各类基本排序算法总结
各类排序实现代码:

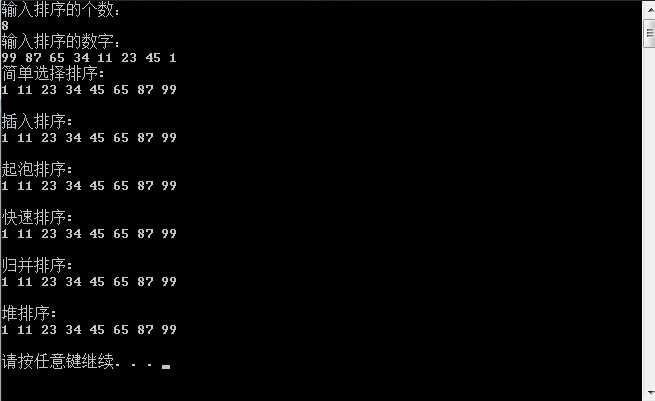
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <math.h> 3 #include <queue> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <stack> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <string> 8 #include <cstring> 9 #include <algorithm> 10 #include <malloc.h> 11 #include <time.h> 12 #include <iostream> 13 using namespace std; 14 15 int a[1010],b[1010]; 16 void Selectsort(int a[],int p)//简单选择排序 17 { 18 int n; 19 int m=p; 20 for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ //选择第i个小的记录,并交换到位 21 int j=i; 22 for(int k = i+1; k < m; k++){ //在a[i...m]中选择最小的记录 23 if(a[k] < a[j]) 24 j=k; 25 } 26 if(i != j){ 27 n=a[j]; a[j]=a[i]; a[i]=n; //与第i个记录交换 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 32 void Insertsort(int a[],int p)//插入排序 33 { 34 int m=p; 35 int j; 36 for(int i = 2; i < p; i++){ 37 if(a[i] < a[i-1]){ //当“<”时,才需将a[i]插入有序子表 38 a[0]=a[i]; //复制为哨兵 39 for(j = i-1; a[0] < a[j]; --j){ 40 a[j+1]=a[j]; //记录后移 41 } 42 a[j+1]=a[0]; //插入到正确位置 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 47 void Bubblesort(int a[],int p)//起泡排序 48 { 49 int n; 50 int m=p; 51 while(m > 1){ //表明上一趟曾进行过记录的交换 52 int lastindex=1; 53 for(int j=1; j < m; j++){ 54 if(a[j-1] > a[j]){ 55 n=a[j]; a[j]=a[j+1]; a[j+1]=n; //互换记录 56 lastindex=j; 57 } 58 } 59 m=lastindex; //一趟排序中无序序列中最后一个记录的位置 60 } 61 } 62 63 void Qsort(int *a, int left, int right)//快速排序 64 { 65 if(left >= right)/*如果左边索引大于或者等于右边的索引就代表已经整理完成一个组了*/ 66 { 67 return ; 68 } 69 int i = left; 70 int j = right; 71 int key = a[left]; 72 73 while(i < j) /*控制在当组内寻找一遍*/ 74 { 75 while(i < j && key <= a[j]) 76 /*而寻找结束的条件就是,1,找到一个小于或者大于key的数(大于或小于取决于你想升 77 序还是降序)2,没有符合条件1的,并且i与j的大小没有反转*/ 78 { 79 j--;/*向前寻找*/ 80 } 81 82 a[i] = a[j]; 83 /*找到一个这样的数后就把它赋给前面的被拿走的i的值(如果第一次循环且key是 84 a[left],那么就是给key)*/ 85 86 while(i < j && key >= a[i]) 87 /*这是i在当组内向前寻找,同上,不过注意与key的大小关系停止循环和上面相反, 88 因为排序思想是把数往两边扔,所以左右两边的数大小与key的关系相反*/ 89 { 90 i++; 91 } 92 93 a[j] = a[i]; 94 } 95 96 a[i] = key;/*当在当组内找完一遍以后就把中间数key回归*/ 97 Qsort(a, left, i - 1);/*最后用同样的方式对分出来的左边的小组进行同上的做法*/ 98 Qsort(a, i + 1, right);/*用同样的方式对分出来的右边的小组进行同上的做法*/ 99 /*当然最后可能会出现很多分左右,直到每一组的i = j 为止*/ 100 } 101 102 void Merge(int sourceArr[],int tempArr[],int start,int mid,int end)//归并排序 103 { 104 int i = start,j=mid+1,k = start; 105 while(i != mid+1 && j != end+1) 106 { 107 if(sourceArr[i] > sourceArr[j]) 108 tempArr[k++] = sourceArr[i++]; 109 else 110 tempArr[k++] = sourceArr[j++]; 111 } 112 while(i != mid+1) 113 tempArr[k++] = sourceArr[i++]; 114 while(j != end+1) 115 tempArr[k++] = sourceArr[j++]; 116 for(i = start; i <= end; i++) 117 sourceArr[i] = tempArr[i]; 118 } 119 120 void MergeSort(int sourceArr[],int tempArr[],int start,int end)//内部使用递归 121 { 122 int mid; 123 if(start > end) 124 { 125 mid = (start + end)/2; 126 MergeSort(sourceArr,tempArr,start,mid); 127 MergeSort(sourceArr,tempArr,mid+1,end); 128 Merge(sourceArr,tempArr,start,mid,end); 129 } 130 } 131 132 void HAdjust(int array[],int i,int nLength) 133 { 134 int nChild; 135 int nTemp; 136 for(;2*i+1<nLength;i=nChild) 137 { 138 //子结点的位置=2*(父结点位置)+1 139 nChild=2*i+1; 140 //得到子结点中较大的结点 141 if(nChild<nLength-1&&array[nChild+1]>array[nChild])++nChild; 142 //如果较大的子结点大于父结点那么把较大的子结点往上移动,替换它的父结点 143 if(array[i]<array[nChild]) 144 { 145 nTemp=array[i]; 146 array[i]=array[nChild]; 147 array[nChild]=nTemp; 148 } 149 else break; //否则退出循环 150 } 151 } 152 153 void HSort(int array[],int length)//堆排序算法 154 { 155 int i; 156 //调整序列的前半部分元素,调整完之后第一个元素是序列的最大的元素 157 //length/2-1是最后一个非叶节点,此处"/"为整除 158 for(i=length/2-1;i>=0;--i) 159 HAdjust(array,i,length); 160 //从最后一个元素开始对序列进行调整,不断的缩小调整的范围直到第一个元素 161 for(i=length-1;i>0;--i) 162 { 163 //把第一个元素和当前的最后一个元素交换, 164 //保证当前的最后一个位置的元素都是在现在的这个序列之中最大的 165 array[i]=array[0]^array[i]; 166 array[0]=array[0]^array[i]; 167 array[i]=array[0]^array[i]; 168 //不断缩小调整heap的范围,每一次调整完毕保证第一个元素是当前序列的最大值 169 HAdjust(array,0,i); 170 } 171 } 172 173 void Input(int a[],int p) 174 { 175 for (int i = 0; i < p; ++i) 176 { 177 cin>>a[i]; 178 } 179 } 180 181 void Output(int a[],int p) 182 { 183 for (int i = 0; i < p-1; ++i) 184 { 185 cout<<a[i]<<" "; 186 } 187 cout<<a[p-1]<<endl; 188 } 189 int main() 190 { 191 int n; 192 193 cout<<"输入排序的个数:"<<endl; 194 cin>>n; 195 196 cout<<"输入排序的数字:"<<endl; 197 Input(a,n); 198 199 cout<<"简单选择排序:"<<endl; 200 Selectsort(a,n); 201 Output(a,n); 202 cout<<endl; 203 204 cout<<"插入排序:"<<endl; 205 Insertsort(a,n); 206 Output(a,n); 207 cout<<endl; 208 209 cout<<"起泡排序:"<<endl; 210 Bubblesort(a,n); 211 Output(a,n); 212 cout<<endl; 213 214 cout<<"快速排序:"<<endl; 215 Qsort(a, 0, n-1);/*这里原文第三个参数要减1否则内存越界*/ 216 Output(a,n); 217 cout<<endl; 218 219 cout<<"归并排序:"<<endl; 220 MergeSort(a,b,0,n-1); 221 Output(a,n); 222 cout<<endl; 223 224 cout<<"堆排序:"<<endl; 225 HSort(a,n); 226 Output(a,n); 227 cout<<endl; 228 return 0; 229 }
结论:
排序方法 平均时间 最坏时间 辅助存储
简单排序 O(n2) O(n2) O(1)
快速排序 O(nlogn) O(n2) O(logn)
堆排序 O(nlogn) O(nlogn) O(1)
归并排序 O(nlogn) O(nlogn) O(n)
基数排序 O(d(n+rd)) O(d(n+rd)) O(rd)
PS:基数排序见下一篇随笔
直接插入排序、冒泡排序为简单排序,希尔排序、堆排序、快速排序为不稳定排序
一、时间性能
按平均的时间性能来分,有三类排序方法:
时间复杂度为O(nlogn)的方法有:快速排序、堆排序和归并排序,其中以快速排序为最好;
时间复杂度为O(n2)的有:直接插入排序、起泡排序和简单选择排序,其中以直接插入为
最好,特别是对那些对关键字近似有序的记录序列尤为如此;
时间复杂度为O(n)的排序方法只有,基数排序。
当待排记录序列按关键字顺序有序时,直接插入排序和起泡排序能达到O(n)的时间复杂度;而对于快速排序而言,这是最不好的情况,此时的时间性能蜕化为O(n2),因此是应该尽量避免的情况。 简单选择排序、堆排序和归并排序的时间性能不随记录序列中关键字的分布而改变。
二、空间性能
指的是排序过程中所需的辅助空间大小。
1. 所有的简单排序方法(包括:直接插入、起泡和简单选择)和堆排序的空间复杂度为O(1);
2. 快速排序为O(logn),为栈所需的辅助空间;
3. 归并排序所需辅助空间最多,其空间复杂度为O(n );
4.链式基数排序需附设队列首尾指针,则空间复杂度为O(rd )。
三、排序方法的稳定性能
1. 稳定的排序方法指的是,对于两个关键字相等的记录,它们在序列中的相对位置,在排序之前和经过排序之后,没有改变。
2. 当对多关键字的记录序列进行LSD方法排序时,必须采用稳定的排序方法。
3. 对于不稳定的排序方法,只要能举出一个实例说明即可。
4. 快速排序和堆排序是不稳定的排序方法



