pydensecrf的使用
参考:https://github.com/lucasb-eyer/pydensecrf
1.使用
对于图像来说,最简单的使用该库的方法是使用DenseCRF2D类:
import numpy as np import pydensecrf.densecrf as dcrf d = dcrf.DenseCRF2D(640, 480, 5) # width, height, nlabels
2.一元势 Unary potential
你可以使用下面的方法设置固定的一元势
一元势即网络预测得到的结果,进行-np.log(py)等操作
U = np.array(...) # Get the unary in some way. print(U.shape) # -> (5, 480, 640) print(U.dtype) # -> dtype('float32') U = U.reshape((5,-1)) # Needs to be flat. d.setUnaryEnergy(U) # Or alternatively: d.setUnary(ConstUnary(U))
记住U应该是负的log概率,所以如果你用概率py,别忘了执行U = -np.log(py)
需要在一元势上进行reshape是我想要修复的API缺陷,但是如果不引入对numpy的显式依赖,我不知道如何解决这个问题。
注意,nlabel维度是这里reshape之前的第一个维度;如果不是这样的话,你可能需要在reshape之前把nlabel移到前面,即U.shape的结果应该为(5, 480, 640),就像这样:
print(U.shape) # -> (480, 640, 5) U = U.transpose(2, 0, 1).reshape((5,-1))
1)Getting a Unary
得到 unary potentials有两种常见的方法:
1)由人类或其他过程产生的硬标签。该方法由from pydensecrf.utils import unary_from_labels实现
2)由概率分布计算得到,例如深度网络的softmax输出。即我们之前先对图片使用训练好的网络预测得到最终经过softmax函数得到的分类结果,这里需要将这个结果转成一元势
对此,请参阅from pydensecrf.utils import unary_from_softmax
1)unary_from_labels(labels, n_labels, gt_prob, zero_unsure=True)函数的使用
简单分类器,该分类器50%确定注释(即从训练好的网络预测img后得到的结果)是正确的。(与推理示例中相同)。
参数:
- labels: numpy.array;标签label映射,即数据的形状的数组,其中每个唯一值对应于一个标签,一种像素值对应一种标签。
- n_labels: int;标签的总数。如果' zero_unsure'参数为True(默认值),这个数字不应该包括' 0 '标签,因为' 0 '不是一个标签!
- gt_prob: float;基本事实的确定性(必须在(0,1)之内)。
- zero_unsure: bool;如果“True”,则将标签值“0”视为“可能是任何东西”,即具有此值的项将得到一致的一元概率,不将其当作标签。如果“False”,不要特别对待值“0”,而是像对待任何其他类一样对待它。
2)unary_from_softmax(sm, scale=None, clip=1e-5)函数的使用
将softmax类概率转换为一元势(每个节点的NLL)。
即我们之前先对图片使用训练好的网络预测得到最终经过softmax函数得到的分类结果,这里需要将这个结果转成一元势
参数
- sm: numpy.array ,第一个维度是类的softmax的输出,其他所有维度都是flattend。这意味着“sm.shape[0] == n_classes”。
- scale: float,softmax输出的确定性(默认为None),需要值在(0,1]。如果不为None,则softmax输出被缩放到从[0,scale]概率的范围。
- clip: float,将概率裁剪到的最小值。这是因为一元函数是概率的负对数,而log(0) = inf,所以我们需要把0概率裁剪成正的值。
在这里因为scale=None,clip=None,所以这个函数的作用其实只进行了下面的操作:
-np.log(sm).reshape([num_cls, -1]).astype(np.float32)
构建好一元势后需要调用:
d.setUnaryEnergy(U)
将该一元势添加到CRF中
3.Pairwise potentials(二元势)
二维情况下,增加最常见的二元势有两种实用方法:
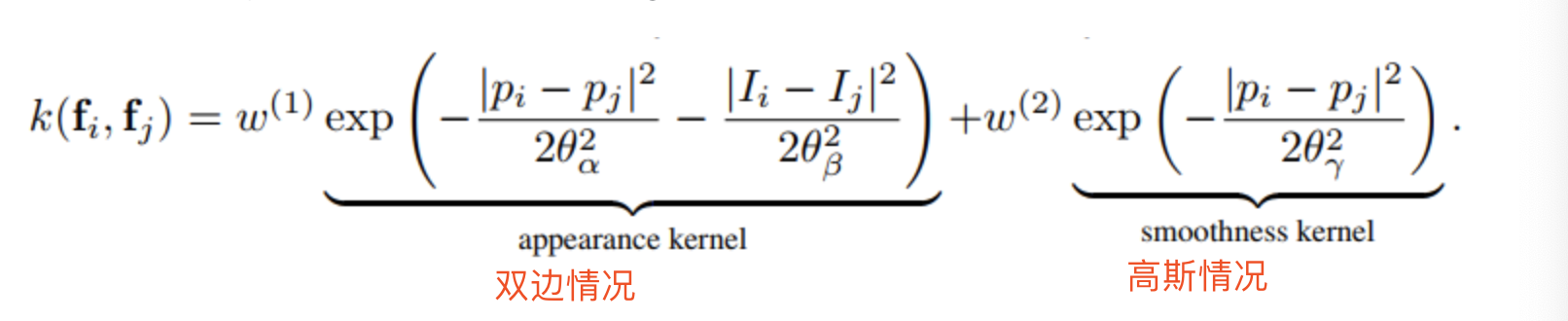
二元势即用于描述像素点和像素点之间的关系,鼓励相似像素分配相同的标签,而相差较大的像素分配不同的标签。这个相似的定义与颜色值srgb和实际相对距离sxy相关,所以CRF能够使图片尽量在边界处分割。
- d.addPairwiseGaussian这个函数创建的是颜色无关特征,这里只有位置特征(只有参数实际相对距离sxy),并添加到CRF中
- d.addPairwiseBilateral这个函数根据原始图像img创建颜色相关和位置相关特征并添加到CRF中,特征为(x,y,r,g,b)
# This adds the color-independent term, features are the locations only. d.addPairwiseGaussian(sxy=(3,3), compat=3, kernel=dcrf.DIAG_KERNEL, normalization=dcrf.NORMALIZE_SYMMETRIC) # This adds the color-dependent term, i.e. features are (x,y,r,g,b). # im is an image-array, e.g. im.dtype == np.uint8 and im.shape == (640,480,3) d.addPairwiseBilateral(sxy=(80,80), srgb=(13,13,13), rgbim=im, compat=10, kernel=dcrf.DIAG_KERNEL, normalization=dcrf.NORMALIZE_SYMMETRIC)
这两种方法都有快捷方式和默认参数,因此最常见的用例可以简化为:
d.addPairwiseGaussian(sxy=3, compat=3) d.addPairwiseBilateral(sxy=80, srgb=13, rgbim=im, compat=10)
im即image
参数映射到本文中的参数如下:高斯情况下的sxy为$\theta_{\gamma}$(即Θγ),双边情况下,sxy和srgb分别映射到$\theta_{\alpha}$(即Θα)和$\theta_{\beta}$(即ΘΒ)。names是“x/y标准偏差”(x/y standard-deviation,sxy)和“rgb标准偏差”(rgb standard-deviation,srgb)的简写,公式为:
1)Non-RGB bilateral
一个重要的警告是,addPairwiseBilateral只适用于RGB图像,即三个通道。如果您的数据与这个简单但常见的情况不同,则需要使用util .create_pairwise_bilateral函数计算你自己的二元能源;有关详细信息,请参阅 generic non-2D case案例。
在examples文件夹中以笔记本的形式提供了一个example of working with Non-RGB data例子。
可见Example of DenseCRF with non-RGB data
2)Compatibilities
compat参数可以是以下任何一种:
- 一个数字,然后使用PottsCompatibility。
- 一个一维数组,然后使用对角兼容性。
- 一个二维数组,然后使用矩阵兼容性。
这些是label-compatibilites µ(xi, xj)的参数可能学到的东西。例如,他们可以指出把鸟的像素误认为天空并不像把猫误认为天空那么糟糕。数组应该有nlabel或(nlabel,nlabel)作为shape和一个float32数据类型。
3)Kernels
kenel参数的可能值有:
CONST_KERNELDIAG_KERNEL(the default)FULL_KERNEL
4)Normalizations
NO_NORMALIZATIONNORMALIZE_BEFORENORMALIZE_AFTERNORMALIZE_SYMMETRIC(the default)
5)Kernel weight权重
4.Inference推理
Q = d.inference(5)
然后MAP预测是:
map = np.argmax(Q, axis=0).reshape((640,480))
如果你对类概率Q感兴趣,你会注意到Q是一个包装好的特征矩阵。本项目的特征包装器实现缓冲接口,可以简单地转换为numpy数组,如下:
proba = np.array(Q)
5.Step-by-step inference一步步推理
如果出于某种原因,你想手动运行推理循环,你可以这样做:
Q, tmp1, tmp2 = d.startInference() for i in range(5): print("KL-divergence at {}: {}".format(i, d.klDivergence(Q))) d.stepInference(Q, tmp1, tmp2)
6.Generic non-2D
DenseCRF类可用于一般(非2d)denseCRFs。它的用法与上面完全一样,只是缺少了特定于2d的二元势addPairwiseGaussian和addPairwiseBilateral。
相反,您需要使用通用的addPairwiseEnergy方法,如下所示:
d = dcrf.DenseCRF(100, 5) # npoints, nlabels feats = np.array(...) # Get the pairwise features from somewhere. print(feats.shape) # -> (7, 100) = (feature dimensionality, npoints) print(feats.dtype) # -> dtype('float32') dcrf.addPairwiseEnergy(feats)
此外,你还可以传递兼容性、内核参数和标准化参数,就像在二维高斯和双边情况下一样。
势函数计算为w*exp(-0.5 * |f_i - f_j|^2)。
当然,首先你要先使用create_pairwise_gaussian和create_pairwise_bilateral,然后才能使用addPairwiseEnergy
1.create_pairwise_gaussian(sdims, shape)函数的使用
创建二元高斯势的Util函数。这适用于所有的图像尺寸。对于2D例子,他等价于DenseCRF2D.addPairwiseGaussian的操作
参数:
- sdims: list or tuple;每个维度的比例因子,等价于DenseCRF2D.addPairwiseGaussian中的sxy参数
- shape: list or tuple;CRF的形状
2.create_pairwise_bilateral(sdims, schan, img, chdim=-1)
创造二元双边势的Util函数。这适用于所有的图像尺寸。对于2D例子,等价于DenseCRF2D.addPairwiseBilateral。
参数:
- sdims: list or tuple;每个维度的比例因子。即DenseCRF2D.addPairwiseBilateral中的“sxy”
- schan: list or tuple;图像中每个通道的比例因子。即DenseCRF2D.addPairwiseBilateral中的“srgb”参数
- img: numpy.array;输入的图片
- chdim: int, optional;这指定了通道维度在图像中的位置。例如,' chdim=2 '用于大小为(240,300,3)的RGB图像,指定维度值3放在索引2的位置处。如果图像没有通道尺寸(例如只有一个通道),则使用' chdim=-1 '
d = dcrf.DenseCRF(img.shape[1] * img.shape[0], n_labels) # get unary potentials (neg log probability) # 得到一元势(即去负对数),labels为对所有像素值标注label后的数组,label类型n_labels=2, U = unary_from_labels(labels, n_labels, gt_prob=0.7, zero_unsure=HAS_UNK) #U.shape为(2, 76800),即(n_labels,len(labels)) d.setUnaryEnergy(U) # This creates the color-independent features and then add them to the CRF feats = create_pairwise_gaussian(sdims=(3, 3), shape=img.shape[:2]) d.addPairwiseEnergy(feats, compat=3, kernel=dcrf.DIAG_KERNEL, normalization=dcrf.NORMALIZE_SYMMETRIC) # This creates the color-dependent features and then add them to the CRF feats = create_pairwise_bilateral(sdims=(80, 80), schan=(13, 13, 13), img=img, chdim=2) d.addPairwiseEnergy(feats, compat=10, kernel=dcrf.DIAG_KERNEL, normalization=dcrf.NORMALIZE_SYMMETRIC)
1)Pairwise potentials for N-D
用户@markusnagel编写了几个numpy函数,将两个经典的二维图像二元势(高斯和双边)推广到任意维数:create_pairwise_gaussian和create_pairwise_bilateral。
你可以从from pydensecrf.utils import create_pairwise_gaussian访问它们,然后查看它们的文档去了解如何使用它们。
7.Learning
这里有一个供初学者参考的指针:第24期。我们需要包装梯度和获取/设置参数。但是,我们还需要对这些做一些事情,最有可能的是从optimization.cpp调用minimizeLBFGS。遵循原始代码中包含的学习示例应该相对简单。



