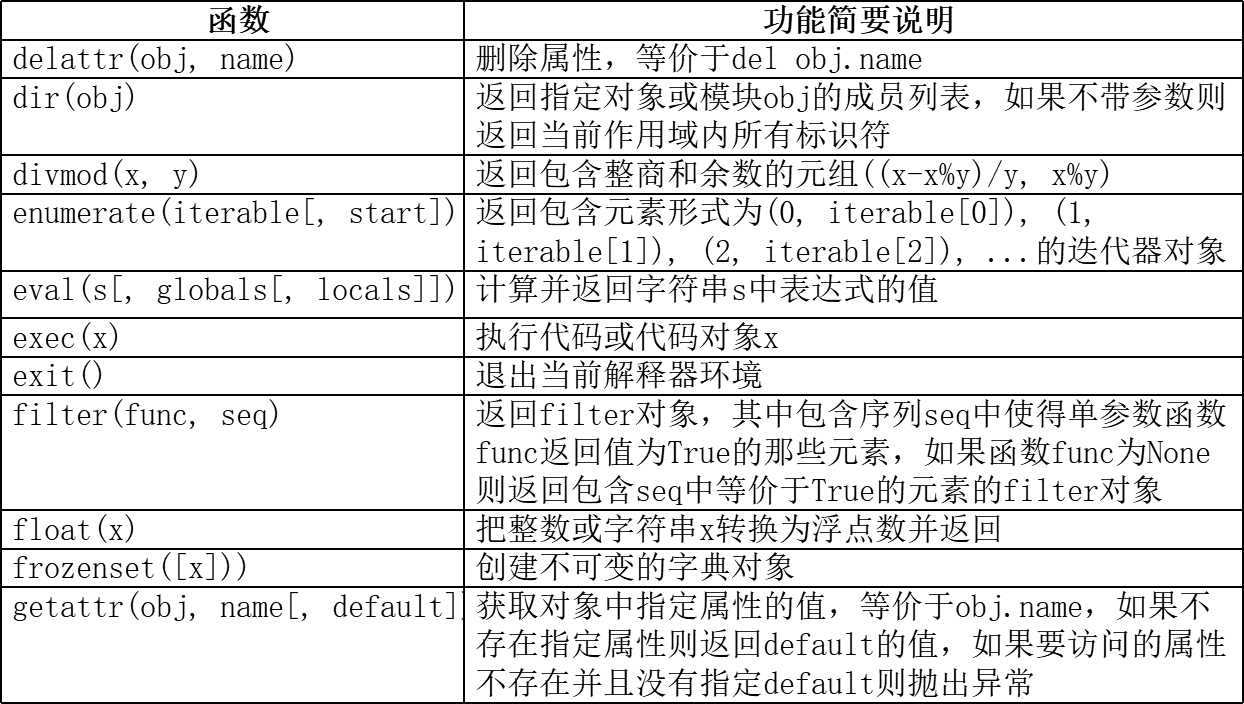
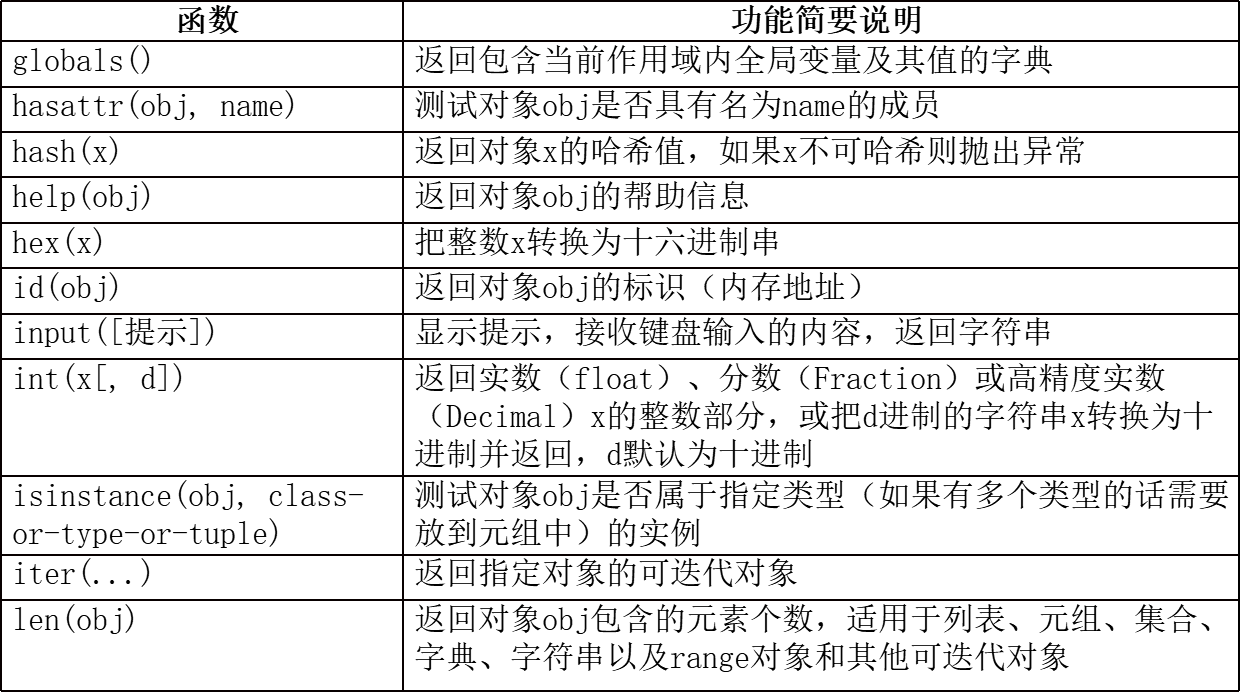

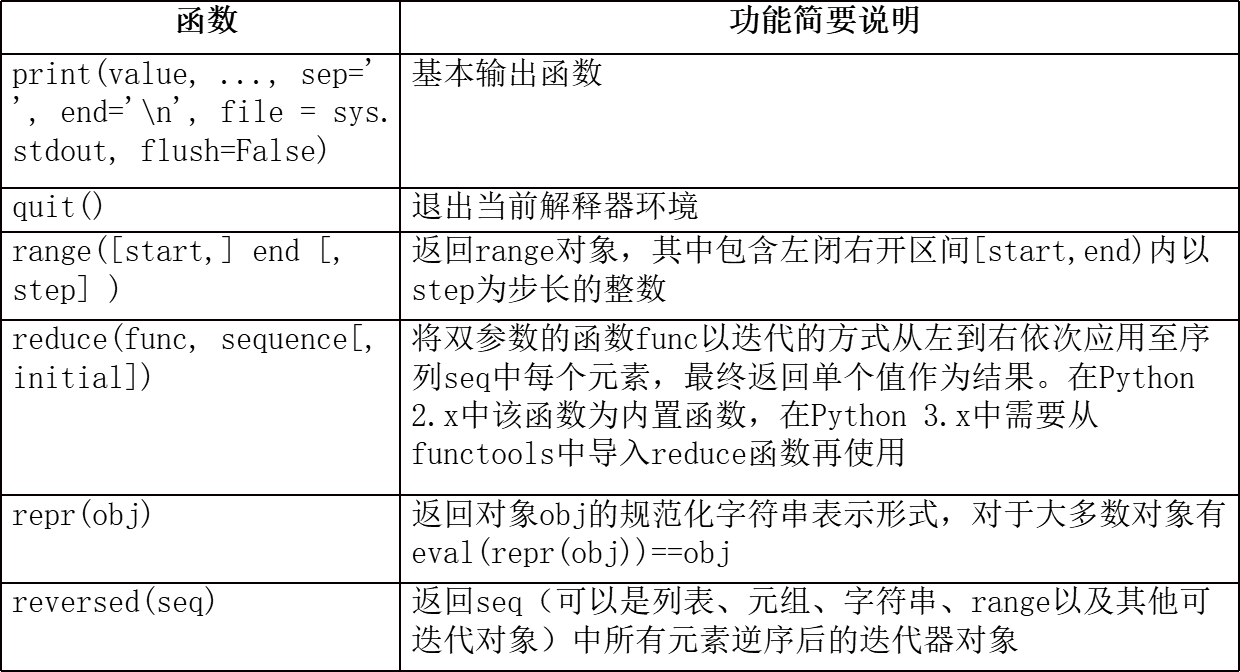
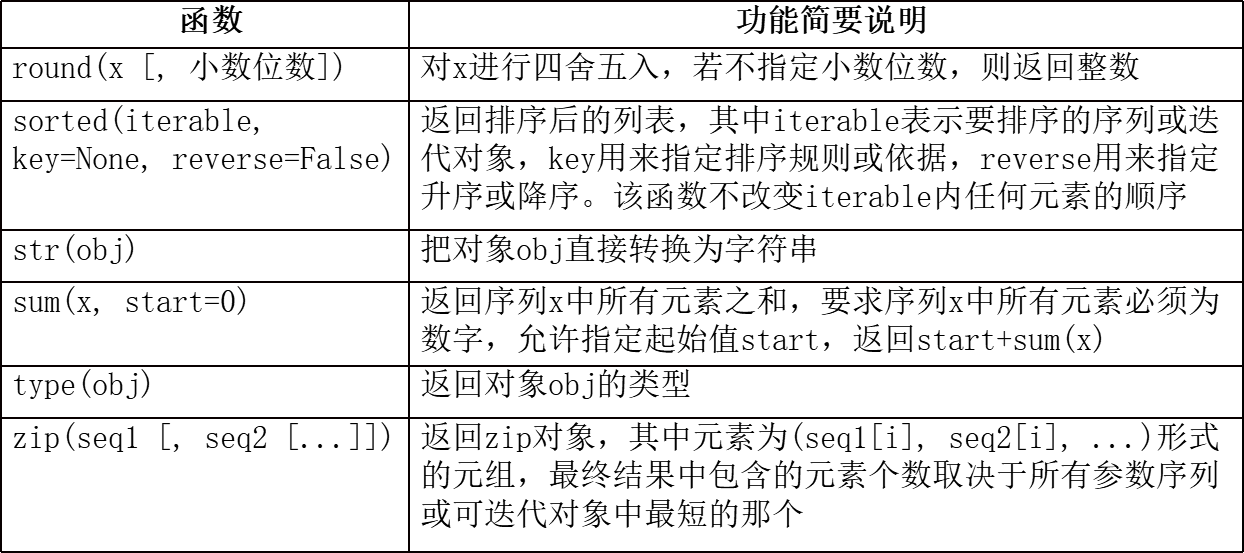
注:
dir()函数可以查看指定模块中包含的所有成员或者指定对象类型所支持的操作;help()函数则返回指定模块或函数的说明文档
常用内置函数示例:

1 # __author__ = "wyb" 2 # date: 2018/3/7 3 4 number = -3 5 print(abs(number)) # 输出结果: 3 6 7 print(all([0, -8, 3])) # 输出结果: False 8 print(any([0, -8, 3])) # 输出结果: True 9 10 value = eval("3+2") # 计算字符串中表达式的值并返回 11 print(value) # 输出结果: 5 12 13 help(print) # 输出结果: print的文档(帮助信息) 14 15 x = 3 16 y = float(x) # 将其他类型转换成浮点型 17 z = str(x) # 将其他类型转换成字符串类型 18 print(x, y, z) # 输出结果: 3 3.0 3 19 print(id(x), id(y), id(z)) # 输出x,y,z的地址信息 20 21 s = "Hello, python!" 22 n = len(s) # 求字符串的长度 23 print(n) # 输出结果: 14 24 25 p = pow(3, 2) # 求3的2次方 26 print(p) # 输出结果: 9 27 28 # zip(): 将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素 29 # 打包成一个元组,然后返回这些元组组成的列表,实例如下: 30 a = [1, 2, 3] 31 b = [4, 5, 6] 32 zipped = zip(a, b) # zipped -> [(1,4),(2,5),(3,6)] 33 print(zipped)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号