Netty 学习笔记(3) ------ ChannelPipeline 和 ChannelHandler
ChannelPipeline通过责任链设计模式组织逻辑代码(ChannelHandler),ChannelHander就如同Servlet的Filter一样一层层处理Channel的读写数据。
ChannelPipeline和ChannelHander的构成
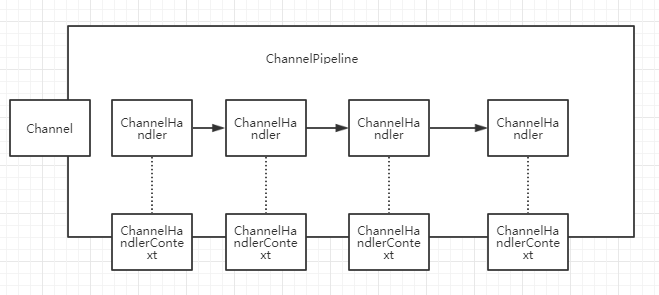
ChannelNetty框架中,一个连接对应一个ChannelChannelPipeline一个Channel绑定一条ChannelPipeline,ChannelPipeline以双向链表的结构组织所属Channel的所有逻辑处理器ChannelHandlerChannelHandler逻辑处理器,ChannelHandler分为ChannelInboundHandler入站处理器(处理读请求)和ChannelOutboundHandler出站处理器(处理写请求)。一个ChannelHander可以添加到多条ChannelPipeline上。ChannelHanderContextChannelHandler添加到一条ChannelPipeline后,该Channelpipeline将创建一个ChannelHandlerContext与ChannelHandler绑定。ChannelHandlerContext能够拿到Channel相关的上下文信息。
ChannelInboundHandler 和 ChannelOutboundHandler
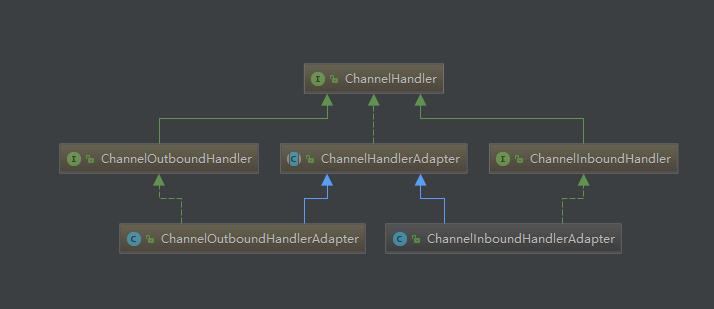
ChannelInboundHandler入站处理器,主要处理读请求的逻辑,它将按照它被添加的顺序处理数据。ChannelOutboundHandler出站处理器,主要处理写请求的逻辑,它将按照被添加的反顺序处理数据。ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter和ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter实现了两大接口的所有功能,默认将事件提交给下一个处理器。
代码例子
入站处理器inboundHandler打印接受数据然后提交给下一个处理器,而出站处理器outboundHander打印写出数据然后提交给下一个处理器,writerHander在有客户端连接成功时写出helloClinet。
public class HanderServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HanderServerDemo server = new HanderServerDemo();
server.init();
}
public void init(){
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.localAddress(8000)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
// inBound,处理读数据的逻辑链
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new InBoundHandlerA());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new InBoundHandlerB());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new InBoundHandlerC());
//channel连接成功,返回hello client
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new WriteHandler());
// outBound,处理写数据的逻辑链
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new OutBoundHandlerA());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new OutBoundHandlerB());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new OutBoundHandlerC());
}
});
serverBootstrap.bind().addListener((future)->{
if(future.isSuccess()){
System.out.println("端口绑定成功");
}else{
System.out.println("端口绑定失败:"+future.cause());
}
});
}
public class InBoundHandlerA extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("InBoundHandlerA: " + msg);
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
}
public class InBoundHandlerB extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("InBoundHandlerB: " + msg);
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
}
public class InBoundHandlerC extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("InBoundHandlerC: " + msg);
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
}
public class WriteHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello client".getBytes()));
}
}
public class OutBoundHandlerA extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println("OutBoundHandlerA: " + msg);
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
}
public class OutBoundHandlerB extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println("OutBoundHandlerB: " + msg);
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
}
public class OutBoundHandlerC extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println("OutBoundHandlerC: " + msg);
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
}
}
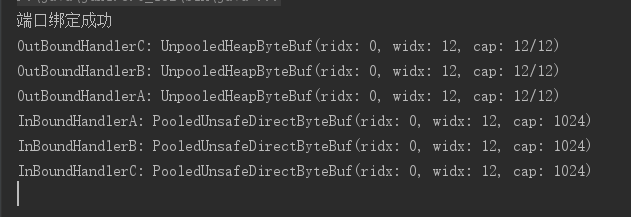
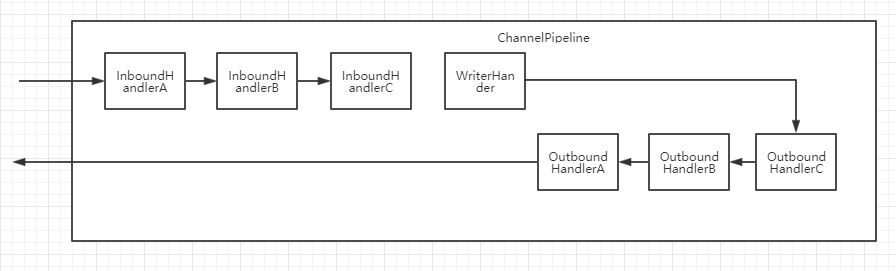
可以看读请求的数据时顺handler添加的顺序处理的,A-->B-->C
而写请求的处理是逆着添加顺序的,C-->B-->A
参考资料
netty in action
Netty 入门与实战:仿写微信 IM 即时通讯系统
一个菜鸟程序员的学习笔记,有问题欢迎指正



