【OpenCV】SIFT原理与源码分析:关键点描述
《SIFT原理与源码分析》系列文章索引:http://www.cnblogs.com/tianyalu/p/5467813.html
由前一篇《方向赋值》,为找到的关键点即SIFT特征点赋了值,包含位置、尺度和方向的信息。接下来的步骤是关键点描述,即用用一组向量将这个关键点描述出来,这个描述子不但包括关键点,也包括关键点周围对其有贡献的像素点。用来作为目标匹配的依据(所以描述子应该有较高的独特性,以保证匹配率),也可使关键点具有更多的不变特性,如光照变化、3D视点变化等。
SIFT描述子h(x,y,θ)是对关键点附近邻域内高斯图像梯度统计的结果,是一个三维矩阵,但通常用一个矢量来表示。矢量通过对三维矩阵按一定规律排列得到。
描述子采样区域
特征描述子与关键点所在尺度有关,因此对梯度的求取应在特征点对应的高斯图像上进行。将关键点附近划分成d×d个子区域,每个子区域尺寸为mσ个像元(d=4,m=3,σ为尺特征点的尺度值)。考虑到实际计算时需要双线性插值,故计算的图像区域为mσ(d+1),再考虑旋转,则实际计算的图像区域为 ,如下图所示:
,如下图所示:
 ,如下图所示:
,如下图所示:
源码
Point pt(cvRound(ptf.x), cvRound(ptf.y)); //计算余弦,正弦,CV_PI/180:将角度值转化为幅度值 float cos_t = cosf(ori*(float)(CV_PI/180)); float sin_t = sinf(ori*(float)(CV_PI/180)); float bins_per_rad = n / 360.f; float exp_scale = -1.f/(d * d * 0.5f); //d:SIFT_DESCR_WIDTH 4 float hist_width = SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR * scl; // SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR: 3 // scl: size*0.5f // 计算图像区域半径mσ(d+1)/2*sqrt(2) // 1.4142135623730951f 为根号2 int radius = cvRound(hist_width * 1.4142135623730951f * (d + 1) * 0.5f); cos_t /= hist_width; sin_t /= hist_width;
区域坐标轴旋转
为了保证特征矢量具有旋转不变性,要以特征点为中心,在附近邻域内旋转θ角,即旋转为特征点的方向。
旋转后区域内采样点新的坐标为: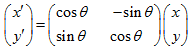
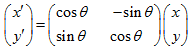
源码
//计算采样区域点坐标旋转 for( i = -radius, k = 0; i <= radius; i++ ) for( j = -radius; j <= radius; j++ ) { /* Calculate sample's histogram array coords rotated relative to ori. Subtract 0.5 so samples that fall e.g. in the center of row 1 (i.e. r_rot = 1.5) have full weight placed in row 1 after interpolation. */ float c_rot = j * cos_t - i * sin_t; float r_rot = j * sin_t + i * cos_t; float rbin = r_rot + d/2 - 0.5f; float cbin = c_rot + d/2 - 0.5f; int r = pt.y + i, c = pt.x + j; if( rbin > -1 && rbin < d && cbin > -1 && cbin < d && r > 0 && r < rows - 1 && c > 0 && c < cols - 1 ) { float dx = (float)(img.at<short>(r, c+1) - img.at<short>(r, c-1)); float dy = (float)(img.at<short>(r-1, c) - img.at<short>(r+1, c)); X[k] = dx; Y[k] = dy; RBin[k] = rbin; CBin[k] = cbin; W[k] = (c_rot * c_rot + r_rot * r_rot)*exp_scale; k++; } }
计算采样区域梯度直方图
将旋转后区域划分为d×d个子区域(每个区域间隔为mσ像元),在子区域内计算8个方向的梯度直方图,绘制每个方向梯度方向的累加值,形成一个种子点。
与求主方向不同的是,此时,每个子区域梯度方向直方图将0°~360°划分为8个方向区间,每个区间为45°。即每个种子点有8个方向区间的梯度强度信息。由于存在d×d,即4×4个子区域,所以最终共有4×4×8=128个数据,形成128维SIFT特征矢量。

对特征矢量需要加权处理,加权采用mσd/2的标准高斯函数。为了除去光照变化影响,还有一步归一化处理。
源码
//计算梯度直方图 for( k = 0; k < len; k++ ) { float rbin = RBin[k], cbin = CBin[k]; float obin = (Ori[k] - ori)*bins_per_rad; float mag = Mag[k]*W[k]; int r0 = cvFloor( rbin ); int c0 = cvFloor( cbin ); int o0 = cvFloor( obin ); rbin -= r0; cbin -= c0; obin -= o0; //n为SIFT_DESCR_HIST_BINS:8,即将360°分为8个区间 if( o0 < 0 ) o0 += n; if( o0 >= n ) o0 -= n; // histogram update using tri-linear interpolation // 双线性插值 float v_r1 = mag*rbin, v_r0 = mag - v_r1; float v_rc11 = v_r1*cbin, v_rc10 = v_r1 - v_rc11; float v_rc01 = v_r0*cbin, v_rc00 = v_r0 - v_rc01; float v_rco111 = v_rc11*obin, v_rco110 = v_rc11 - v_rco111; float v_rco101 = v_rc10*obin, v_rco100 = v_rc10 - v_rco101; float v_rco011 = v_rc01*obin, v_rco010 = v_rc01 - v_rco011; float v_rco001 = v_rc00*obin, v_rco000 = v_rc00 - v_rco001; int idx = ((r0+1)*(d+2) + c0+1)*(n+2) + o0; hist[idx] += v_rco000; hist[idx+1] += v_rco001; hist[idx+(n+2)] += v_rco010; hist[idx+(n+3)] += v_rco011; hist[idx+(d+2)*(n+2)] += v_rco100; hist[idx+(d+2)*(n+2)+1] += v_rco101; hist[idx+(d+3)*(n+2)] += v_rco110; hist[idx+(d+3)*(n+2)+1] += v_rco111; }
关键点描述源码
// SIFT关键点特征描述 // SIFT描述子是关键点领域高斯图像提取统计结果的一种表示 static void calcSIFTDescriptor( const Mat& img, Point2f ptf, float ori, float scl, int d, int n, float* dst ) { Point pt(cvRound(ptf.x), cvRound(ptf.y)); //计算余弦,正弦,CV_PI/180:将角度值转化为幅度值 float cos_t = cosf(ori*(float)(CV_PI/180)); float sin_t = sinf(ori*(float)(CV_PI/180)); float bins_per_rad = n / 360.f; float exp_scale = -1.f/(d * d * 0.5f); //d:SIFT_DESCR_WIDTH 4 float hist_width = SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR * scl; // SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR: 3 // scl: size*0.5f // 计算图像区域半径mσ(d+1)/2*sqrt(2) // 1.4142135623730951f 为根号2 int radius = cvRound(hist_width * 1.4142135623730951f * (d + 1) * 0.5f); cos_t /= hist_width; sin_t /= hist_width; int i, j, k, len = (radius*2+1)*(radius*2+1), histlen = (d+2)*(d+2)*(n+2); int rows = img.rows, cols = img.cols; AutoBuffer<float> buf(len*6 + histlen); float *X = buf, *Y = X + len, *Mag = Y, *Ori = Mag + len, *W = Ori + len; float *RBin = W + len, *CBin = RBin + len, *hist = CBin + len; //初始化直方图 for( i = 0; i < d+2; i++ ) { for( j = 0; j < d+2; j++ ) for( k = 0; k < n+2; k++ ) hist[(i*(d+2) + j)*(n+2) + k] = 0.; } //计算采样区域点坐标旋转 for( i = -radius, k = 0; i <= radius; i++ ) for( j = -radius; j <= radius; j++ ) { /* Calculate sample's histogram array coords rotated relative to ori. Subtract 0.5 so samples that fall e.g. in the center of row 1 (i.e. r_rot = 1.5) have full weight placed in row 1 after interpolation. */ float c_rot = j * cos_t - i * sin_t; float r_rot = j * sin_t + i * cos_t; float rbin = r_rot + d/2 - 0.5f; float cbin = c_rot + d/2 - 0.5f; int r = pt.y + i, c = pt.x + j; if( rbin > -1 && rbin < d && cbin > -1 && cbin < d && r > 0 && r < rows - 1 && c > 0 && c < cols - 1 ) { float dx = (float)(img.at<short>(r, c+1) - img.at<short>(r, c-1)); float dy = (float)(img.at<short>(r-1, c) - img.at<short>(r+1, c)); X[k] = dx; Y[k] = dy; RBin[k] = rbin; CBin[k] = cbin; W[k] = (c_rot * c_rot + r_rot * r_rot)*exp_scale; k++; } } len = k; fastAtan2(Y, X, Ori, len, true); magnitude(X, Y, Mag, len); exp(W, W, len); //计算梯度直方图 for( k = 0; k < len; k++ ) { float rbin = RBin[k], cbin = CBin[k]; float obin = (Ori[k] - ori)*bins_per_rad; float mag = Mag[k]*W[k]; int r0 = cvFloor( rbin ); int c0 = cvFloor( cbin ); int o0 = cvFloor( obin ); rbin -= r0; cbin -= c0; obin -= o0; //n为SIFT_DESCR_HIST_BINS:8,即将360°分为8个区间 if( o0 < 0 ) o0 += n; if( o0 >= n ) o0 -= n; // histogram update using tri-linear interpolation // 双线性插值 float v_r1 = mag*rbin, v_r0 = mag - v_r1; float v_rc11 = v_r1*cbin, v_rc10 = v_r1 - v_rc11; float v_rc01 = v_r0*cbin, v_rc00 = v_r0 - v_rc01; float v_rco111 = v_rc11*obin, v_rco110 = v_rc11 - v_rco111; float v_rco101 = v_rc10*obin, v_rco100 = v_rc10 - v_rco101; float v_rco011 = v_rc01*obin, v_rco010 = v_rc01 - v_rco011; float v_rco001 = v_rc00*obin, v_rco000 = v_rc00 - v_rco001; int idx = ((r0+1)*(d+2) + c0+1)*(n+2) + o0; hist[idx] += v_rco000; hist[idx+1] += v_rco001; hist[idx+(n+2)] += v_rco010; hist[idx+(n+3)] += v_rco011; hist[idx+(d+2)*(n+2)] += v_rco100; hist[idx+(d+2)*(n+2)+1] += v_rco101; hist[idx+(d+3)*(n+2)] += v_rco110; hist[idx+(d+3)*(n+2)+1] += v_rco111; } // finalize histogram, since the orientation histograms are circular // 最后确定直方图,目标方向直方图是圆的 for( i = 0; i < d; i++ ) for( j = 0; j < d; j++ ) { int idx = ((i+1)*(d+2) + (j+1))*(n+2); hist[idx] += hist[idx+n]; hist[idx+1] += hist[idx+n+1]; for( k = 0; k < n; k++ ) dst[(i*d + j)*n + k] = hist[idx+k]; } // copy histogram to the descriptor, // apply hysteresis thresholding // and scale the result, so that it can be easily converted // to byte array float nrm2 = 0; len = d*d*n; for( k = 0; k < len; k++ ) nrm2 += dst[k]*dst[k]; float thr = std::sqrt(nrm2)*SIFT_DESCR_MAG_THR; for( i = 0, nrm2 = 0; i < k; i++ ) { float val = std::min(dst[i], thr); dst[i] = val; nrm2 += val*val; } nrm2 = SIFT_INT_DESCR_FCTR/std::max(std::sqrt(nrm2), FLT_EPSILON); for( k = 0; k < len; k++ ) { dst[k] = saturate_cast<uchar>(dst[k]*nrm2); } }
至此SIFT描述子生成,SIFT算法也基本完成了~参见《SIFT原理与源码分析》



