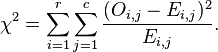原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/tovin/p/4019131.html
在spark mllib 1.1版本中增加stat包,里面包含了一些统计相关的函数,本文主要分析其中的卡方检验的原理与实现:
一、基本原理
在stat包中实现了皮尔逊卡方检验,它主要包含以下两类
(1)适配度检验(Goodness of Fit test):验证一组观察值的次数分配是否异于理论上的分配。
(2)独立性检验(independence test) :验证从两个变量抽出的配对观察值组是否互相独立(例如:每次都从A国和B国各抽一个人,看他们的反应是否与国籍无关)
计算公式:
其中O表示观测值,E表示期望值
详细原理可以参考:http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%9A%AE%E7%88%BE%E6%A3%AE%E5%8D%A1%E6%96%B9%E6%AA%A2%E5%AE%9A
二、java api调用example
三、源码分析
1、外部api
通过Statistics类提供了4个外部接口
// Goodness of Fit test def chiSqTest(observed: Vector, expected: Vector): ChiSqTestResult = { ChiSqTest.chiSquared(observed, expected) } //Goodness of Fit test def chiSqTest(observed: Vector): ChiSqTestResult = ChiSqTest.chiSquared(observed) //independence test def chiSqTest(observed: Matrix): ChiSqTestResult = ChiSqTest.chiSquaredMatrix(observed) //independence test def chiSqTest(data: RDD[LabeledPoint]): Array[ChiSqTestResult] = { ChiSqTest.chiSquaredFeatures(data) }
2、Goodness of Fit test实现
这个比较简单,关键是根据(observed-expected)2/expected计算卡方值
/* * Pearon's goodness of fit test on the input observed and expected counts/relative frequencies. * Uniform distribution is assumed when `expected` is not passed in. */ def chiSquared(observed: Vector, expected: Vector = Vectors.dense(Array[Double]()), methodName: String = PEARSON.name): ChiSqTestResult = { // Validate input arguments val method = methodFromString(methodName) if (expected.size != 0 && observed.size != expected.size) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("observed and expected must be of the same size.") } val size = observed.size if (size > 1000) { logWarning("Chi-squared approximation may not be accurate due to low expected frequencies " + s" as a result of a large number of categories: $size.") } val obsArr = observed.toArray
// 如果expected值没有设置,默认取1.0 / size val expArr = if (expected.size == 0) Array.tabulate(size)(_ => 1.0 / size) else expected.toArray
/ 如果expected、observed值都必须要大于1 if (!obsArr.forall(_ >= 0.0)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative entries disallowed in the observed vector.") } if (expected.size != 0 && ! expArr.forall(_ >= 0.0)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative entries disallowed in the expected vector.") } // Determine the scaling factor for expected val obsSum = obsArr.sum val expSum = if (expected.size == 0.0) 1.0 else expArr.sum val scale = if (math.abs(obsSum - expSum) < 1e-7) 1.0 else obsSum / expSum // compute chi-squared statistic val statistic = obsArr.zip(expArr).foldLeft(0.0) { case (stat, (obs, exp)) => if (exp == 0.0) { if (obs == 0.0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Chi-squared statistic undefined for input vectors due" + " to 0.0 values in both observed and expected.") } else { return new ChiSqTestResult(0.0, size - 1, Double.PositiveInfinity, PEARSON.name, NullHypothesis.goodnessOfFit.toString) } }
// 计算(observed-expected)2/expected if (scale == 1.0) { stat + method.chiSqFunc(obs, exp) } else { stat + method.chiSqFunc(obs, exp * scale) } } val df = size - 1 val pValue = chiSquareComplemented(df, statistic) new ChiSqTestResult(pValue, df, statistic, PEARSON.name, NullHypothesis.goodnessOfFit.toString) }
3、independence test实现
先通过下面的公式计算expected值,矩阵共有 r 行 c 列
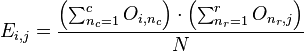
然后根据(observed-expected)2/expected计算卡方值
/* * Pearon's independence test on the input contingency matrix. * TODO: optimize for SparseMatrix when it becomes supported. */ def chiSquaredMatrix(counts: Matrix, methodName:String = PEARSON.name): ChiSqTestResult = { val method = methodFromString(methodName) val numRows = counts.numRows val numCols = counts.numCols // get row and column sums val colSums = new Array[Double](numCols) val rowSums = new Array[Double](numRows) val colMajorArr = counts.toArray var i = 0 while (i < colMajorArr.size) { val elem = colMajorArr(i) if (elem < 0.0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Contingency table cannot contain negative entries.") } colSums(i / numRows) += elem rowSums(i % numRows) += elem i += 1 } val total = colSums.sum // second pass to collect statistic var statistic = 0.0 var j = 0 while (j < colMajorArr.size) { val col = j / numRows val colSum = colSums(col) if (colSum == 0.0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Chi-squared statistic undefined for input matrix due to" + s"0 sum in column [$col].") } val row = j % numRows val rowSum = rowSums(row) if (rowSum == 0.0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Chi-squared statistic undefined for input matrix due to" + s"0 sum in row [$row].") } val expected = colSum * rowSum / total statistic += method.chiSqFunc(colMajorArr(j), expected) j += 1 } val df = (numCols - 1) * (numRows - 1) val pValue = chiSquareComplemented(df, statistic) new ChiSqTestResult(pValue, df, statistic, methodName, NullHypothesis.independence.toString) }
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/tovin/p/4019131.html