纸上谈兵: 队列 (queue)
作者:Vamei 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei 欢迎转载,也请保留这段声明。谢谢!
队列(queue)是一个简单而常见的数据结构。队列也是有序的元素集合。队列最大的特征是First In, First Out (FIFO,先进先出),即先进入队列的元素,先被取出。这一点与栈(stack)形成有趣的对比。队列在生活中很常见,排队买票、排队等车…… 先到的人先得到服务并离开队列,后来的人加入到队列的最后。队列是比较公平的分配有限资源的方式,可以让队列的人以相似的等待时间获得服务。

队列支持两个操作,队首的元素离开队列(dequeue),和新元素加入队尾(enqueue)。
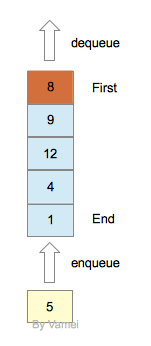
队列
队列在计算机中应用很广泛。一个经典的应用是消息队列(参考Linux进程间通信),实际上就是利用队列来分配有限的进程。还有FIFO文件(哦,你可以看到,这种文件叫做FIFO,肯定是和队列有关),用以实现管道传输。再比如,我们将多个打印任务发送给打印机,打印机也是使用队列来安排任务的顺序。
队列的C实现 (基于表)
和栈相似,队列也可以有多种实现方式,这里是基于单链表的实现。
与表(list)中的实现方式略有不同的是,这里的head node有两个指针,一个(next)指向下一个元素,一个(end)指向队列的最后一个元素。这样做的目的是方便我们找到队尾,以方便的进行enqueue操作。我们依然可以使用之前定义的表,在需要找到队尾的时候遍历搜索到最后一个元素。

用于队列的表
下面是代码:
/* By Vamei */
/* use single-linked list to implement queue */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node *position;
typedef int ElementTP;
// point to the head node of the list
typedef struct HeadNode *QUEUE;
struct node {
ElementTP element;
position next;
};
/*
* CAUTIOUS: "HeadNode" is different from "node",
* it's another struct
* end: points to the last value in the queue
*/
struct HeadNode {
ElementTP element;
position next;
position end;
};
/*
* Operations
*/
QUEUE init_queue(void);
void delete_queue(QUEUE);
void enqueue(QUEUE, ElementTP);
ElementTP dequeue(QUEUE);
int is_null(QUEUE);
/*
* Test
*/
void main(void)
{
ElementTP a;
int i;
QUEUE qu;
qu = init_queue();
enqueue(qu, 1);
enqueue(qu, 2);
enqueue(qu, 8);
printf("Queue is null? %d\n", is_null(qu));
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
a = dequeue(qu);
printf("dequeue: %d\n", a);
}
printf("Queue is null? %d\n", is_null(qu));
delete_queue(qu);
}
/*
* initiate the queue
* malloc the head node.
* Head node doesn't store valid data
* head->next is the first node in the queue.
*/
QUEUE init_queue(void)
{
QUEUE hnp;
hnp = (QUEUE) malloc(sizeof(struct HeadNode));
hnp->next = NULL; // qu->next is the first node
hnp->end = NULL;
return hnp;
}
/*
* dequeue all elements
* and then delete head node
*/
void delete_queue(QUEUE qu)
{
while(!is_null(qu)) {
dequeue(qu);
}
free(qu);
}
/*
* enqueue a value to the end of the queue
*/
void enqueue(QUEUE qu, ElementTP value)
{
position np, oldEnd;
oldEnd = qu->end;
np = (position) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
np->element = value;
np->next = NULL;
/* if queue is empyt, then oldEnd is NULL */
if (oldEnd) {
oldEnd->next = np;
}
else {
qu->next = np;
}
qu->end = np;
}
/*
* dequeue the first value
*/
ElementTP dequeue(QUEUE qu)
{
ElementTP element;
position first, newFirst;
if (is_null(qu)) {
printf("dequeue() on an empty queue");
exit(1);
}
else {
first = qu->next;
element = first->element;
newFirst = first->next;
qu->next = newFirst;
free(first);
return element;
}
}
/*
* check: queue is empty?
*/
int is_null(QUEUE qu)
{
return (qu->next == NULL);
}
运行结果如下:
Queue is null? 0
dequeue: 1
dequeue: 2
dequeue: 8
Queue is null? 1
总结
队列,FIFO
enqueue, dequeue
欢迎继续阅读“纸上谈兵: 算法与数据结构”系列。
如果你喜欢这篇文章,欢迎推荐。

