多柱汉诺塔可以用Frame–Stewart算法来解决。
The Frame–Stewart algorithm, giving a presumably optimal solution for four (or even more) pegs, is described below:
- Let
 be the number of disks.
be the number of disks. - Let
 be the number of pegs.
be the number of pegs. - Define
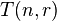 to be the minimum number of moves required to transfer n disks using r pegs
to be the minimum number of moves required to transfer n disks using r pegs
The algorithm can be described recursively:
- For some
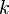 ,
,  , transfer the top
, transfer the top 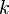 disks to a single peg other than the start or destination pegs, taking
disks to a single peg other than the start or destination pegs, taking 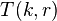 moves.
moves. - Without disturbing the peg that now contains the top
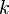 disks, transfer the remaining
disks, transfer the remaining  disks to the destination peg, using only the remaining
disks to the destination peg, using only the remaining 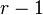 pegs, taking
pegs, taking  moves.
moves. - Finally, transfer the top
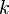 disks to the destination peg, taking
disks to the destination peg, taking 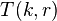 moves.
moves.
The entire process takes  moves. Therefore, the count
moves. Therefore, the count 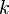 should be picked for which this quantity is minimum.
should be picked for which this quantity is minimum.
This algorithm (with the above choice for 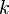 ) is presumed to be optimal, and no counterexamples are known.
) is presumed to be optimal, and no counterexamples are known.
4柱的可以借助3柱的来完成,5柱的借助4柱的来完成,等等。下面是从网上找来的4柱汉诺塔的分析过程。
四塔问题:设有A,B,C,D四个柱子(有时称塔),在A柱上有由小到大堆放的n个盘子,如图所示。
今将A柱上的盘子移动到D柱上去。可以利用B,C柱作为工作栈用,移动的规则如下:
①每次只能移动一个盘子。
②在移动的过程中,小盘子只能放到大盘子的上面。
设计并实现一个求解四塔问题的动态规划算法,并分析时间和空间复杂性。
算法思想:
用如下算法移动盘子(记为FourPegsHanoi):
1)、将A柱上n个盘子划分为上下两部分,下方部分共有k(1≤k≤n)个盘子,上方部分共有n - k个盘子。
2)、将A柱上面部分n–k个盘子使用FourPegsHanoi算法经过C、D柱移至B柱。
3)、将A柱剩余的k个盘子使用ThreePegsHanoi算法经过C柱移至D柱。
4)、将B柱上的n–k个盘子使用FourPegsHanoi算法经过A、C柱移至D柱。
ThreePegsHanoi算法如下(设三个柱子分别为A、B、C,A柱上共有k个盘子):
1)、将A柱上方k-1个盘子使用ThreePegsHanoi算法经过B柱移至C柱。
2)、将C柱上最后一个盘子直接移至C盘。
3)、将B柱上k-1个盘子使用ThreePegsHanoi算法经过A柱移至C柱。
算法步骤:
根据动态规划的四个步骤,求解如下:
1)、最优子结构性质:
四柱汉诺塔问题的最优解是用最少的移动次数将A柱上的盘子全部移到D柱上。当盘子总数为i时,我们不妨设使用FourPegsHanoi的最少移动次数为f(i)。相应的ThreePegsHanoi 算法移动次数为g(k),由于g(k)=2g(k-1)+1=2k -1,当k确定时,g(k)也是不变的。
f(i)为最优解时,其子问题f(i-k)也必为最优解。如果f(i-k)不是最优解,那么存在f’(i-k) < f(i-k)。用f’(i-k)替换f(i-k)将产生一个比f(i)更优的解。这与f(i)为最优解是矛盾的。所以本问题具有最优子结构性质。
2)、递归地定义问题的最优解:
根据上述FourPegsHanoi算法得到最少移动次数f(i):
通过这个表达式我们可以知道,k取那个值时f(i)的值,也就是说,不用具体操作,就可以知道移动的最少次数,并且知道k的值,所以在算法实现时,求出k的值是非常重要的。下面的代码就是用来求k的。
{
int min = -1;
moves[0][0] = 0;
splitter[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<= m_Plates;i++)
{
min = 1000000000;
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
moves[i][j] = 2*moves[i-j][splitter[i-j]] -1 + (2<<(j-1)) ;
if(moves[i][j] < min)
{
min = moves[i][j];
splitter[i] = j;
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=m_Plates;i++)
cout<<splitter[i]<<endl;
return moves[m_Plates][splitter[m_Plates]];
}
时间空间复杂度分析:
1、时间复杂度
MinMovements算法的时间复杂度为:
T(n) = 1 + 2 + ... + n = n(n+1)/2 = O(n2)
2、空间复杂度
MinMovements算法占用的空间为m 和 s数组的大小:
即 (n+1)2 + (n+1) = O(n2)
通过分析m数组中记录了一些与结果不相关的数据,所以通过对MinMovements进行改进,可使占用空间减小为O(n)。





【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步