瀑布流-02-手把手教你封装自定义布局
概述
- 对于经常使用的控件或类,通常将其分装为一个单独的类来供外界使用,以此达到事半功倍的效果
- 由于分装的类不依赖于其他的类,所以若要使用该类,可直接将该类拖进项目文件即可
- 在进行分装的时候,通常需要用到代理设计模式
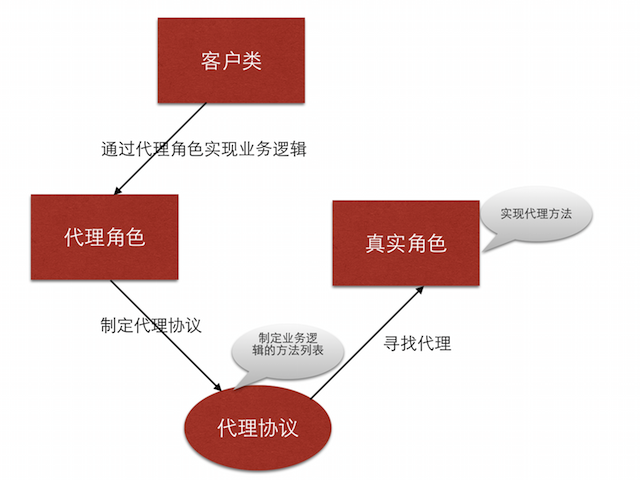
代理设计模式
-
代理设计模式的组成
- 客户类(通常作为代理)
- 通常委托这是角色来完成业务逻辑
- 真实角色
- 将客户类的业务逻辑转化为方法列表,即代理协议
- 代理协议
- 定义了需要实现的业务逻辑
- 定义了一组方法列表,包括必须实现的方法或选择实现的方法
- 代理协议是代理对象所要遵循一组规则
- 代理角色
- 若要作为代理,需要遵守代理协议,并且实现必须实现的代理方法
- 代理角色可以通过调用代理协议中的方法完成业务逻辑,也可以附加自己的操作
- 客户类(通常作为代理)
-
文字描述通常是抽象的,一下通过图示来阐述代理设计模式
自定义布局类的封装
-
业务逻辑
-
如图

-
-
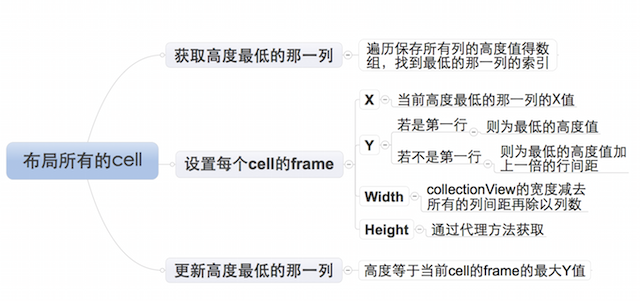
布局每个cell的业务逻辑
-
由于设置每个cell的布局属性的业务逻辑较复杂,特附上如下思维导图
-
-
封装思路
封装需要根据客户类业务逻辑需求来提供接口- 通过代理协议的可选实现的方法获取的属性值的属性,需要设置默认值
- 未提供默认值的且必须使用的属性,需要通过必须实现的方法来获得
- 自定义布局提供的接口
可选- 列数
- 列之间的间距
- 行之间的间距
- 内边距
- 自定义布局提供的接口
必选- 每个元素的高度,宽度可以通过列数和列间距计算得到
封装步骤
-
设置代理协议,提供接口
//声明LYPWaterFlowLayout为一个类 @class LYPWaterFlowLayout; @protocol LYPWaterFlowLayoutDelegate <NSObject> //必须实现的方法 @required /**获取瀑布流每个元素的高度*/ - (CGFloat)waterFlowLayout:(LYPWaterFlowLayout *)waterFlowLayout heightForItemAtIndex:(NSInteger)index itemWith:(CGFloat)itemWith; //可选实现的方法 @optional /**获取瀑布流的列数*/ - (NSInteger)columnCountInWaterFlowLayout:(LYPWaterFlowLayout *)waterFlowLayout; /**获取瀑布流列间距*/ - (CGFloat)columnMarginInWaterFlowLayout:(LYPWaterFlowLayout *)waterFlowLayout; /**获取瀑布流的行间距*/ - (CGFloat)rowMarginInWaterFlowLayout:(LYPWaterFlowLayout *)waterFlowLayout; /**获取瀑布流的内边距*/ - (UIEdgeInsets)edgeInsetsInWaterFlowLayout:(LYPWaterFlowLayout *)waterFlowLayout; @end -
设置代理属性
@interface LYPWaterFlowLayout : UICollectionViewLayout /**代理*/ @property (nonatomic, weak) id<LYPWaterFlowLayoutDelegate> delegate; @end -
设置通过可选代理方法获取属性值的属性的默认值
/**默认的列数*/ static const NSInteger LYPDefaultColumnCount = 3; /**默认每一列之间的间距*/ static const CGFloat LYPDefaultColumMargin = 10; /**默认每一行之间的间距*/ static const CGFloat LYPDefaultRowMargin = 10; /**默认边缘间距*/ static const UIEdgeInsets LYPDefaultEdgeInsets = {10, 10, 10, 10}; -
设置通过可选代理方法获取属性值的属性的访问方式
若代理提供属性值,则忽略默认值- (NSInteger)columnCount { //判断代理是否实现了获取列数的可选方法 if ([self.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(columnCountInWaterFlowLayout:)]) { //实现,返回通过代理设置的列数 return [self.delegate columnCountInWaterFlowLayout:self]; } else { //为实现,返回默认的列数 return LYPDefaultColumnCount; } }- 注:其他属性值的获取与上述方法几乎完全相同,不再赘述
-
设置布局
-
设置需要的成员属性
/**所有cell的布局属性*/ @property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *attrsArray; /**所有列的当前高度*/ @property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *columnHeights; -
通过懒加载的方式初始化成员属性
/**--attrsArray--懒加载*/ - (NSMutableArray *)attrsArray { if (_attrsArray == nil) { _attrsArray = [NSMutableArray array]; } return _attrsArray; } /**--columnHeights--懒加载*/ - (NSMutableArray *)columnHeights { if (_columnHeights == nil) { _columnHeights = [NSMutableArray array]; } return _columnHeights; } -
初始化布局
- (void)prepareLayout { [super prepareLayout]; /**清除之前跟布局相关的所有属性,重新设置新的布局*/ //清除之前计算的所有列的高度 [self.columnHeights removeAllObjects]; //设置所有列的初始高度 for (NSInteger i = 0; i<self.columnCount; i++) { self.columnHeights[i] = @(self.edgeInsets.top); } //清除之前所有的布局属性 [self.attrsArray removeAllObjects]; /**开始创建每一个cell对应的布局属性*/ NSInteger count = [self.collectionView numberOfItemsInSection:0]; for (NSInteger i = 0; i<count; i++) { NSIndexPath *indexPath = [NSIndexPath indexPathForItem:i inSection:0]; //获取indexPath位置cell对应的布局属性 UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attrs = [self layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath:indexPath]; //将indexPath位置的cell的布局属性添加到所有cell的布局属性数组中 [self.attrsArray addObject:attrs]; } } -
返回包含所有cell的布局属性的数组
- (nullable NSArray<UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *> *)layoutAttributesForElementsInRect:(CGRect)rect { return self.attrsArray; } -
设置每一个cell的布局属性
- (nullable UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *)layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath:(nonnull NSIndexPath *)indexPath { //获取indexPath位置的布局属性 UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attrs = [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes layoutAttributesForCellWithIndexPath:indexPath]; /**设置cell布局属性的frame*/ /***确定cell的尺寸***/ //获取collectionView的宽度 CGFloat collectionViewWidth = self.collectionView.frame.size.width; //cell宽度 CGFloat width = ((collectionViewWidth - self.edgeInsets.left - self.edgeInsets.right - (self.columnCount - 1) * self.columMargin)) / self.columnCount; //cell高度 CGFloat height = [self.delegate waterFlowLayout:self heightForItemAtIndex:indexPath.item itemWith:width]; /***设置cell的位置***/ NSInteger destColumn = 0; CGFloat minColumnHeight = [self.columnHeights[0] doubleValue]; for (NSInteger i = 1; i<self.columnCount; i++) { CGFloat columnHeight = [self.columnHeights[i] doubleValue]; if (minColumnHeight > columnHeight) { minColumnHeight = columnHeight; destColumn = i; } } //计算cell的位置 CGFloat x = self.edgeInsets.left + destColumn * (width + self.columMargin); CGFloat y = minColumnHeight; //判断是不是第一行 if (y != self.edgeInsets.top) { //若不是第一行,需要加上行间距 y += self.rowMargin; } /**给cell的布局属性的frame赋值*/ attrs.frame = CGRectMake(x, y, width, height); //更新最短那列的高度 self.columnHeights[destColumn] = @(CGRectGetMaxY(attrs.frame)); /**返回indexPath位置的cell的布局属性*/ return attrs; } -
设置collectionView内容的尺寸
- (CGSize)collectionViewContentSize { //获取最高的那一列的高度 CGFloat maxColumnHeight = [self.columnHeights[0] doubleValue]; for (NSInteger i = 1; i<self.columnCount; i++) { CGFloat columnHeight = [self.columnHeights[i] doubleValue]; if (maxColumnHeight < columnHeight) { maxColumnHeight = columnHeight; } } //返回collectionView的contentSize,高度为最高的高度加上一个行间距 return CGSizeMake(0, maxColumnHeight + self.rowMargin); }
-


 阐述封装自定义布局的详细步骤(使用委托模式提供接口),若在项目中用到自定义布局,可以直接将文件拖入项目,并实现代理方法即可。
阐述封装自定义布局的详细步骤(使用委托模式提供接口),若在项目中用到自定义布局,可以直接将文件拖入项目,并实现代理方法即可。
