【lombok】lombok---帮你简化生成必要但臃肿的java代码工具 【映射注解和lombok注解同时使用 以及 映射注解放在属性和get方法上的区别】
官方地址:https://projectlombok.org/
GitHub:https://github.com/rzwitserloot/lombok
指导说明文档:http://jnb.ociweb.com/jnb/jnbJan2010.html
===============================================================================================================
本来来说,lombok作为一个目前为止【2017-11-27】java并未将其作为标准来推广。还有很多人问使用它是否合适。
这里不做这种讨论!!!
===============================================================================================================
在使用之前,要明确一点,在开发过程中,一般情况下,仅使用@Data 即可满足生成entity类的大部分情况。
摘自指导文档:
Essentially, using @Data on a class is the same as annotating the class with a default @ToString and @EqualsAndHashCode as well as annotating each field with both @Getter and @Setter.
实质上,在一个类上使用@Data与用默认的@ToString和@EqualsAndHashCode注释这个类以及用@Getter和@Setter注释每个字段是一样的。
===============================================================================================================
使用起来:
一.安装lombok插件【idea使用为例】
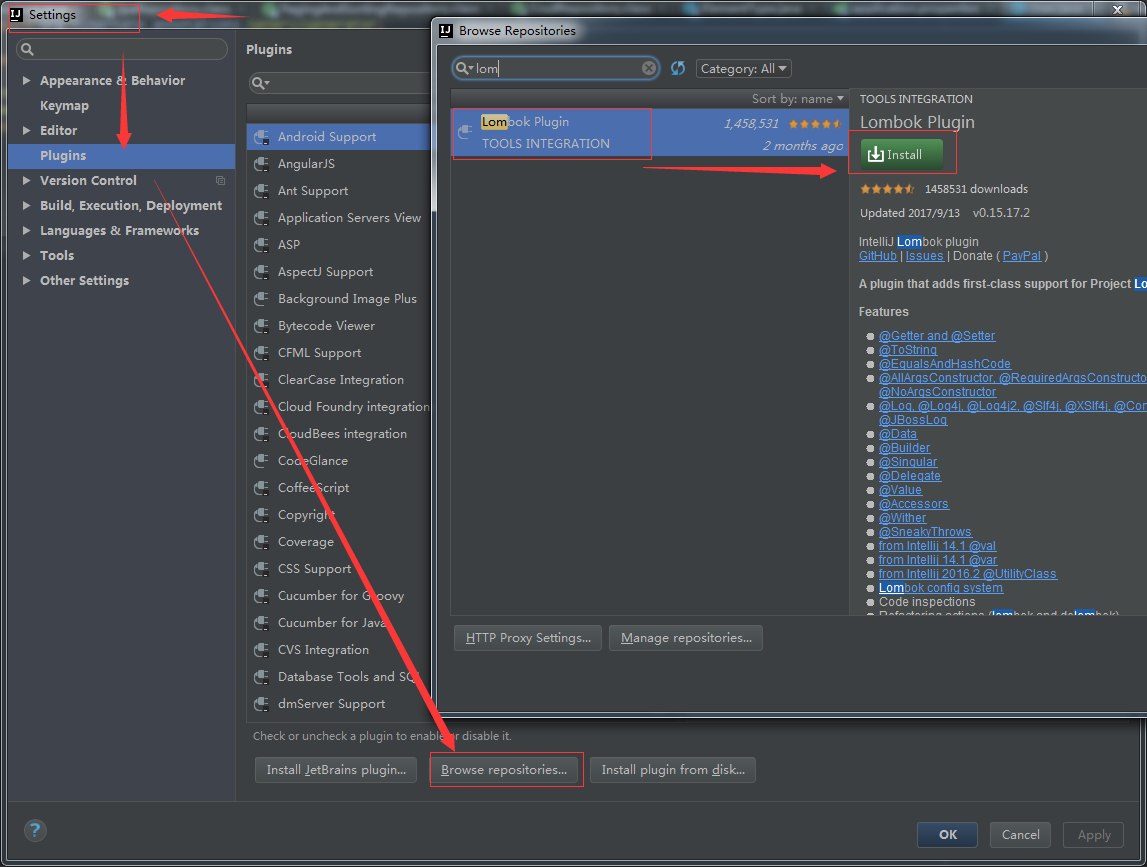
二.项目引入lombok依赖
<!--lombok--> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency>
版本这里不给了,想使用最新版本的,可以自己加上。
三.lombok注解使用详解
在上面安装插件的时候,可以看到有很多的注解是被支持的:

官方的指导文档,时间久远。所以就找到下面的注解进行详解。
@Getter and @Setter
【属性级别,生成本属性的get和set方法】
AccessLevel.PROTECTED 默认生成的方法为public,此属性可以设置生成方法的访问修饰符【非必须】
转化前:

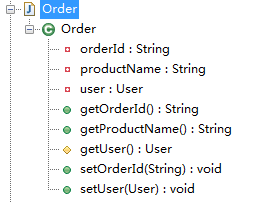
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.AccessLevel; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; public class Order { @Getter @Setter private String orderId; @Getter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED) @Setter private User user; @Getter @Setter(AccessLevel.NONE) private String productName; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public void setOrderId(String orderId) { this.orderId = orderId; } public String getOrderId() { return this.orderId; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } protected User getUser() { return this.user; } public String getProductName() { return this.productName; } }
=============================================================================
@ToString
【类级别,生成自定义的toString()方法】
exclude="{字段1,字段2}" 生成的toString()不包含哪些字段【非必须】
callSuper=true 如果继承的有父类的话,可以设置callSuper 让其调用父类的toString()方法【非必须】
转化前:

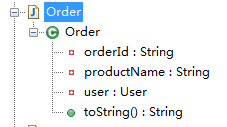
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.ToString; @ToString(exclude = {"orderId","user"},callSuper = false) public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public String toString() { return "Order(productName=" + this.productName + ")"; } }
不使用上述属性值的话:
转化前:

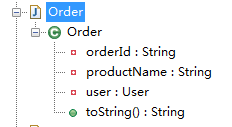
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.ToString; @ToString public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public String toString() { return "Order(orderId=" + this.orderId + ", user=" + this.user + ", productName=" + this.productName + ")"; } }
===================================================================================
@EqualsAndHashCode
【类级别,生成自定义的equals()方法和HashCode()方法】
exclude="{字段1,字段2}" 生成的方法不包含哪些字段【非必须】
callSuper=true 如果继承的有父类的话,可以设置callSuper 让其调用父类的方法【非必须】
转化前:

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode; @EqualsAndHashCode(exclude = {"orderId","user"},callSuper = false) public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
编译后:

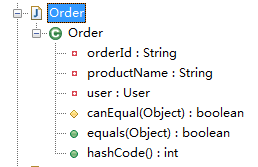
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public int hashCode() { int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $productName = this.productName;result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result; } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof Order; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } if (!(o instanceof Order)) { return false; } Order other = (Order)o; if (!other.canEqual(this)) { return false; } Object this$productName = this.productName;Object other$productName = other.productName;return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName); } }
=====================================================================================
@NonNull
【属性级别,验证不能为null的注解,如果执行加了这个注解的setter方法时设置为Null,抛异常java.lang.NullPointerException】
转化前:

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NonNull; import lombok.Setter; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; @NonNull @Getter @Setter private String productName; public Order() { } }
编译后:

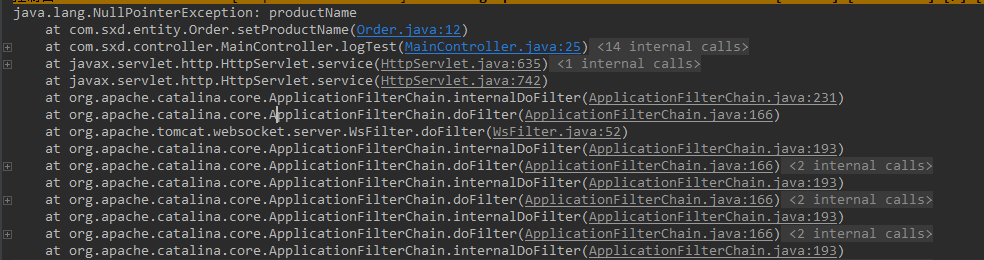
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.NonNull; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; @NonNull private String productName; public void setProductName(@NonNull String productName) { if (productName == null) { throw new NullPointerException("productName"); } this.productName = productName; } @NonNull public String getProductName() { return this.productName; } }
如果去执行setter方法并赋值Null,则报错:

注意报错行数:
===========================================================================================
@NoArgsConstructor
【类级别,生成无参构造方法】
focus=true 当类中有final字段没有被初始化时,编译器会报错,此时可用@NoArgsConstructor(force = true),然后就会为没有初始化的final字段设置默认值 0 / false / null。对于具有约束的字段(例如@NonNull字段),不会生成检查或分配,因此请注意,正确初始化这些字段之前,这些约束无效。
转化前:

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; @NoArgsConstructor(force = true) public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
=====================================================================================
@RequiredArgsConstructor
【类级别,生成有 或 无参的静态方法,用于获取本对象】
staticName = "自定义静态方法名"
转化前:

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor; @RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "build") public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
转化后:

package com.sxd.entity; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public static Order build() { return new Order(); } }

===============================================================================
@AllArgsConstructor
【类级别,生成全参构造方法】
转化前:

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; @AllArgsConstructor public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
编译后:

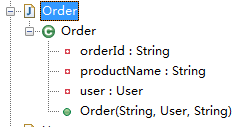
package com.sxd.entity; import java.beans.ConstructorProperties; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; @ConstructorProperties({"orderId", "user", "productName"}) public Order(String orderId, User user, String productName) { this.orderId = orderId;this.user = user;this.productName = productName; } }
================================================================================
@Data
【类级别,此注解为lombok中最常用注解】
【@Data 包含了@ToString,@EqualsAndHashCode,@Getter / @Setter和@RequiredArgsConstructor的功能】
staticConstructor="静态实例化方法名"
转化前:

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Data; @Data(staticConstructor = "build") public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
编译后:

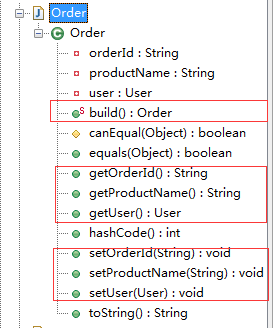
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public static Order build() { return new Order(); } public int hashCode() { int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $orderId = getOrderId();result = result * 59 + ($orderId == null ? 43 : $orderId.hashCode());Object $user = getUser();result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $productName = getProductName();result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result; } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof Order; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } if (!(o instanceof Order)) { return false; } Order other = (Order)o; if (!other.canEqual(this)) { return false; } Object this$orderId = getOrderId();Object other$orderId = other.getOrderId(); if (this$orderId == null ? other$orderId != null : !this$orderId.equals(other$orderId)) { return false; } Object this$user = getUser();Object other$user = other.getUser(); if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) { return false; } Object this$productName = getProductName();Object other$productName = other.getProductName();return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName); } public void setOrderId(String orderId) { this.orderId = orderId; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } public void setProductName(String productName) { this.productName = productName; } public String toString() { return "Order(orderId=" + getOrderId() + ", user=" + getUser() + ", productName=" + getProductName() + ")"; } public String getOrderId() { return this.orderId; } public User getUser() { return this.user; } public String getProductName() { return this.productName; } }
@Accessors
【类级别,控制get、set方法】
- fluent boolean值,默认为false。此字段主要为控制生成的getter和setter方法前面是否带get/set;false带,true不带
- chain boolean值,默认false。如果设置为true,setter返回的是此对象,方便链式调用方法
- prefix 设置前缀 例如:@Accessors(prefix = "abc") private String abcAge 当生成get/set方法时,会把此前缀去掉
转化前:【注意三个属性设值以及生成】

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Data; import lombok.experimental.Accessors; @Data @Accessors(fluent = false,chain = false,prefix = "aaa") public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public String toString() { return "Order(orderId=" + this.orderId + ", user=" + this.user + ", productName=" + this.productName + ")"; } public int hashCode() { int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $orderId = this.orderId;result = result * 59 + ($orderId == null ? 43 : $orderId.hashCode());Object $user = this.user;result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $productName = this.productName;result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result; } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof Order; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } if (!(o instanceof Order)) { return false; } Order other = (Order)o; if (!other.canEqual(this)) { return false; } Object this$orderId = this.orderId;Object other$orderId = other.orderId; if (this$orderId == null ? other$orderId != null : !this$orderId.equals(other$orderId)) { return false; } Object this$user = this.user;Object other$user = other.user; if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) { return false; } Object this$productName = this.productName;Object other$productName = other.productName;return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName); } }
===========================================================
转化前:【注意fluent】

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Data; import lombok.experimental.Accessors; @Data @Accessors(fluent = true,chain = false) public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public void productName(String productName) { this.productName = productName; } public int hashCode() { int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $orderId = orderId();result = result * 59 + ($orderId == null ? 43 : $orderId.hashCode());Object $user = user();result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $productName = productName();result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result; } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof Order; } public void orderId(String orderId) { this.orderId = orderId; } public void user(User user) { this.user = user; } public String toString() { return "Order(orderId=" + orderId() + ", user=" + user() + ", productName=" + productName() + ")"; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } if (!(o instanceof Order)) { return false; } Order other = (Order)o; if (!other.canEqual(this)) { return false; } Object this$orderId = orderId();Object other$orderId = other.orderId(); if (this$orderId == null ? other$orderId != null : !this$orderId.equals(other$orderId)) { return false; } Object this$user = user();Object other$user = other.user(); if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) { return false; } Object this$productName = productName();Object other$productName = other.productName();return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName); } public String orderId() { return this.orderId; } public User user() { return this.user; } public String productName() { return this.productName; } }

==============================================================================
转化前:【注意chain】

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Data; import lombok.experimental.Accessors; @Data @Accessors(fluent = false,chain = true) public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public Order setProductName(String productName) { this.productName = productName;return this; } public int hashCode() { int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $orderId = getOrderId();result = result * 59 + ($orderId == null ? 43 : $orderId.hashCode());Object $user = getUser();result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $productName = getProductName();result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result; } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof Order; } public Order setOrderId(String orderId) { this.orderId = orderId;return this; } public Order setUser(User user) { this.user = user;return this; } public String toString() { return "Order(orderId=" + getOrderId() + ", user=" + getUser() + ", productName=" + getProductName() + ")"; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } if (!(o instanceof Order)) { return false; } Order other = (Order)o; if (!other.canEqual(this)) { return false; } Object this$orderId = getOrderId();Object other$orderId = other.getOrderId(); if (this$orderId == null ? other$orderId != null : !this$orderId.equals(other$orderId)) { return false; } Object this$user = getUser();Object other$user = other.getUser(); if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) { return false; } Object this$productName = getProductName();Object other$productName = other.getProductName();return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName); } public String getOrderId() { return this.orderId; } public User getUser() { return this.user; } public String getProductName() { return this.productName; } }
===================================================================
转化前:【注意prefix】

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Data; import lombok.experimental.Accessors; @Data @Accessors(fluent = false,chain = true,prefix = "product") public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public String toString() { return "Order(orderId=" + this.orderId + ", user=" + this.user + ", productName=" + getName() + ")"; } public int hashCode() { int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $orderId = this.orderId;result = result * 59 + ($orderId == null ? 43 : $orderId.hashCode());Object $user = this.user;result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $productName = getName();result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result; } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof Order; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } if (!(o instanceof Order)) { return false; } Order other = (Order)o; if (!other.canEqual(this)) { return false; } Object this$orderId = this.orderId;Object other$orderId = other.orderId; if (this$orderId == null ? other$orderId != null : !this$orderId.equals(other$orderId)) { return false; } Object this$user = this.user;Object other$user = other.user; if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) { return false; } Object this$productName = getName();Object other$productName = other.getName();return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName); } public Order setName(String productName) { this.productName = productName;return this; } public String getName() { return this.productName; } }

=========================================================================
@Cleanup
【代码级别,清理资源/关闭资源注解】
转化前:

public void testCleanUp() { try { @Cleanup ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); baos.write(new byte[] {'Y','e','s'}); System.out.println(baos.toString()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
编译后:

public void testCleanUp() { try { ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); try { baos.write(new byte[]{'Y', 'e', 's'}); System.out.println(baos.toString()); } finally { baos.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
=========================================================================
@Synchronized
【方法级别,同步/线程安全注解】
转化前:

private DateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("MM-dd-YYYY"); @Synchronized public String synchronizedFormat(Date date) { return format.format(date); }
编译后:

private final java.lang.Object $lock = new java.lang.Object[0]; private DateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("MM-dd-YYYY"); public String synchronizedFormat(Date date) { synchronized ($lock) { return format.format(date); } }
=========================================================================
@Wither
【属性级别,提供了给final字段赋值的一种方法】
转化前:

import lombok.AccessLevel; import lombok.NonNull; import lombok.experimental.Wither; public class WitherExample { @Wither private final int age; @Wither(AccessLevel.PROTECTED) @NonNull private final String name; public WitherExample(String name, int age) { if (name == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } }
编译后:

import lombok.NonNull; public class WitherExample { private final int age; private @NonNull final String name; public WitherExample(String name, int age) { if (name == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public WitherExample withAge(int age) { return this.age == age ? this : new WitherExample(age, name); } protected WitherExample withName(@NonNull String name) { if (name == null) throw new java.lang.NullPointerException("name"); return this.name == name ? this : new WitherExample(age, name); } }
==================================================================================
@Builder
【类级别,为你的类生成复杂的构建器API】
转化前:

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Builder; @Builder public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; import java.beans.ConstructorProperties; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public static class OrderBuilder { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public String toString() { return "Order.OrderBuilder(orderId=" + this.orderId + ", user=" + this.user + ", productName=" + this.productName + ")"; } public Order build() { return new Order(this.orderId, this.user, this.productName); } public OrderBuilder productName(String productName) { this.productName = productName;return this; } public OrderBuilder user(User user) { this.user = user;return this; } public OrderBuilder orderId(String orderId) { this.orderId = orderId;return this; } } public static OrderBuilder builder() { return new OrderBuilder(); } @ConstructorProperties({"orderId", "user", "productName"}) Order(String orderId, User user, String productName) { this.orderId = orderId;this.user = user;this.productName = productName; } }
==============================================================
@Delegate
【属性级别,同化所在属性的类型的方法到本类中】
转化前:【本属性类型为String】

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.experimental.Delegate; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; @Delegate private String productName; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.stream.IntStream; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; public IntStream codePoints() { return this.productName.codePoints(); } public IntStream chars() { return this.productName.chars(); } public String intern() { return this.productName.intern(); } public char[] toCharArray() { return this.productName.toCharArray(); } public String trim() { return this.productName.trim(); } public String toUpperCase() { return this.productName.toUpperCase(); } public String toUpperCase(Locale arg0) { return this.productName.toUpperCase(arg0); } public String toLowerCase() { return this.productName.toLowerCase(); } public String toLowerCase(Locale arg0) { return this.productName.toLowerCase(arg0); } public String[] split(String arg0) { return this.productName.split(arg0); } public String[] split(String arg0, int arg1) { return this.productName.split(arg0, arg1); } public String replace(CharSequence arg0, CharSequence arg1) { return this.productName.replace(arg0, arg1); } public String replaceAll(String arg0, String arg1) { return this.productName.replaceAll(arg0, arg1); } public String replaceFirst(String arg0, String arg1) { return this.productName.replaceFirst(arg0, arg1); } public boolean contains(CharSequence arg0) { return this.productName.contains(arg0); } public boolean matches(String arg0) { return this.productName.matches(arg0); } public String replace(char arg0, char arg1) { return this.productName.replace(arg0, arg1); } public String concat(String arg0) { return this.productName.concat(arg0); } public CharSequence subSequence(int arg0, int arg1) { return this.productName.subSequence(arg0, arg1); } public String substring(int arg0, int arg1) { return this.productName.substring(arg0, arg1); } public String substring(int arg0) { return this.productName.substring(arg0); } public int lastIndexOf(String arg0, int arg1) { return this.productName.lastIndexOf(arg0, arg1); } public int lastIndexOf(String arg0) { return this.productName.lastIndexOf(arg0); } public int indexOf(String arg0, int arg1) { return this.productName.indexOf(arg0, arg1); } public int indexOf(String arg0) { return this.productName.indexOf(arg0); } public int lastIndexOf(int arg0, int arg1) { return this.productName.lastIndexOf(arg0, arg1); } public int lastIndexOf(int arg0) { return this.productName.lastIndexOf(arg0); } public int indexOf(int arg0, int arg1) { return this.productName.indexOf(arg0, arg1); } public int indexOf(int arg0) { return this.productName.indexOf(arg0); } public boolean endsWith(String arg0) { return this.productName.endsWith(arg0); } public boolean startsWith(String arg0) { return this.productName.startsWith(arg0); } public boolean startsWith(String arg0, int arg1) { return this.productName.startsWith(arg0, arg1); } public boolean regionMatches(boolean arg0, int arg1, String arg2, int arg3, int arg4) { return this.productName.regionMatches(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4); } public boolean regionMatches(int arg0, String arg1, int arg2, int arg3) { return this.productName.regionMatches(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3); } public int compareToIgnoreCase(String arg0) { return this.productName.compareToIgnoreCase(arg0); } public int compareTo(String arg0) { return this.productName.compareTo(arg0); } public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String arg0) { return this.productName.equalsIgnoreCase(arg0); } public boolean contentEquals(CharSequence arg0) { return this.productName.contentEquals(arg0); } public boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer arg0) { return this.productName.contentEquals(arg0); } public byte[] getBytes() { return this.productName.getBytes(); } public byte[] getBytes(Charset arg0) { return this.productName.getBytes(arg0); } public byte[] getBytes(String arg0) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { return this.productName.getBytes(arg0); } @Deprecated public void getBytes(int arg0, int arg1, byte[] arg2, int arg3) { this.productName.getBytes(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3); } public void getChars(int arg0, int arg1, char[] arg2, int arg3) { this.productName.getChars(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3); } public int offsetByCodePoints(int arg0, int arg1) { return this.productName.offsetByCodePoints(arg0, arg1); } public int codePointCount(int arg0, int arg1) { return this.productName.codePointCount(arg0, arg1); } public int codePointBefore(int arg0) { return this.productName.codePointBefore(arg0); } public int codePointAt(int arg0) { return this.productName.codePointAt(arg0); } public char charAt(int arg0) { return this.productName.charAt(arg0); } public boolean isEmpty() { return this.productName.isEmpty(); } public int length() { return this.productName.length(); } }
==========================================================================
转化前:【所在属性类型为List】

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.experimental.Delegate; import java.util.List; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; @Delegate private List<Integer> arrList; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import java.util.ListIterator; import java.util.Spliterator; import java.util.function.UnaryOperator; public class Order { private String orderId; private User user; private String productName; private List<Integer> arrList; public Spliterator<Integer> spliterator() { return this.arrList.spliterator(); } public List<Integer> subList(int arg0, int arg1) { return this.arrList.subList(arg0, arg1); } public ListIterator<Integer> listIterator(int arg0) { return this.arrList.listIterator(arg0); } public ListIterator<Integer> listIterator() { return this.arrList.listIterator(); } public int lastIndexOf(Object arg0) { return this.arrList.lastIndexOf(arg0); } public int indexOf(Object arg0) { return this.arrList.indexOf(arg0); } public Integer remove(int arg0) { return (Integer)this.arrList.remove(arg0); } public void add(int arg0, Integer arg1) { this.arrList.add(arg0, arg1); } public Integer set(int arg0, Integer arg1) { return (Integer)this.arrList.set(arg0, arg1); } public Integer get(int arg0) { return (Integer)this.arrList.get(arg0); } public void clear() { this.arrList.clear(); } public void sort(Comparator<? super Integer> arg0) { this.arrList.sort(arg0); } public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<Integer> arg0) { this.arrList.replaceAll(arg0); } public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> arg0) { return this.arrList.retainAll(arg0); } public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> arg0) { return this.arrList.removeAll(arg0); } public boolean addAll(int arg0, Collection<? extends Integer> arg1) { return this.arrList.addAll(arg0, arg1); } public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends Integer> arg0) { return this.arrList.addAll(arg0); } public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> arg0) { return this.arrList.containsAll(arg0); } public boolean remove(Object arg0) { return this.arrList.remove(arg0); } public boolean add(Integer arg0) { return this.arrList.add(arg0); } public <T> T[] toArray(T[] arg0) { return this.arrList.toArray(arg0); } public Object[] toArray() { return this.arrList.toArray(); } public Iterator<Integer> iterator() { return this.arrList.iterator(); } public boolean contains(Object arg0) { return this.arrList.contains(arg0); } public boolean isEmpty() { return this.arrList.isEmpty(); } public int size() { return this.arrList.size(); } }
============================================================================
@SneakyThrows
【异常处理注解,这里不做详细解释】
转化前:

@SneakyThrows public void testSneakyThrows() { throw new IllegalAccessException(); }
编译后:

public void testSneakyThrows() { try { throw new IllegalAccessException(); } catch (java.lang.Throwable $ex) { throw lombok.Lombok.sneakyThrow($ex); } }
============================================================================
@_({注解1,注解2})或@_(注解) 配合onMethod=使用
【属性级别,用于将注解放在注解中使用】
转化前:

package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Id; public class Order { @Getter(onMethod = @_({@Column,@Id})) @Setter private String id; }
编译后:

package com.sxd.entity; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Id; public class Order { private String id; @Column @Id public String getId() { return this.id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } }
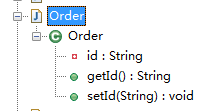
【注意:这个时而有用,时而报错,具体问题依旧找不到~~~~~~~~~~~~具体看附录2】
============================================================================================================
最后,如果使用了lombok的话,如何在实体类上声明实体对数据表的映射?
注意:@Column等注解是可以直接放在字段上而不用放在get方法上
例如:创建不同包下同名的实体类User.java
自己写get/set方法的User类如下:

package com.sxd.entity; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; import javax.persistence.*; @Entity @GenericGenerator(name = "uuid2", strategy = "org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator" ) public class User { private String id; private String username; private String password; private Integer age; @Id @GeneratedValue(generator = "uuid2") public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } @Column(nullable = false) public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } @Column(nullable = false) public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } @Column(nullable = false) public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public User() { } public User(String id, String username, String password, Integer age) { this.id = id; this.username = username; this.password = password; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "id='" + id + '\'' + ", username='" + username + '\'' + ", password='" + password + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }
编译完是:

package com.sxd.entity; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity @GenericGenerator(name="uuid2", strategy="org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator") public class User { private String id; private String username; private String password; private Integer age; @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="uuid2") public String getId() { return this.id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } @Column(nullable=false) public String getUsername() { return this.username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } @Column(nullable=false) public String getPassword() { return this.password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } @Column(nullable=false) public Integer getAge() { return this.age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public User() {} public User(String id, String username, String password, Integer age) { this.id = id; this.username = username; this.password = password; this.age = age; } public String toString() { return "User{id='" + this.id + '\'' + ", username='" + this.username + '\'' + ", password='" + this.password + '\'' + ", age=" + this.age + '}'; } }
=================== ==================================
使用lombok之后如下:

package com.sxd.controller; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import lombok.experimental.Accessors; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; @Entity @GenericGenerator(name = "uuid2", strategy = "org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator" ) @Data(staticConstructor = "of") @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Accessors(chain = true) public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator = "uuid2")private String id; private String username; @Column(nullable = false) private String password; @Column(nullable = false) private Integer age; }
编译完是:

package com.sxd.controller; import java.beans.ConstructorProperties; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity @GenericGenerator(name="uuid2", strategy="org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator") public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="uuid2") private String id; private String username; @Column(nullable=false) private String password; @Column(nullable=false) private Integer age; public User setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age;return this; } public String toString() { return "User(id=" + getId() + ", username=" + getUsername() + ", password=" + getPassword() + ", age=" + getAge() + ")"; } public int hashCode() { int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $id = getId();result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode());Object $username = getUsername();result = result * 59 + ($username == null ? 43 : $username.hashCode());Object $password = getPassword();result = result * 59 + ($password == null ? 43 : $password.hashCode());Object $age = getAge();result = result * 59 + ($age == null ? 43 : $age.hashCode());return result; } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof User; } public User setId(String id) { this.id = id;return this; } public User setUsername(String username) { this.username = username;return this; } public User setPassword(String password) { this.password = password;return this; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } if (!(o instanceof User)) { return false; } User other = (User)o; if (!other.canEqual(this)) { return false; } Object this$id = getId();Object other$id = other.getId(); if (this$id == null ? other$id != null : !this$id.equals(other$id)) { return false; } Object this$username = getUsername();Object other$username = other.getUsername(); if (this$username == null ? other$username != null : !this$username.equals(other$username)) { return false; } Object this$password = getPassword();Object other$password = other.getPassword(); if (this$password == null ? other$password != null : !this$password.equals(other$password)) { return false; } Object this$age = getAge();Object other$age = other.getAge();return this$age == null ? other$age == null : this$age.equals(other$age); } @ConstructorProperties({"id", "username", "password", "age"}) public User(String id, String username, String password, Integer age) { this.id = id;this.username = username;this.password = password;this.age = age; } public String getId() { return this.id; } public String getUsername() { return this.username; } public String getPassword() { return this.password; } public Integer getAge() { return this.age; } public User() {} }
有一个疑问,映射注解放在属性上和放在get方法上有什么区别???【看附录3】
===============================================================附录1:equals()方法和hashCode()方法的意义==========================================================
摘录:
1.hashcode是用来查找的,如果你学过数据结构就应该知道,在查找和排序这一章有
例如内存中有这样的位置
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
而我有个类,这个类有个字段叫ID,我要把这个类存放在以上8个位置之一,如果不用hashcode而任意存放,那么当查找时就需要到这八个位置里挨个去找,或者用二分法一类的算法。
但如果用hashcode那就会使效率提高很多。
我们这个类中有个字段叫ID,那么我们就定义我们的hashcode为ID%8,然后把我们的类存放在取得得余数那个位置。比如我们的ID为9,9除8的余数为1,那么我们就把该类存在1这个位置,如果ID是13,求得的余数是5,那么我们就把该类放在5这个位置。这样,以后在查找该类时就可以通过ID除 8求余数直接找到存放的位置了。
2.但是如果两个类有相同的hashcode怎么办那(我们假设上面的类的ID不是唯一的),例如9除以8和17除以8的余数都是1,那么这是不是合法的,
回答是:可以这样。那么如何判断呢?在这个时候就需要定义 equals了。
也就是说,我们先通过 hashcode来判断两个类是否存放某个桶里,但这个桶里可能有很多类,那么我们就需要再通过 equals 来在这个桶里找到我们要的类。
那么。重写了equals(),为什么还要重写hashCode()呢?
想想,你要在一个桶里找东西,你必须先要找到这个桶啊,你不通过重写hashcode()来找到桶,光重写equals()有什么用啊
==============================================================附录2:@Getter()等lombok注解配合hibernate的映射注解怎么使用===========================================================
如果在项目中真的使用lombok的注解的话,映射注解应该如何处理呢?
寥寥无几的资料中有大概类似于如下的写法:
@Getter(onMethod = @_({@Id,@Column(name="id",nullable=false),@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.AUTO)}))
@Setter
private Integer id;
亲自试了一下,
如下:
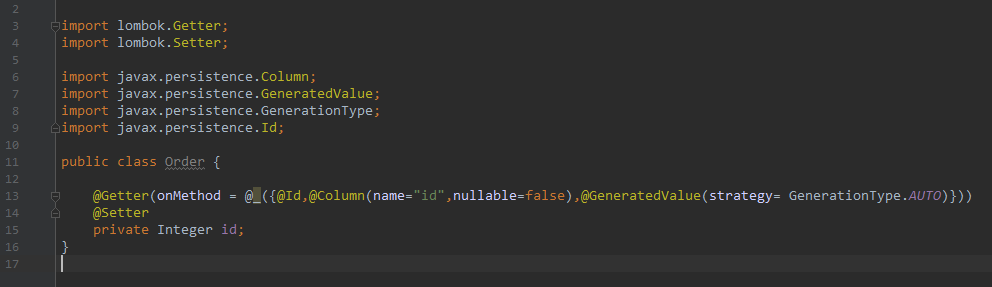
报错如下:

其实在@Getter()注解接口中定义如下:
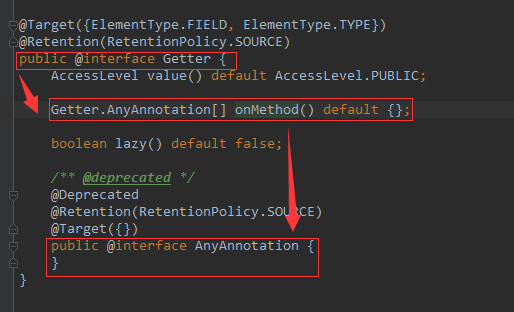
但是具体怎么去写,还没有研究出来。
【如有解决方法,不吝赐教!!】
所以,最终按照并列将注解写在属性上,而不是在@Getter()注解中写@Column()注解。
如下:

@Data(staticConstructor = "of") @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Accessors(chain = true) @Entity @GenericGenerator(name = "uuid2", strategy = "org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator" ) public class Member { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator = "uuid2") @Column(name = "memberId") private String memberId; @OneToOne(cascade = {CascadeType.MERGE,CascadeType.REFRESH},fetch = FetchType.EAGER) private User user; @Column(name="memberGrade",nullable = false) @NonNull private Integer memberGrade; }
编译完成如下:

package com.sxd.entity; import java.beans.ConstructorProperties; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.FetchType; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.OneToOne; import lombok.NonNull; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity @GenericGenerator(name="uuid2", strategy="org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator") public class Member { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="uuid2") @Column(name="memberId") private String memberId; @OneToOne(cascade={javax.persistence.CascadeType.MERGE, javax.persistence.CascadeType.REFRESH}, fetch=FetchType.EAGER) private User user; @Column(name="memberGrade", nullable=false) @NonNull private Integer memberGrade; public String toString() { return "Member(memberId=" + getMemberId() + ", user=" + getUser() + ", memberGrade=" + getMemberGrade() + ")"; } public int hashCode() { int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $memberId = getMemberId();result = result * 59 + ($memberId == null ? 43 : $memberId.hashCode());Object $user = getUser();result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $memberGrade = getMemberGrade();result = result * 59 + ($memberGrade == null ? 43 : $memberGrade.hashCode());return result; } public Member setMemberId(String memberId) { this.memberId = memberId;return this; } public Member setUser(User user) { this.user = user;return this; } public Member setMemberGrade(@NonNull Integer memberGrade) { if (memberGrade == null) { throw new NullPointerException("memberGrade"); } this.memberGrade = memberGrade;return this; } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof Member; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } if (!(o instanceof Member)) { return false; } Member other = (Member)o; if (!other.canEqual(this)) { return false; } Object this$memberId = getMemberId();Object other$memberId = other.getMemberId(); if (this$memberId == null ? other$memberId != null : !this$memberId.equals(other$memberId)) { return false; } Object this$user = getUser();Object other$user = other.getUser(); if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) { return false; } Object this$memberGrade = getMemberGrade();Object other$memberGrade = other.getMemberGrade();return this$memberGrade == null ? other$memberGrade == null : this$memberGrade.equals(other$memberGrade); } @ConstructorProperties({"memberId", "user", "memberGrade"}) public Member(String memberId, User user, @NonNull Integer memberGrade) { if (memberGrade == null) { throw new NullPointerException("memberGrade"); } this.memberId = memberId;this.user = user;this.memberGrade = memberGrade; } public String getMemberId() { return this.memberId; } public User getUser() { return this.user; } @NonNull public Integer getMemberGrade() { return this.memberGrade; } public Member() {} }

那么最后看 附录3,了解最后一个问题,映射注解放在属性上和放在get方法上有什么区别?
=======================================================================附录3:映射注解放在属性上和放在get()方法上有什么区别======================================================================
摘录自:http://blog.csdn.net/most_rabbitfishes/article/details/70904949
对于属性字段和表的字段关系对应的注解属性的位置,一般我们采用以下两种方式:
第一种:
是把注解@Column(name ="xx")放在field上,一种是把注解放在get方法上一般放在field上看起来比较集中、清晰;
第二种:
是把注解@Column(name= "xx")放在get方法上,这种方式看起来比较散漫、不很清楚;
但是第一种方式这样做实际上破坏了java面向对象的封装性,原因是一般我们写javaBean,成员变量通常定义为private,目的就是不让别人来直接访问的私有属性,而我们把注解放在私有成员的变量上,就是默认hibernate可以直接访问我们的私有的成员变量,所以我们定义属性为private,就实际没有多大意义,至于hibernate为什么能访问,hibernate采用java的反射机制完全可以访问私有成员变量!所以应该放在get方法上,第二种方式这个时候就显得更加合理。
随即,我采用了附录2中实体用于hibernate自动生成数据表的表结构:

Hibernate自动帮我们建表:
如果我们采用注解的方式在我们的实体Bean上,又想通过扫描这些注解的Bean,通过Hibernate自动帮我们建表,那么你就会发现字段注解的位置不同甚至会影响到建表的结构,尤其是大字段、外键约束的生成效果。
如果采用第一种方式注解到私有字段上,这种帮我们建立表结构、约束条件和大字段Lob类型这些都是非常正常的,而通过第二种方式注解到get方法上,这种帮我们的建立的表大部分正常字段正常,而外键关联的和大字段就会出现问题.
虽然项目的开发我们不采用hibernate帮我们自动建表,通常我们还是要手动的建表,所以这一些是对于通过Hibernate帮我们自动建表要考虑的!而实际开发中,已注解在get方法上为多数!
结论:如上 将注解建立在属性上,生成的表结构,约束条件,外键等都正常,所以,如果你要使用hibernate的生成策略,在你建立好实体之后自动去建立数据表的话,同时使用lombok的注解和映射注解都放在属性上是合适的!!!





