现在我们要对商店商品进行折扣服务.每个折扣代码对应不同的折扣率,使用一个枚举变量Discount.Code来实现这一想法,具体代码如下所示.
以枚举类型定义的折扣代码
/**
* 折扣服务api
*
* @author Darcy
* Created by Administrator on 2017/3/17.
*/
public class Discount {
public enum Code {
NONE(0), SILVER(0), GOLD(10), PLATINUM(15), DIAMOND(20);
private final int percentage;
Code(int percentage) {
this.percentage = percentage;
}
}
public static String applyDiscount(Quote quote) {
return quote.getShopName() + " price is " + Discount.apply(quote.getPrice(), quote.getDiscountCode());
}
private static double apply(double price, Code code) {
delay();
return price * (100 - code.percentage) / 100;
}
/**
* 模拟计算,查询数据库等耗时
*/
public static void delay() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
修改商店返回价格的格式:
public String getPrice(String product) {
double price = calculatePrice(product);
Discount.Code code = Discount.Code.values()[
random.nextInt(Discount.Code.values().length)];
return String.format("%s:%.2f:%s", name, price, code);
}
* 实现折扣服务
我们的商店已经能从不同的商店获得商品价格,解析结果字符串,针对每个字符串,查询折扣服务器取的折扣代码.这个流程决定了请求商品的最终折扣价格.我们将对商店返回的字符串的解析操作封装到了下面的Quote类中:
/**
* 商店返回消息实体,不可变对象模式 线程安全
* @author Darcy
* Created by Administrator on 2017/3/17.
*/
public final class Quote {
private final String shopName;
private final double price;
private final Discount.Code discountCode;
public Quote(String shopName, double price, Discount.Code discountCode) {
this.shopName = shopName;
this.price = price;
this.discountCode = discountCode;
}
public static Quote parse(String s) {
String[] split = s.split(":");
String shopName = split[0];
double price = Double.parseDouble(split[1]);
Discount.Code discountCode = Discount.Code.valueOf(split[2]);
return new Quote(shopName, price, discountCode);
}
public String getShopName() {
return shopName;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public Discount.Code getDiscountCode() {
return discountCode;
}
}
Discount服务还提供了一个applyDiscount方法,它接收一个Quote对象,返回一个字符串,表示生成该Quote的shop中的折扣价格,代码如下:
public static String applyDiscount(Quote quote) {
return quote.getShopName() + " 商品原价: " + quote.getPrice() + " 折扣后价格: " + Discount.apply(quote.getPrice(), quote.getDiscountCode());
}
private static double apply(double price, Code code) {
delay();
return price * (100 - code.percentage) / 100;
}
* 使用Discount服务
/**
* 商店折扣价格查询器
*
* @param product 商品
* @return
*/
public static List<String> findprices(String product) {
return shops
.stream()
.map(shop -> shop.getPrice(product))
.map(Quote::parse)
.map(Discount::applyDiscount)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
执行结果:

换成并行流:
/**
* 商店折扣价格查询器
*
* @param product 商品
* @return
*/
public static List<String> findprices(String product) {
return shops
.parallelStream()
.map(shop -> shop.getPrice(product))
.map(Quote::parse)
.map(Discount::applyDiscount)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
执行结果:

看到差距了吧
* 构建同步和异步操作
我们再次使用ComoletableFuture提供的特性.以异步方式重新实现findPrices方法,详细代码如下:
/**
* 商店折扣价格查询器(CompletableFuture方式)
*
* @param product 商品
* @return
*/
public static List<String> findPrices(String product) {
List<CompletableFuture<String>> collect = shops
.stream()
//以异步凡是取得每个shop中指定产品的原始价格
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> shop.getPrice(product), executor))
//Quote对象存在时,对其返回值进行转换
.map(future -> future.thenApply(Quote::parse))
//使用另一个异步任务构建期望的Future,申请折扣 thenCompose 将多个future组合 一个一个执行
.map(future -> future.thenCompose(quote -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> Discount.applyDiscount(quote), executor)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return collect
.stream()
//等待流中所有的future执行完毕,并提取各自的返回值
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
* 对最佳价格查询器应用的优化
上面的所有例子中都是通过响应之前添加1秒延迟的等待时间模拟方法的远程调用,毫无疑问,现实生活中,你的应用访问各个远程服务器时很可能遭遇无法预知的延迟,触发原因多种多样,从服务器的负荷到网络的延迟,有些甚至是源于远程服务如何评估你应用的商业价值,
由于这些原因,你希望购买的商品在某些原因的查询速度要比另一些商店更快,我们模拟了操作:
/**
* 模拟不同的商店 延迟不一样的情况
*/
public static void randomDelay() {
int delay = 500 + random.nextInt(2000);
try {
Thread.sleep(delay);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
重构findPrices方法 返回一个由Future构成的流:
/**
* 重构findPrices方法 返回一个由Future构成的流
*
* @param product 商品
* @return
*/
public static Stream<CompletableFuture<String>> findProcesStream(String product) {
return shops
.stream()
//以异步凡是取得每个shop中指定产品的原始价格
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> shop.getPrice(product), executor))
//Quote对象存在时,对其返回值进行转换
.map(future -> future.thenApply(Quote::parse))
//使用另一个异步任务构建期望的Future,申请折扣 thenCompose 将多个future组合 一个一个执行
.map(future -> future.thenCompose(quote -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> Discount.applyDiscount(quote), executor)));
}
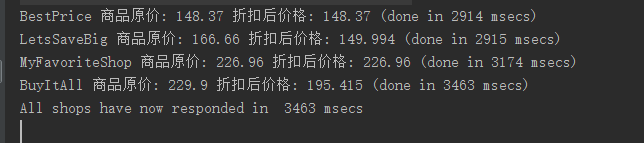
付诸实现:
long start = System.nanoTime();
CompletableFuture[] futures = findProcesStream("myPhones27s")
//Java 8的CompletableFuture通过thenAccept方法 他接收CompletableFuture执行完毕的返回值作为参数.
.map(f -> f.thenAccept(
s -> System.out.println(s + " (done in " +
((System.nanoTime() - start) / 1_000_000) + " msecs)")))
.toArray(CompletableFuture[]::new);
//allOf工厂方法接收一个由CompletableFuture构成的数组,数组中所有的CompletableFuture对象执行完毕后,它返回一个
//CompletableFuture<Void>对象,这意味着你需要等待最初Stream中所有的CompletableFuture对象执行完毕
//angOf该方法接收一个CompletableFuture对象构成的数组,返回由第一个执行完毕的CompletableFuture对象的返回值构成的CompletableFuture<Object>
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures).join();
System.out.println("All shops have now responded in " + ((System.nanoTime() - start) / 1_000_000) + " msecs");
执行结果: