KMP——模板 练手题
1. 洛谷 P3375 【模板】KMP字符串匹配
题目描述
如题,给出两个字符串s1和s2,其中s2为s1的子串,求出s2在s1中所有出现的位置。
为了减少骗分的情况,接下来还要输出子串的前缀数组next。如果你不知道这是什么意思也不要问,去百度搜[kmp算法]学习一下就知道了。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第一行为一个字符串,即为s1(仅包含大写字母)
第二行为一个字符串,即为s2(仅包含大写字母)
输出格式:
若干行,每行包含一个整数,表示s2在s1中出现的位置
接下来1行,包括length(s2)个整数,表示前缀数组next[i]的值。
输入输出样例
ABABABC ABA
1 3 0 0 1
说明
时空限制:1000ms,128M
数据规模:
设s1长度为N,s2长度为M
对于30%的数据:N<=15,M<=5
对于70%的数据:N<=10000,M<=100
对于100%的数据:N<=1000000,M<=1000
样例说明:
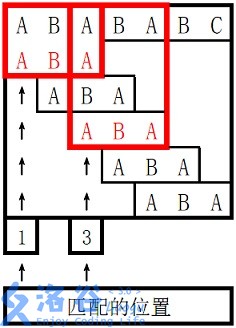
所以两个匹配位置为1和3,输出1、3
血的教训啊,调了一上午的代码,居然错在了输入上,谨记大佬教诲,能不用gets就不用gets!!!
(⊙v⊙)嗯~ 代码1:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 const int N = 1000001; 7 int n,m,nxt[N],j; 8 char s1[N],s2[N]; 9 10 void INT() { 11 nxt[0]=0,nxt[1]=0; 12 for(int i=1; i<m; i++) { 13 j = nxt[i]; 14 while(j>0 && s2[i]!=s2[j]) j=nxt[j]; 15 if(s2[i]==s2[j]) nxt[i+1]=j+1; 16 else nxt[i+1] = 0; 17 } 18 } 19 20 void find() { 21 j=0; 22 for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { 23 while(j>0&&s1[i]!=s2[j]) j=nxt[j]; 24 if(s1[i]==s2[j]) j++; 25 if(j == m) 26 cout<<i-m+2<<endl; 27 } 28 } 29 30 int main() { 31 /*gets(s1); 32 gets(s2);*/ //无情的删去 33 cin>>s1>>s2; 34 n=strlen(s1); m=strlen(s2); 35 INT(); 36 find(); 37 for(int i=1; i<=m; i++) 38 cout<<nxt[i]<<" "; 39 return 0; 40 }
(⊙v⊙)嗯~ 代码2:
算法详解直播间ing
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> using namespace std; string s,p; int nxt[1000003]; void getnxt(string p) { int k=-1,j=0; nxt[0]=-1; int lenp=p.length(); while(j<lenp) { /*①*/if(k==-1||p[j]==p[k]) { j++; //与注释部分作用相同 k++; nxt[j]=k; /* nxt[j]=k+1; k++; */ } /*②*/ else k=nxt[k]; } } void kmp(string s,string p) { int i=0,j=0; int lens=s.length(), lenp=p.length(); while(i<lens) { /*③*/ if(j==-1||s[i]==p[j]) { i++; j++; } /*④*/ else j=nxt[j]; if(j==lenp) { cout<<i-lenp+1<<endl; j=0,i--; } } for(int i=1; i<=lenp; i++) { cout<<nxt[i]<<" "; } return ; } int main() { cin>>s; cin>>p; getnxt(p); kmp(s,p); return 0; }
不懂的,看这里:


2. POJ 3461 Oulipo
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 40182 | Accepted: 16143 |
Description
The French author Georges Perec (1936–1982) once wrote a book, La disparition, without the letter 'e'. He was a member of the Oulipo group. A quote from the book:
Tout avait Pair normal, mais tout s’affirmait faux. Tout avait Fair normal, d’abord, puis surgissait l’inhumain, l’affolant. Il aurait voulu savoir où s’articulait l’association qui l’unissait au roman : stir son tapis, assaillant à tout instant son imagination, l’intuition d’un tabou, la vision d’un mal obscur, d’un quoi vacant, d’un non-dit : la vision, l’avision d’un oubli commandant tout, où s’abolissait la raison : tout avait l’air normal mais…
Perec would probably have scored high (or rather, low) in the following contest. People are asked to write a perhaps even meaningful text on some subject with as few occurrences of a given “word” as possible. Our task is to provide the jury with a program that counts these occurrences, in order to obtain a ranking of the competitors. These competitors often write very long texts with nonsense meaning; a sequence of 500,000 consecutive 'T's is not unusual. And they never use spaces.
So we want to quickly find out how often a word, i.e., a given string, occurs in a text. More formally: given the alphabet {'A', 'B', 'C', …, 'Z'} and two finite strings over that alphabet, a word W and a text T, count the number of occurrences of W in T. All the consecutive characters of W must exactly match consecutive characters of T. Occurrences may overlap.
Input
The first line of the input file contains a single number: the number of test cases to follow. Each test case has the following format:
- One line with the word W, a string over {'A', 'B', 'C', …, 'Z'}, with 1 ≤ |W| ≤ 10,000 (here |W| denotes the length of the string W).
- One line with the text T, a string over {'A', 'B', 'C', …, 'Z'}, with |W| ≤ |T| ≤ 1,000,000.
Output
For every test case in the input file, the output should contain a single number, on a single line: the number of occurrences of the word W in the text T.
Sample Input
3
BAPC
BAPC
AZA
AZAZAZA
VERDI
AVERDXIVYERDIAN
Sample Output
1
3
0
Source
(⊙v⊙)嗯~ 代码:
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 char t[1000001],p[1000001]; 6 int lt,lp,f[1000001],ans,s; 7 void INT() 8 { 9 f[1]=0; 10 for(int i=1;i<lp;i++) 11 { 12 int j=f[i]; 13 while(j&&p[i]!=p[j]) j=f[j]; 14 f[i+1]= p[i]==p[j] ? j+1 : 0; 15 } 16 } 17 void Find() 18 { 19 int j=0; 20 for(int i=0;i<lt;i++) 21 { 22 while(j&&(p[j]!=t[i])) j=f[j]; 23 if(p[j]==t[i]) j++; 24 if(j==lp) ans++; 25 } 26 } 27 int main() 28 { 29 cin>>s; 30 while(s--) { 31 ans=0; 32 memset(f,0,sizeof(f)); 33 cin>>p>>t; 34 lt=strlen(t); 35 lp=strlen(p); 36 INT(); 37 Find(); 38 cout<<ans<<endl; 39 } 40 return 0; 41 }
自己选的路,跪着也要走完!


