Ubuntu下的MySQL安装
1.安装mysql-server
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install mysql-server mysql-client
2.重新启动mysql服务
sudo service mysql restart
3.让apache支持mysql
sudo apt-get install libapache2-mod-auth-mysql
16.04使用下面命令
sudo apt-get install libmysqlclient-dev
4.登录mysql
mysql -u root -p
如果修改了配置文件my.cnf配置文件,需要重启数据库(修改方法在下面),重启数据库之前需要先重新载入apparmor配置文件,使用下面命令重新载入:
重新启动数据库
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start
5.查看数据库的编码
1.查看MySQL数据库服务器和数据库MySQL字符集。
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'character_set_%';
如果需要修改的话
set character_set_client=utf8;
2.查看MySQL数据表(table)的MySQL字符集,spring_user是数据库的名字,t_user是表名
mysql> show table status from spring_user like '%t_user%';
或者
mysql> show create table t_user;
修改方法:
alter table t_user convert to character set utf8;
3.查看MySQL数据列(column)的MySQL字符集,t_user是表名
mysql> show full columns from t_user;
6.修改mysql配置文件
sudo vim /etc/my.cnf
因为ubuntu下mySQL默认的数据库的路径是在/var/lib/mysql,所以要修改这个路径的话,参考
http://www.2cto.com/database/201501/373939.html
注意修改的时候/mysql要加上
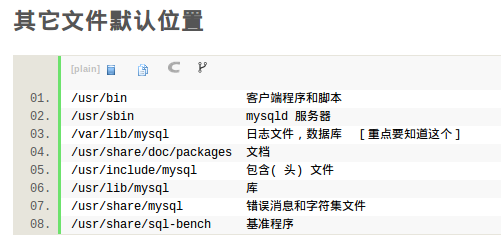
ubuntu下mysql的默认配置地址
sudo vim /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
如果要开放myslq的外网访问权限,在该配置文件中添加
bind-address = 0.0.0.0
如果bind到127.0.0.1的话,使用netstat命令可以看到local address是127.0.0.1,此时只能本地访问
sudo netstat -nltp | grep mysql
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 31772/mysqld
修改后重新mysql服务
sudo systemctl restart mysql
此时就可以看到local address变成0.0.0.0
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 31989/mysqld
修改的my.cnf文件,修改完切记一定要重启mysql服务
# # The MySQL database server configuration file. # # You can copy this to one of: # - "/etc/mysql/my.cnf" to set global options, # - "~/.my.cnf" to set user-specific options. # # One can use all long options that the program supports. # Run program with --help to get a list of available options and with # --print-defaults to see which it would actually understand and use. # # For explanations see # http://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql/en/server-system-variables.html # This will be passed to all mysql clients # It has been reported that passwords should be enclosed with ticks/quotes # escpecially if they contain "#" chars... # Remember to edit /etc/mysql/debian.cnf when changing the socket location. [client] port = 3306 socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock default-character-set=utf8 # Here is entries for some specific programs # The following values assume you have at least 32M ram # This was formally known as [safe_mysqld]. Both versions are currently parsed. [mysqld_safe] default-character-set=utf8 character_set_server = utf8 socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock nice = 0 [mysqld] # # * Basic Settings # user = mysql pid-file = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock character_set_server=utf8 init_connect='SET NAMES utf8' port = 3306 basedir = /usr datadir = /home/common/software/database/mysql tmpdir = /tmp lc-messages-dir = /usr/share/mysql skip-external-locking # # Instead of skip-networking the default is now to listen only on # localhost which is more compatible and is not less secure. bind-address = 127.0.0.1 # # * Fine Tuning # key_buffer = 16M max_allowed_packet = 16M thread_stack = 192K thread_cache_size = 8 # This replaces the startup script and checks MyISAM tables if needed # the first time they are touched myisam-recover = BACKUP #max_connections = 100 #table_cache = 64 #thread_concurrency = 10 # # * Query Cache Configuration # query_cache_limit = 1M query_cache_size = 16M # # * Logging and Replication # # Both location gets rotated by the cronjob. # Be aware that this log type is a performance killer. # As of 5.1 you can enable the log at runtime! #general_log_file = /var/log/mysql/mysql.log #general_log = 1 # # Error log - should be very few entries. # log_error = /var/log/mysql/error.log # # Here you can see queries with especially long duration #log_slow_queries = /var/log/mysql/mysql-slow.log #long_query_time = 2 #log-queries-not-using-indexes # # The following can be used as easy to replay backup logs or for replication. # note: if you are setting up a replication slave, see README.Debian about # other settings you may need to change. #server-id = 1 #log_bin = /var/log/mysql/mysql-bin.log expire_logs_days = 10 max_binlog_size = 100M #binlog_do_db = include_database_name #binlog_ignore_db = include_database_name # # * InnoDB # # InnoDB is enabled by default with a 10MB datafile in /var/lib/mysql/. # Read the manual for more InnoDB related options. There are many! # # * Security Features # # Read the manual, too, if you want chroot! # chroot = /var/lib/mysql/ # # For generating SSL certificates I recommend the OpenSSL GUI "tinyca". # # ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/cacert.pem # ssl-cert=/etc/mysql/server-cert.pem # ssl-key=/etc/mysql/server-key.pem [mysqldump] quick quote-names max_allowed_packet = 16M [mysql] default-character-set=utf8 #no-auto-rehash # faster start of mysql but no tab completition [isamchk] key_buffer = 16M # # * IMPORTANT: Additional settings that can override those from this file! # The files must end with '.cnf', otherwise they'll be ignored. # !includedir /etc/mysql/conf.d/
Ubuntu下Eclipse部署MySQL JDBC驱动
参考http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2011-10/44355.htm中的上半部分
Linux下自动启动MySQL

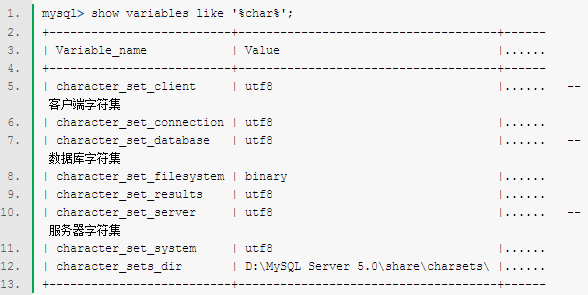
一、查看MySQL数据库服务器和数据库MySQL字符集。
命令:
mysql> show variables like '%char%'; |
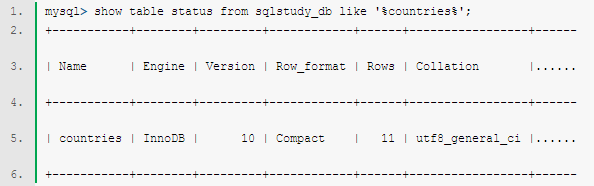
二、查看MySQL数据表(table)的MySQL字符集。
命令:
mysql> show table status from sqlstudy_db like '%countries%'; |
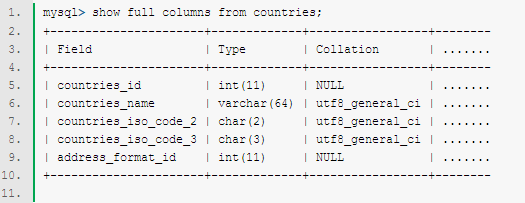
三、查看MySQL数据列(column)的MySQL字符集。
命令:
mysql> show full columns from countries; |
四、修改MySQL的密码
首先用root登录MySQL,然后执行
UPDATE user SET password=PASSWORD('123456') WHERE user='root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
或者
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('newpass');
如果要安装5.6版本的mysql
sudo add-apt-repository 'deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty universe' sudo apt-get update sudo apt install mysql-server-5.6 mysql-client-5.6
如果卸载5.7再安装的时候遇到
/var/cache/apt/archives/mysql-server-5.6_5.6.16-1~exp1_amd64.deb E: Sub-process /usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code (1)
sudo apt-get remove --purge mysql-server mysql-client mysql-common sudo apt-get autoremove sudo apt-get autoclean
先确保 mysql service是启动的,没启动会报找不到mysqld.sock
service mysql status service mysql start
本文只发表于博客园和tonglin0325的博客,作者:tonglin0325,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tonglin0325/p/5299031.html





