JAVA-二叉线索树(Threaded binary tree)
2012-07-10 11:27 coodoing 阅读(1338) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报二叉线索树(Threaded binary tree)基础知识
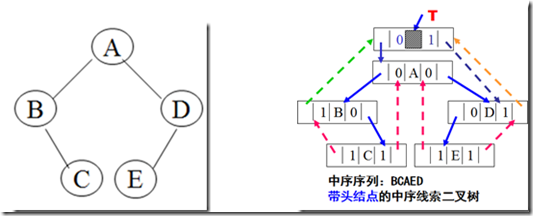
二叉树是一种非线性结构,对二叉树进行遍历时,实际上那个是将二叉树这种非线性结构按某种需要转化成线性序列,但每次遍历二叉树时,都要用递归对其进行遍历,当二叉树的节点较多时,这样的效率是很低的。所以我们有没有办法把我们遍历的二叉树保存,方便以后遍历呢?
在一棵只有n个结点的二叉树中,假设有n个结点,那么就有2n个指针域,因为二叉树只用到了其中的n-1个结点,所以只要利用剩下的n+1个节点,我们就能把中需遍历时所得到的中序二叉树保存下来,以便下次访问。
中序二叉树的指针域有两种类型:一是用于链接二叉树本身;二是用于链接中序遍历序列。这类型的指针,左指指向中序遍历时节点顺序的前驱,右指针指向中序遍历时的后继。为了区别这两种指针域类型,我们在树的结点中要加上两个标志lchild和rchild,分别标志左右指针域的类型。 其数据结构如下:
其中LTag = 0 lchild域指示节点的左孩子;LTag=1 lchild域指示节点的前驱。
RTag = 0 rchild域指示节点的左孩子;RTag=1 rchild域指示节点的前驱。
为了简化二叉树的线索化,这里采用中序线索链表的方式,对二叉树进行遍历,找出叶子节点的前驱和后继。后序后继线索二叉树以后再做讨论。
线索二叉树及其中序线索链表结构如下:
二叉线索树的定义
节点结构的定义:
int data;
int LTag; // 0,1
int RTag; // 0,1
TBTreeNode lchild;
TBTreeNode rchild;
为了仿照线性表的存储结构,在二叉树的线索链表上添加一个头结点,令其lchild域指向二叉树的根节点,其rchild域的指针指向中序遍历访问的最后一个节点。反之,令二叉树中序序列中的第一个节点的lchild域指针和最后一个节点的rchild域的指针均指向头结点。
二叉线索树的定义:
TBTreeNode head; // 头结点 TBTreeNode root; // 根节点
在定义二叉树的数据结构后,需要对二叉树遍历进行线索化。
二叉树的线索化(动画演示)
如何进行二叉树的线索化呢? 由于线索化的是指是将二叉链表中的空指针改为指向前驱和后继的线索,而前驱或后继的信息只有在遍历的时侯才用的到,因此线索化的过程即为在遍历的过程中修改空指针的过程。
创造中序线索树的具体过程:
递归实现,函数的参数为当前结点current,和上次访问的结点previous.
(1)若previous的右指针为空,则把previous的右指针指向current,并把previous的RTag设置为true;
(2)若current的左指针为空,则把current的左指针指向previous,并把current的LTag设置为true;
代码,默认建立的二叉树结构如下:
/************************ * 构造的二叉树结构为: * 2 * / \ * 1 8 * / \ * 7 9 * / * 4 * / \ * 3 6 * / * 5 * **********************/
 ThreadedBinaryTree
ThreadedBinaryTree
1 class TBTreeNode { 2 int data; 3 int LTag; // 0,1 4 int RTag; // 0,1 5 TBTreeNode lchild; 6 TBTreeNode rchild; 7 8 public TBTreeNode(int data) { 9 this(data, null, null, 0, 0); 10 } 11 12 public TBTreeNode(int data, TBTreeNode lchild, TBTreeNode rchild, int LTag, 13 int RTag) { 14 this.data = data; 15 this.lchild = lchild; 16 this.rchild = rchild; 17 this.LTag = LTag; 18 this.RTag = RTag; 19 } 20 } 21 22 class ThreadedBinaryTree { 23 TBTreeNode head; 24 TBTreeNode root; 25 26 public void initTBTree() { 27 head = new TBTreeNode(-1); 28 } 29 30 public void buildTBTree(int[] data) { 31 head = null; 32 root = new TBTreeNode(data[0]); 33 for (int i = 1; i < data.length; i++) { 34 TBTreeNode tmpNode = root; 35 while (true) { 36 if (tmpNode.data == data[i]) 37 break; 38 // 小于等于根节点 39 if (tmpNode.data > data[i]) { 40 // 如果左孩子为空,这把当前数组元素插入到左孩子节点的位置 41 if (tmpNode.lchild == null) { 42 tmpNode.lchild = new TBTreeNode(data[i]); 43 break; 44 } 45 // 如果不为空的话,则把左孩子节点用来和当前数组元素作比较 46 tmpNode = tmpNode.lchild; 47 } else // 大于根节点 48 { 49 // 如果右孩子为空,这把当前数组元素插入到左孩子节点的位置 50 if (tmpNode.rchild == null) { 51 tmpNode.rchild = new TBTreeNode(data[i]); 52 break; 53 } 54 // 如果不为空的话,则把右孩子节点用来和当前数组元素作比较 55 tmpNode = tmpNode.rchild; 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 61 // 中序遍历二叉树,并将其中序线索化 62 public void inOrderThreading() { 63 TBTreeNode current; 64 TBTreeNode previous; 65 66 initTBTree();// head节点的初始化,root节点为用户创建的二叉树 67 68 head.LTag = 0; 69 head.RTag = 1; 70 // 二叉树为空的时候,头结点指向其本身 71 if (root == null) { 72 head.lchild = head.rchild = head; 73 } else { 74 current = root; 75 76 head.lchild = current; 77 previous = head; 78 previous = inThreading(current, previous); 79 System.out.println("建立线索二叉树后,previous指针的值为:" + previous.data); 80 previous.RTag = 1; 81 previous.rchild = head; 82 head.rchild = previous; 83 System.out.println("建立线索二叉树后,最后一个节点为:" + previous.data 84 + ",对应的后继节点为:" + previous.rchild.data); 85 } 86 } 87 88 // 前驱后继都是相对于头结点和叶子节点而言 89 // 其中current指针指向当前访问的节点;previous节点指向刚刚访问过的节点 90 private TBTreeNode inThreading(TBTreeNode current, TBTreeNode previous) { 91 if (current != null) { 92 TBTreeNode tmpNode = inThreading(current.lchild, previous); 93 // 前驱线索 94 if (current.lchild == null && current.LTag == 0) { 95 current.LTag = 1; 96 current.lchild = previous; 97 } 98 previous = tmpNode; 99 // 后继线索 100 if (previous.rchild == null && previous.RTag == 0) { 101 previous.RTag = 1; 102 previous.rchild = current; 103 } 104 105 previous = current;// 保持previous指向current的前驱 106 previous = inThreading(current.rchild, previous); 107 108 return previous; 109 } 110 return previous; 111 } 112 113 // 查找二叉查找树的最小节点:线索化二叉树前后的区别 114 public TBTreeNode getFirstTBTNode(TBTreeNode node) { 115 if (head != null) { 116 while (node.lchild != head) { 117 node = node.lchild; 118 } 119 } else { 120 while (node.lchild != null) { 121 node = node.lchild; 122 } 123 } 124 return node; 125 } 126 127 // 查找二叉查找树的最大节点 128 public TBTreeNode getLastTBTNode(TBTreeNode node) { 129 if (head == null) { 130 while (node.rchild != null) { 131 node = node.rchild; 132 } 133 } else { 134 while (node.rchild != head) { 135 node = node.rchild; 136 } 137 } 138 return node; 139 } 140 141 // 查找节点的前驱节点 142 public TBTreeNode getPredecessor(TBTreeNode node) { 143 if (node.lchild != null) { 144 return getLastTBTNode(node.lchild);// 左子树的最大值 145 } 146 TBTreeNode parent = getParent(node); 147 while (parent != null && node == parent.lchild) {// 向上找到最近的一个节点,其父亲节点的右子树包涵了当前节点或者其父亲节点为空 148 node = parent; 149 parent = getParent(parent); 150 } 151 return parent; 152 } 153 154 // 查找节点的后继节点 155 public TBTreeNode getSuccessor(TBTreeNode node) { 156 if (node.rchild != null) { 157 return getFirstTBTNode(node.rchild);// 右子树的最小值 158 } 159 TBTreeNode parent = getParent(node); 160 if (parent == null) 161 return null; 162 while (parent != null) { 163 if (parent.lchild == node) { 164 return parent; // 为左子树情况,后继为父节点 165 } else { 166 node = parent; // 否则递归 167 parent = getParent(parent); 168 } 169 } 170 return parent; 171 } 172 173 // 求出父亲节点,在定义节点类BSTreeNode的时候,没有申明父亲节点,所以这里专门用parent用来输出父亲节点(主要是不想修改代码了,就在这里加一个parent函数吧) 174 public TBTreeNode getParent(TBTreeNode node) { 175 TBTreeNode p = root; 176 TBTreeNode tmp = null; 177 while (p != null && p.data != node.data) {// 最后的p为p.data等于k.data的节点,tmp为p的父亲节点 178 if (p.data > node.data) { 179 tmp = p;// 临时存放父亲节点 180 p = p.lchild; 181 } else { 182 tmp = p;// 临时存放父亲节点 183 p = p.rchild; 184 } 185 } 186 return tmp; 187 } 188 189 /** 190 * 线索化的递归遍历二叉树 191 */ 192 public void inOrderReaversal() { 193 TBTreeNode node; 194 if (head != null) { 195 node = head.lchild; // node表示head头指针指向的root节点 196 // 空树或者遍历结束 node==head 197 while (node != head) { 198 // 访问左子树 199 while (node.LTag == 0) 200 node = node.lchild; 201 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 202 while (node.RTag == 1 && node.rchild != head) { 203 // 访问叶子节点的后继 204 node = node.rchild; 205 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 206 } 207 // 访问完叶子节点的后继后,访问右子树 208 node = node.rchild; 209 } 210 } 211 } 212 213 /** 214 * 未线索化的中序递归遍历二叉树 215 */ 216 public void traversalTBTree() { 217 traversalTBTree(root); 218 System.out.println(); 219 } 220 221 private void traversalTBTree(TBTreeNode node) { 222 if (node != null) { 223 traversalTBTree(node.lchild); 224 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 225 traversalTBTree(node.rchild); 226 } 227 } 228 } 229 230 public class ThreadedBinaryTreeTest { 231 public static void main(String[] args) { 232 ThreadedBinaryTree tbTree = new ThreadedBinaryTree(); 233 /*********************************************************************** 234 * 初始化操作 235 **********************************************************************/ 236 int[] data = { 2, 8, 7, 4, 9, 3, 1, 6, 7, 5 }; // { 8, 7, 1, 6, 4, 5, 237 // 10, 3, 2, 9 }; 238 tbTree.buildTBTree(data); 239 System.out.println("########################################"); 240 System.out.println("未进行线索化前,二叉树中序遍历结果:"); 241 tbTree.traversalTBTree(); 242 System.out.println(tbTree.head == null); 243 System.out.println("未进行线索化前,二叉树中第一个节点和最后一个节点值分别为:" 244 + tbTree.getFirstTBTNode(tbTree.root).data + " " 245 + tbTree.getLastTBTNode(tbTree.root).data); 246 247 /*********************************************************************** 248 * 中序线索化操作 249 **********************************************************************/ 250 System.out.println("########################################"); 251 System.out.println("线索化后,二叉树遍历结果:"); 252 tbTree.inOrderThreading(); 253 tbTree.inOrderReaversal(); 254 System.out.println(); 255 System.out.println("线索化后,head头指针的左子节点和后继节点分别为:" 256 + tbTree.head.lchild.data + " " + tbTree.head.rchild.data); 257 System.out.println("线索化后,二叉树中第一个节点和最后一个节点值分别为:" 258 + tbTree.getFirstTBTNode(tbTree.root).data + " " 259 + tbTree.getLastTBTNode(tbTree.root).data); 260 261 } 262 }
附属links: